
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate maternal and fetal circulations, and is an important endocrine organ, producing hormones that regulate both maternal and fetal physiology during pregnancy. The placenta connects to the fetus via the umbilical cord, and on the opposite aspect to the maternal uterus in a species-dependent manner. In humans, a thin layer of maternal decidual (endometrial) tissue comes away with the placenta when it is expelled from the uterus following birth. Placentas are a defining characteristic of placental mammals, but are also found in marsupials and some non-mammals with varying levels of development.

An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. Infant is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term baby. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of other organisms. A newborn is, in colloquial use, an infant who is only hours, days, or up to one month old. In medical contexts, a newborn or neonate is an infant in the first 28 days after birth; the term applies to premature, full term, and postmature infants.

Nut, also known by various other transcriptions, is the goddess of the sky, stars, cosmos, mothers, astronomy, and the universe in the ancient Egyptian religion. She was seen as a star-covered nude woman arching over the Earth, or as a cow. She was depicted wearing the water-pot sign (nw) that identifies her.
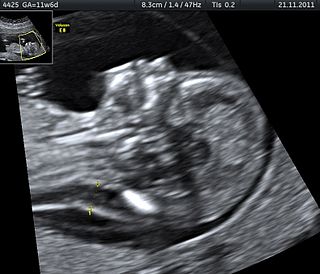
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can often result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage, which is an early pregnancy loss, and sudden infant death syndrome, where the baby dies a short time after being born alive.

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and normally contains two arteries and one vein, buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps low-oxygen, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.
Asena is the name of a she-wolf associated with the Gokturk foundation myth. The ancestress of the Göktürks is a she-wolf, mentioned yet unnamed in two different "Wolf Tales". The legend of Asena tells of a young boy who survived a battle; a female wolf finds the injured child and nurses him back to health. The she-wolf, impregnated by the boy, escapes her enemies by crossing the Western Sea to a cave near the Qocho mountains and a city of the Tocharians, giving birth to ten half-wolf, half-human boys. Of these, Yizhi Nishidu becomes their leader and establishes the Ashina clan, which ruled over the Göktürk and other Turkic nomadic empires.
Umay is the goddess of fertility in Turkic mythology and Tengrism and as such related to women, mothers, and children. Umay not only protects and educates babies, but also may separate the soul from the dead, especially young children. She lives in heaven and is invisible to the common people. Souls of babies-to-be-born are kept in her "temple" of Mount Ymay-tas or Amay. The Khakas emphasize her in particular. From Umai, the essence of fire was born.

Birthday is a story collection by Japanese writer Koji Suzuki and first published on February 5, 1999 in Japan. It is the fourth installment of Suzuki's Ring series.

Midwifery is a women's profession that assists women from pregnancy to newborn care. In some traditional Maya communities, a goddess of midwifery is invoked, and midwives are generally believed to be assigned their profession through signs and visions. In pre-Spanish Yucatan, the aged midwife goddess was called Ixchel.

The Inuit are indigenous people who live in the Arctic and subarctic regions of North America. The ancestors of the present-day Inuit are culturally related to Iñupiat and Yupik, and the Aleut, who live in the Aleutian Islands of Siberia and Alaska. The word "Eskimo" has been used to encompass the Inuit and Yupik, and other indigenous Alaskan and Siberian peoples, but this usage is in decline.

Shashthi or Shashti is a Hindu goddess, venerated in Nepal and India as the benefactor and protector of children. She is also the deity of vegetation and reproduction and is believed to bestow children and assist during childbirth. She is often pictured as a motherly figure, riding a cat and nursing one or more infants. She is symbolically represented in a variety of forms, including an earthenware pitcher, a banyan tree or part of it or a red stone beneath such a tree; outdoor spaces termed shashthitala are also consecrated for her worship. The worship of Shashthi is prescribed to occur on the sixth day of each lunar month of the Hindu calendar as well as on the sixth day after a child's birth. Barren women desiring to conceive and mothers seeking to ensure the protection of their children will worship Shashthi and request her blessings and aid. She is especially venerated in eastern India.
This article deals with childbirth in Japan, and the specific details of childbirth exclusive to Japan in relation to beliefs, attitudes and healthcare.

Issues and practices related to childbirth in Sri Lanka are influenced by the sociocultural composition, political history and violence within the country.
This article documents traditional and some modern childbirth practices in Thailand. Traditional principles are largely influenced by the folk beliefs in Central and North Thailand, and modern practices by the western medical model.

Women in Aztec civilization shared some equal opportunities. Aztec civilization saw the rise of a military culture that was closed off to women and made their role more prescribed to domestic and reproductive labor and less equal. The status of Aztec women in society was further altered in the 16th century, when Spanish conquest forced European norms onto the indigenous culture. However, many pre-Columbian norms survived and their legacy still remains.
Plain Truth is a 2004 TV drama directed by Paul Shapiro, starring Mariska Hargitay, Alison Pill and Jan Niklas. The film is based on Jodi Picoult's book Plain Truth, in which an Amish teen hides a pregnancy, gives birth in secret, and then flatly denies it all when the baby's body is found. An urban defense attorney, Ellie Harrison, decides to represent her when she's charged with murder.
The maternal mortality rate is 224 deaths per 100,000 births, which is the 23rd highest in the world. The mean age of mothers at birth is 19.3 years old, and the fertility rate is 5.72 children born per woman, which is the 7th highest in the world. The contraceptive rate is only 40.8%, and the birth rate is the 4th highest in the world at 42.13 births/1,000 population. Infectious disease is a key contributor to the poor health of the nation, and the risk is very high for diseases such as protozoal and bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, typhoid fever, malaria, dengue fever, schistosomiasis, and rabies. The adult prevalence rate of HIV/AIDS is 12.37%, which is the 7th highest in the world.

Emergency childbirth is the precipitous birth of an infant in an unexpected setting. In planned childbirth, mothers choose the location and obstetric team ahead of time. Options range from delivering at home, at a hospital, a medical facility or a birthing center. Sometimes, birth can occur on the way to these facilities, without a healthcare team. The rates of unplanned childbirth are low. If the birth is imminent, emergency measures may be needed. Emergency services can be contacted for help in some countries.











