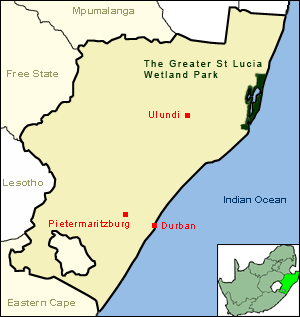
KwaZulu-Natal is a province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the government merged the Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu and Natal Province.

Maputo Province is a province of Mozambique; the province excludes the city of Maputo. The province has an area of 22,693 km2 (8,762 sq mi) and a population of 1,968,906. Its capital is the city of Matola.

iSimangaliso Wetland Park is situated on the east coast of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, about 235 km (146 mi) north of Durban by road. It is South Africa's third-largest protected area, spanning 280 km (170 mi) of coastline, from the Mozambican border in the north to Mapelane south of the Lake St. Lucia estuary, and made up of around 3,280 km2 of natural ecosystems, managed by the iSimangaliso Authority.
The Lubombo Transfrontier Conservation Area was born out of the Peace Park Foundation’s vision to establish a network of transfrontier conservation areas in southern Africa. It straddles the border between South Africa’s KwaZulu-Natal province, southern Mozambique, and Eswatini.

A shark net is a submerged section of gillnets placed at beaches designed to intercept large marine animals including sharks, with the aim to reduce the likelihood of shark attacks on swimmers. Shark nets used are gillnets which is a wall of netting that hangs in the water and captures the marine animals by entanglement, however only around 10% of catch is the intended target shark species. The nets in Queensland, Australia, are typically 186m long, set at a depth of 6m, have a mesh size of 500mm and are designed to catch sharks longer than 2m in length. The nets in New South Wales, Australia, are typically 150m long, set on the sea floor, extending approximately 6m up the water column, are designed to catch sharks longer than 2m in length. Shark nets do not create an exclusion zone between sharks and humans, and are not to be confused with shark barriers.

Ballito is an affluent coastal town located in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Ballito is about 40 kilometres (25 mi) north of Durban and 24 kilometres south of KwaDukuza. It forms part of the KwaDukuza Local Municipality, and iLembe District Municipality. Dolphins and Whales are common on this stretch of the North Coast shoreline, hence the nickname Dolphin Coast.

The KwaZulu-Natal sardine run of southern Africa occurs from May through July when billions of sardines – or more specifically the Southern African pilchard Sardinops sagax – spawn in the cool waters of the Agulhas Bank and move northward along the east coast of South Africa. Their sheer numbers create a feeding frenzy along the coastline. The run, containing millions of individual sardines, occurs when a current of cold water heads north from the Agulhas Bank up to Mozambique where it then leaves the coastline and goes further east into the Fisherman are sometimes observed singing songs while hauling in the fishing nets in typical South African style. It is estimated that the sardine run is the biggest Biomass migration in terms of numbers.
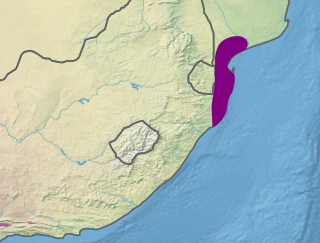
The Maputaland coastal forest mosaic is a subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion on the Indian Ocean coast of Southern Africa. It covers an area of 29,961 square kilometres (11,568 sq mi) in southern Mozambique, Eswatini, and the KwaZulu-Natal Province of South Africa. Mozambique's capital Maputo lies within the ecoregion.

Sodwana Bay is a bay in South Africa on the KwaZulu Natal north coast, between St. Lucia and Lake Sibhayi. It is in the Sodwana Bay National Park, and the Maputaland Marine Reserve, and is a popular recreational diving destination. The term is commonly used to refer to both the marine reserve and the terrestrial park, as well as the geographical bay.

Raphia australis, the giant palm or rafia, is a species of raffia palm in the family Arecaceae. It is found around Kosi Bay in southern Mozambique and northeastern KwaZulu Natal in South Africa. It is threatened by habitat loss caused by drainage of its habitat for agriculture; it is being threatened in the Bobole Special Reserve but is more secure in the Kosi Bay area.
kwaNgwanase, also known as Kosi Bay Town, is a small town in Umkhanyakude District Municipality in the KwaZulu-Natal province of South Africa. It is located some 15 km south of the Mozambique–South Africa border, and is situated near Kosi Bay. The town is inhabited by thonga (Amathonga) the Bantu speaking people who flee from Shaka and settled between pongola river Jozini, South Africa and KaTembe river in Southern Mozambique.

Ponta do Ouro-Kosi Bay Transfrontier Conservation Area (TFCA) is a larger conservation area conceived as an extension of the existing conservation parkland area of the iSimangaliso Wetland Park, to extend north into a similar area on the Mozambique side of the border, and including several other parks in the process. The parks to be included are:

The Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany Hotspot (MPA) is a biodiversity hotspot, a biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity, in Southern Africa. It is situated near the south-eastern coast of Africa, occupying an area between the Great Escarpment and the Indian Ocean. The area is named after Maputaland, Pondoland and Albany. It stretches from the Albany Centre of Plant Endemism in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa, through the Pondoland Centre of Plant Endemism and KwaZulu-Natal Province, the eastern side of Eswatini and into southern Mozambique and Mpumalanga. The Maputaland Centre of Plant Endemism is contained in northern KwaZulu-Natal and southern Mozambique.

Maputaland is a natural region of Southern Africa. It is located in the northern part of the province of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa between Eswatini and the coast. In a wider sense it may also include the southernmost region of Mozambique. The bird routes and coral reefs off the coast are major tourist attractions.
Pseudargyrochlamys is a genus of flies in the family Dolichopodidae. It was first established by Igor Grichanov in 2006 for four species of Paracleius from eastern South Africa. A fifth species from South Africa was described in 2020. Members of the genus are restricted to the coast of southern Africa between East London in South Africa and Maputo in Mozambique. The genus is closely related to Argyrochlamys and Phoomyia, which are also found in coastal habitats.

Delagoa is a marine ecoregion along the eastern coast of Africa. It extends along the coast of Mozambique and South Africa from the Bazaruto Archipelago to Lake St. Lucia in South Africa in South Africa's Kwazulu-Natal province. It adjoins the Bight of Sofala/Swamp Coast ecoregion to the north, and the Natal ecoregion to the south. It has Africa's southernmost tropical coral reefs and mangrove forests. It is the southernmost Indo-Pacific ecoregion, marking the transition from the tropical Indo-Pacific to Temperate Southern Africa.