Related Research Articles

Polyurethane refers to a class of polymers composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane term does not refer to the single type of polymer but a group of polymers. Unlike polyethylene and polystyrene polyurethanes can be produced from a wide range of starting materials resulting various polymers within the same group. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, and coatings, adhesives, electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and polyurethane laminate (PUL). Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016.

Petrochemicals are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as maize, palm fruit or sugar cane.

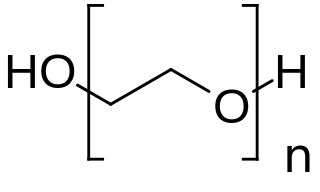
Polyethylene glycol (PEG; ) is a polyether compound derived from petroleum with many applications, from industrial manufacturing to medicine. PEG is also known as polyethylene oxide (PEO) or polyoxyethylene (POE), depending on its molecular weight. The structure of PEG is commonly expressed as H−(O−CH2−CH2)n−OH.

Castor oil is a vegetable oil pressed from castor beans, the seeds of the plant Ricinus communis. The seeds are 40 to 60 percent oil. It is a colourless or pale yellow liquid with a distinct taste and odor. Its boiling point is 313 °C (595 °F) and its density is 0.961 g/cm3. It includes a mixture of triglycerides in which about 90 percent of fatty acids are ricinoleates. Oleic acid and linoleic acid are the other significant components.
Transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic functional group R″ of an ester with the organic group R' of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. Strong acids catalyze the reaction by donating a proton to the carbonyl group, thus making it a more potent electrophile. Bases catalyze the reaction by removing a proton from the alcohol, thus making it more nucleophilic. The reaction can also be accomplished with the help of enzymes, particularly lipases.
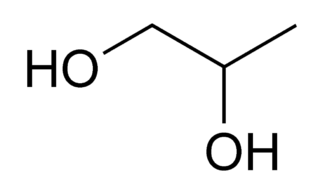
Propylene glycol (IUPAC name: propane-1,2-diol) is a viscous, colorless liquid. It is almost odorless and has a faintly sweet taste. Its chemical formula is CH3CH(OH)CH2OH. As it contains two alcohol groups, it is classified as a diol. An aliphatic diol may also be called a glycol. It is miscible with a broad range of solvents, including water, acetone, and chloroform. In general, glycols are non-irritating and have very low volatility.

Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the formula C2H4O. It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor. Because it is a strained ring, ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Ethylene oxide is isomeric with acetaldehyde and with vinyl alcohol. Ethylene oxide is industrially produced by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of a silver catalyst.

Curcumin is a bright yellow chemical produced by plants of the Curcuma longa species. It is the principal curcuminoid of turmeric, a member of the ginger family, Zingiberaceae. It is sold as a herbal supplement, cosmetics ingredient, food flavoring, and food coloring.
An antifreeze is an additive which lowers the freezing point of a water-based liquid. An antifreeze mixture is used to achieve freezing-point depression for cold environments. Common antifreezes also increase the boiling point of the liquid, allowing higher coolant temperature. However, all common antifreeze additives also have lower heat capacities than water, and do reduce water's ability to act as a coolant when added to it.
An excipient is a substance formulated alongside the active ingredient of a medication. They may be used to enhance the active ingredient’s therapeutic properties; to facilitate drug absorption; to reduce viscosity; to enhance solubility; to improve long-term stabilization ; or to add bulk to solid formulations that have small amounts of potent active ingredients. During the manufacturing process, excipients can improve the handling of active substances and facilitate powder flow. The choice of excipients depends on factors such as the intended route of administration, the dosage form, and compatibility with the active ingredient.

Brake fluid is a type of hydraulic fluid used in hydraulic brake and hydraulic clutch applications in automobiles, motorcycles, light trucks, and some bicycles. It is used to transfer force into pressure, and to amplify braking force. It works because liquids are not appreciably compressible.

Ropivacaine (rINN) is a local anaesthetic drug belonging to the amino amide group. The name ropivacaine refers to both the racemate and the marketed S-enantiomer. Ropivacaine hydrochloride is commonly marketed by AstraZeneca under the brand name Naropin.

Polysorbate 80 is a nonionic surfactant and emulsifier often used in pharmaceuticals, foods, and cosmetics. This synthetic compound is a viscous, water-soluble yellow liquid.
Glycol ethers are a class of chemical compounds consisting of alkyl ethers that are based on glycols such as ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. They are commonly used as solvents in paints and cleaners. They have good solvent properties while having higher boiling points than the lower-molecular-weight ethers and alcohols.

Lotion is a low-viscosity topical preparation intended for application to the skin. By contrast, creams and gels have higher viscosity, typically due to lower water content. Lotions are applied to external skin with bare hands, a brush, a clean cloth, or cotton wool.
Alfaxolone/alfadolone is a short acting intravenous anesthetic agent. It was withdrawn from the market due to severe drug reactions. It is composed of a 3:1 mixture of alfaxalone and alfadolone, two neurosteroids.

Polyglycerol polyricinoleate (PGPR), E476, is an emulsifier made from glycerol and fatty acids. In chocolate, compound chocolate and similar coatings, PGPR is mainly used with another substance like lecithin to reduce viscosity. It is used at low levels, and works by decreasing the friction between the solid particles in molten chocolate, reducing the yield stress so that it flows more easily, approaching the behaviour of a Newtonian fluid. It can also be used as an emulsifier in spreads and in salad dressings, or to improve the texture of baked goods. It is made up of a short chain of glycerol molecules connected by ether bonds, with ricinoleic acid side chains connected by ester bonds.
PEGylation is the process of both covalent and non-covalent attachment or amalgamation of polyethylene glycol polymer chains to molecules and macrostructures, such as a drug, therapeutic protein or vesicle, which is then described as PEGylated. PEGylation affects the resulting derivatives or aggregates interactions, which typically slows down their coalescence and degradation as well as elimination in vivo.

Egg oil, also known as egg yolk oil or ovum oil, is derived from the yolk of chicken eggs consisting mainly of triglycerides with traces of lecithin, cholesterol, biotin, xanthophylls lutein and zeaxanthin, and immunoglobulins. It is free of egg proteins and hence may be used safely by people who are allergic to eggs, for topical applications such as hair and skin care. The product has several historical references in Unani (Greek) medicine for hair care. Traditional Chinese medicine uses egg oil for burns, eczema, dermatitis, mouth ulcers, skin ulcers, chapped nipples, tinea capitis, ringworm, nasal vestibulitis, frostbite, and hemorrhoids.

Topical cream formulation is an emulsion semisolid dosage form that is used for skin external application. Most of the topical cream formulations contain more than 20 per cent of water and volatiles and/or less than 50 per cent of hydrocarbons, waxes, or polyethylene glycols as the vehicle for external skin application. In a topical cream formulation, ingredients are dissolved or dispersed in either a water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion or an oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion. The topical cream formulation has a higher content of oily substance than gel, but a lower content of oily ingredient than ointment. Therefore, the viscosity of topical cream formulation lies between gel and ointment. The pharmacological effect of the topical cream formulation is confined to the skin surface or within the skin. Topical cream formulation penetrates through the skin by transcellular route, intercellular route, or trans-appendageal route. Topical cream formulation is used for a wide range of diseases and conditions, including atopic dermatitis (eczema), psoriasis, skin infection, acne, and wart. Excipients found in a topical cream formulation include thickeners, emulsifying agents, preservatives, antioxidants, and buffer agents. Steps required to manufacture a topical cream formulation include excipient dissolution, phase mixing, introduction of active substances, and homogenization of the product mixture.
References
- ↑ "Kolliphor EL" . Retrieved 2010-12-16.
- ↑ Clarke, R. S.; Dundee, J. W.; Carson, I. W. (1973). "New Drugs in Anæsthesia: A New Steroid Anaesthetic-Althesin". Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine. 66 (10): 1027–1030. doi:10.1177/003591577306601023. PMC 1645602 . PMID 4148526. See page 1/49, Methods and Materials.
- ↑ "Kolliphor® ELP". BASF Pharma. Retrieved 2022-06-11.