| Kotaneelee River | |
|---|---|
| Territories | Yukon, Northwest Territories |
| Country | Canada |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source | La Biche Range 1,600 m (5,200 ft) 60°49′15.13″N124°31′57.47″W / 60.8208694°N 124.5326306°W |
| River mouth | Liard River 230 m (750 ft) 60°10′50.23″N123°42′01.73″W / 60.1806194°N 123.7004806°W Coordinates: 60°10′50.23″N123°42′01.73″W / 60.1806194°N 123.7004806°W |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries |
|
The Kotaneelee River is a river in the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is a tributary of the Liard River.

The Northwest Territories is a federal territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately 1,144,000 km2 (442,000 sq mi) and a 2016 census population of 41,786, it is the second-largest and the most populous of the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated population as of 2018 is 44,445. Yellowknife became the territorial capital in 1967, following recommendations by the Carrothers Commission.

Canada is a country in the northern part of North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometres, making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Canada's southern border with the United States is the world's longest bi-national land border. Its capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. As a whole, Canada is sparsely populated, the majority of its land area being dominated by forest and tundra. Consequently, its population is highly urbanized, with over 80 percent of its inhabitants concentrated in large and medium-sized cities, many near the southern border. Canada's climate varies widely across its vast area, ranging from arctic weather in the north, to hot summers in the southern regions, with four distinct seasons.

The Liard River flows through Yukon, British Columbia and the Northwest Territories, Canada. Rising in the Saint Cyr Range of the Pelly Mountains in southeastern Yukon, it flows 1,115 kilometres (693 mi) southeast through British Columbia, marking the northern end of the Rocky Mountains and then curving northeast back into Yukon and Northwest Territories, draining into the Mackenzie River at Fort Simpson, Northwest Territories. The river drains approximately 277,100 square kilometres (107,000 sq mi) of boreal forest and muskeg.
Contents
It gives the name to the Kotaneelee Formation, a stratigraphical unit of the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin.
The Kotaneelee Formation is a stratigraphical unit of Late Cretaceous age in the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin.

Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has two related subfields: lithostratigraphy and biostratigraphy.
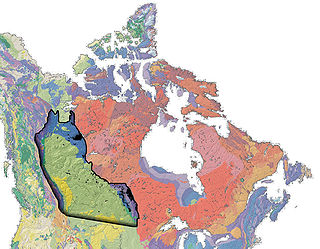
The Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin (WCSB) is a vast sedimentary basin underlying 1,400,000 square kilometres (540,000 sq mi) of Western Canada including southwestern Manitoba, southern Saskatchewan, Alberta, northeastern British Columbia and the southwest corner of the Northwest Territories. It consists of a massive wedge of sedimentary rock extending from the Rocky Mountains in the west to the Canadian Shield in the east. This wedge is about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) thick under the Rocky Mountains, but thins to zero at its eastern margins. The WCSB contains one of the world's largest reserves of petroleum and natural gas and supplies much of the North American market, producing more than 16,000,000,000 cubic feet (450,000,000 m3) per day of gas in 2000. It also has huge reserves of coal. Of the provinces and territories within the WCSB, Alberta has most of the oil and gas reserves and almost all of the oil sands.