
Fort Dunree is a coastal defence fortification located on the west side of the Inishowen peninsula, County Donegal, Ireland.

Lenan Head Fort, Lough Swilly, Inishowen, County Donegal was built in 1895, initially with three 9.2 inch Breech Loading (BL) guns. Following recommendations of the Owen Committee in 1905, it was refitted in 1911 with two newer Mark X 9.2 inch models. Both guns were operational during the First World War.

Ned's Point Fort is one of several Napoleonic batteries built along the shores of Lough Swilly in county Donegal, to defend the north west of Ireland. It was part of a scheme to fortify Lough Swilly and Lough Foyle against French Invasion during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. It is situated on Ned's Point, near the once important naval town of Buncrana, and its current form largely dates to works completed between 1812 and 1813. It comprised a rectangular blockhouse mounting two guns and a supporting battery mounting four guns. The fort is surrounded by a ditch.

Lough Swilly in Ireland is a glacial fjord or sea inlet lying between the western side of the Inishowen Peninsula and the Fanad Peninsula, in County Donegal. Along with Carlingford Lough and Killary Harbour it is one of three glacial fjords in Ireland.

The Rodman gun is any of a series of American Civil War–era columbiads designed by Union artilleryman Thomas Jackson Rodman (1815–1871). The guns were designed to fire both shot and shell. These heavy guns were intended to be mounted in seacoast fortifications. They were built in 8-inch, 10-inch, 13-inch, 15-inch, and 20-inch bore. Other than size, the guns were all nearly identical in design, with a curving bottle shape, large flat cascabels with ratchets or sockets for the elevating mechanism. Rodman guns were true guns that did not have a howitzer-like powder chamber, as did many earlier columbiads. Rodman guns differed from all previous artillery because they were hollow cast, a new technology that Rodman developed that resulted in cast-iron guns that were much stronger than their predecessors.

Dahlgren guns were muzzle-loading naval artillery designed by Rear Admiral John A. Dahlgren USN, mostly used in the period of the American Civil War. Dahlgren's design philosophy evolved from an accidental explosion in 1849 of a 32 lb (14.5 kg) gun being tested for accuracy, killing a gunner. He believed a safer, more powerful naval cannon could be designed using more scientific design criteria. Dahlgren guns were designed with a smooth curved shape, equalizing strain and concentrating more weight of metal in the gun breech where the greatest pressure of expanding propellant gases needed to be met to keep the gun from bursting. Because of their rounded contours, Dahlgren guns were nicknamed "soda bottles", a shape which became their most identifiable characteristic.

Coastal artillery is the branch of the armed forces concerned with operating anti-ship artillery or fixed gun batteries in coastal fortifications.

Field artillery in the American Civil War refers to the artillery weapons, equipment, and practices used by the Artillery branch to support the infantry and cavalry forces in the field. It does not include siege artillery, use of artillery in fixed fortifications, or coastal or naval artillery. Nor does it include smaller, specialized artillery classified as small arms.

The columbiad was a large-caliber, smoothbore, muzzle-loading cannon able to fire heavy projectiles at both high and low trajectories. This feature enabled the columbiad to fire solid shot or shell to long ranges, making it an excellent seacoast defense weapon for its day. Invented by Colonel George Bomford, United States Army, in 1811, columbiads were used in United States seacoast defense from the War of 1812 until the early years of the 20th century. Very few columbiads were used outside of the U.S. and Confederate Armies; nevertheless, the columbiad is considered by some as the inspiration for the later shell-only cannons developed by Frenchman Henri-Joseph Paixhans some 30 years later.

Seacoast defense was a major concern for the United States from its independence until World War II. Before airplanes, many of America's enemies could only reach it from the sea, making coastal forts an economical alternative to standing armies or a large navy. After the 1940s, it was recognized that fixed fortifications were obsolete and ineffective against aircraft and missiles. However, in prior eras foreign fleets were a realistic threat, and substantial fortifications were built at key locations, especially protecting major harbors.

Siege artillery is heavy artillery primarily used in military attacks on fortified positions. At the time of the American Civil War, the U.S. Army classified its artillery into three types, depending on the gun's weight and intended use. Field artillery were light pieces that often traveled with the armies. Siege and garrison artillery were heavy pieces that could be used either in attacking or defending fortified places. Seacoast artillery were the heaviest pieces and were intended to be used in permanent fortifications along the seaboard. They were primarily designed to fire on attacking warships. The distinctions are somewhat arbitrary, as field, siege and garrison, and seacoast artillery were all used in various attacks and defenses of fortifications. This article will focus on the use of heavy artillery in the attack of fortified places during the American Civil War.

Lascaris Battery, also known as Fort Lascaris or Lascaris Bastion, is an artillery battery located on the east side of Valletta, Malta. The battery was built by the British in 1854, and it is connected to the earlier St. Peter & Paul Bastion of the Valletta Land Front. In World War II, the Lascaris War Rooms were dug close to the battery, and they served as Britain's secret headquarters for the defence of the island.

Camden Fort Meagher is a coastal defence fortification close to Crosshaven, County Cork, Ireland. Together with similar structures at Fort Mitchell, Fort Davis (Whitegate), and Templebreedy Battery, the fort was built to defend the mouth of Cork Harbour. Though originally constructed in the 16th century, the current structures of the fort date to the 1860s. Originally named Fort Camden and operated by the British Armed Forces, the fort was handed-over to the Irish Defence Forces in 1938. Renamed Fort Meagher in honour of Thomas Francis Meagher, it remained an Irish military installation until 1989 when the Irish Army handed the fort over to Cork County Council. It remained largely overgrown until 2010 when a group of local volunteers began restoration and development of the fort for heritage and tourism purposes. The fort was renamed Camden Fort Meagher and is now open seasonally to visitors, with exhibits on the fort's Brennan torpedo installation.

Fort Davis, is a coastal defence fortification close to Whitegate, County Cork, Ireland. Together with similar structures at Fort Mitchel, Fort Camden (Crosshaven), and Templebreedy Battery, the fort was built to defend the mouth of Cork Harbour. Though used as a fortification from the early 17th century, the current structures of the 74-acre site date primarily from the 1860s. Originally named Fort Carlisle and operated by the British Armed Forces, the fort was handed-over to the Irish Defence Forces in 1938, and renamed Fort Davis. The facility is owned by the Department of Defence, and is used as a military training site with no public access.
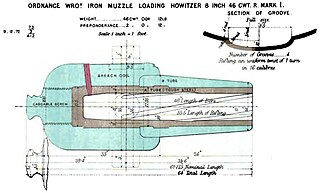
The RML 8-inch howitzer was a British Rifled, Muzzle Loading (RML) Howitzer manufactured in England in the 19th century, which fired a projectile weighing approximately 180 pounds (82 kg). It was used in siege batteries and in fortifications.

Inch Fort, Lough Swilly, Inishowen, County Donegal was built between 1812 and 1813, during the Napoleonic Wars. It had positions for nine guns, six in an open battery and a further three in a blockhouse. Following the peace in 1815, the defences of Lough Swilly were neglected.

Macamish Fort is one of several Napoleonic batteries built along the shores of Lough Swilly in county Donegal, to defend the north west of Ireland. It was part of a scheme to fortify Lough Swilly and Lough Foyle against French Invasion during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars and was completed between 1812 and 1813. It was built on a rock outcrop overlooking the lough. It comprises a Martello Tower mounting a single gun and battery mounting three guns. The fort was originally entered by a drawbridge.

The M1841 12-pounder howitzer was a bronze smoothbore muzzle-loading artillery piece that was adopted by the United States Army in 1841 and employed from the Mexican–American War to the American Civil War. It fired a 8.9 lb (4.0 kg) shell up to a distance of 1,072 yd (980 m) at 5° elevation. It could also fire canister shot and spherical case shot. The howitzer proved effective when employed by light artillery units during the Mexican–American War. The howitzer was used throughout the American Civil War, but it was outclassed by the 12-pounder Napoleon which combined the functions of both field gun and howitzer. In the US Army, the 12-pounder howitzers were replaced as soon as more modern weapons became available. Though none were manufactured after 1862, the weapon was not officially discarded by the US Army until 1868. The Confederate States of America also manufactured and employed the howitzer during the American Civil War. The Confederate armies used the outmoded howitzer for a longer period.

The M1841 24-pounder howitzer was a bronze smoothbore muzzle-loading artillery piece adopted by the United States Army in 1841 and employed from the Mexican–American War through the American Civil War. It fired a 18.4 lb (8.3 kg) shell to a distance of 1,322 yd (1,209 m) at 5° elevation. It could also fire canister shot and spherical case shot. The howitzer was designed to be employed in a mixed battery with 12-pounder field guns. By the time of the American Civil War, the 24-pounder howitzer was superseded by the 12-pounder Napoleon, which combined the functions of both field gun and howitzer. The 24-pounder howitzer's use as field artillery was limited during the conflict and production of the weapon in the North ended in 1863. The Confederate States of America manufactured a few 24-pounder howitzers and imported others from the Austrian Empire.

The M1857 12-pounder Napoleon or Light 12-pounder gun or 12-pounder gun-howitzer was a bronze smoothbore muzzle-loading artillery piece that was adopted by the United States Army in 1857 and extensively employed in the American Civil War. The gun was the American-manufactured version of the French canon obusier de 12 which combined the functions of both field gun and howitzer. The weapon proved to be simple to produce, reliable, and robust. It fired a 12.3 lb (5.6 kg) round shot shell a distance of 1,619 to 1,680 yd at 5° elevation. It could also fire canister shot, common shell, and spherical case shot. The 12-pounder Napoleon outclassed and soon replaced the M1841 6-pounder field gun and the M1841 12-pounder howitzer in the US Army, while replacement of these older weapons was slower in the Confederate States Army. A total of 1,157 were produced for the US Army, all but a few in the period 1861–1863. The Confederate States of America utilized captured US 12-pounder Napoleons and also manufactured about 500 during the war. The weapon was named after Napoleon III of France who helped develop the weapon.




















