Related Research Articles

The Nile is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer. Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About 6,650 km (4,130 mi) long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Sudan, and Egypt. In particular, the Nile is the primary water source of Egypt, Sudan and South Sudan. Additionally, the Nile is an important economic river, supporting agriculture and fishing.
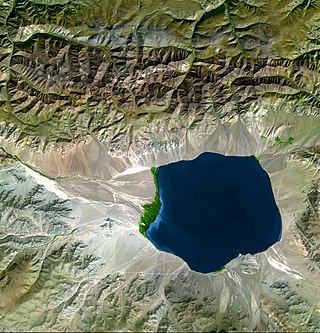
An endorheic basin is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other, external bodies of water ; instead, the water drainage flows into permanent and seasonal lakes and swamps that equilibrate through evaporation. Endorheic basins are also called closed basins, terminal basins, and internal drainage systems.

Lake Balkhash is a lake in southeastern Kazakhstan, one of the largest lakes in Asia and the 15th largest in the world. It is located in the eastern part of Central Asia and sits in the Balkhash-Alakol Basin, an endorheic (closed) basin. The basin drains seven rivers, the primary of which is the Ili, bringing most of the riparian inflow; others, such as the Karatal, bring surface and subsurface flow. The Ili is fed by precipitation, largely vernal snowmelt, from the mountains of China's Xinjiang region.

Lake Abaya is a lake in the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region of Ethiopia. It is located in the Main Ethiopian Rift, east of the Guge Mountains.

The Okavango River, is a river in southwest Africa. It is known by this name in Botswana, and as Cubango in Angola, and Kavango in Namibia. It is the fourth-longest river system in southern Africa, running southeastward for 1,600 km (1,000 mi). It begins at an elevation of 1,300 metres (4,300 ft) in the sandy highlands of Angola. Farther south, it forms part of the border between Angola and Namibia, and then flows into Botswana. The Okavango does not have an outlet to the sea. Instead, it discharges into the Okavango Delta or Okavango Alluvial Fan, in an endorheic basin in the Kalahari Desert. The Cuito River is a major tributary.

The Rift Valley lakes are a series of lakes in the East African Rift valley that runs through eastern Africa from Ethiopia in the north to Malawi in the south, and includes the African Great Lakes in the south. These include some of the world's oldest lakes, deepest lakes, largest lakes by area, and largest lakes by volume. Many are freshwater ecoregions of great biodiversity, while others are alkaline "soda lakes" supporting highly specialised organisms.

Arba Minch is a city and separate woreda in the southern part of Ethiopia. "Arba Minch" means "40 Springs", originated from the presence of more than 40 springs. It is located in the Gamo Zone of the South Ethiopia Regional State, about 500 kilometers south of Addis Ababa, at an elevation of 1285 meters above sea level. It is the largest town in Gamo Zone. It is surrounded by Arba Minch Zuria woreda. This Town has plenty of natural gifts including the bridge of God, Crocodile ranch, crocodile market, different fruits and vegetables, different fishes farmed from Chamo and Abaya Lakes, more than 40 springs, different cereals, and crops, surprisingly having the two big Lakes in the country, lake Abaya and Chamo, respectively, next to Lake Tana, etc. This makes the town one of the tourist destinations in Ethiopia, which comprises Nech Sar National Park, home to the country's varied wildlife and plant species.
Nechisar National Park is a national park in the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region of Ethiopia. It is in the Great Rift Valley within the southwestern Ethiopian Highlands.

The Umfolozi River is a river in KwaZulu-Natal, a province of South Africa. It is formed by the confluence of the Black and White Umfolozi Rivers near the southeastern boundary of the Hluhluwe-Umfolozi Game Reserve. The isiZulu name imFolozi is generally considered to describe the zigzag course followed by both tributaries, though other explanations have been given.
Boreda Abaya was one of the 77 woredas in the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region of Ethiopia. Part of the Semien Omo Zone, Boreda Abaya was bordered on the south by Arba Minch Zuria, on the southwest by Chencha, on the west by Kucha, on the north by Humbo, and on the east by Lake Abaya which separates it from the Oromia Region. Aruro Island, the largest island in Lake Abaya, was administratively part of this woreda. Towns in Boreda Abaya included Birbir and Zefene. Boreda Abaya was separated for Boreda and Mirab Abaya woredas.
Chencha is a woreda in Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region, Ethiopia. Part of the Gamo Zone, Chencha is bordered on the south by Arba Minch Zuria, on the west by Dita & Gofa on the north by Kucha and Boreda, and on the east by Mirab Abaya. Towns in Chencha include Chencha, Dorze, Dokko and Ezo.
Arba Minch Zuria is a woreda in Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region, Ethiopia. A part of the Gamo Zone located in the Great Rift Valley, Arba Minch Zuria is bordered on the south by the Dirashe special woreda, on the west by Bonke, on the north by Dita and Chencha, on the northeast by Mirab Abaya, on the east by the Oromia Region, and on the southeast by the Amaro special woreda. This woreda also includes portions of two lakes and their islands, Abaya found in Lante kebele and Chamo found in all Ganta Kanchama Ochole and Zeyise kebeles. Nechisar National Park is located between these lakes. City of Arba Minch is surrounded by Arba Minch Zuria.

Lake Chamo is a lake in the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region of southern Ethiopia. Located in the Main Ethiopian Rift, it is at an elevation of 1,110 meters. The Chamo lake is just to the south of Lake Abaya and the city of Arba Minch, east of the Guge Mountains, and west of the Amaro Mountains.
Arba Minch Airport is a public airport serving Arba Minch, a city in the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region (SNNPR) in Ethiopia. The name of the city and airport may also be transliterated as Arba Mintch. The airport is located 5 km northeast of the city centre, near Lake Abaya.

Arba Minch University is a residential national university in Arba Minch, Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region, Ethiopia. It is approximately 435 kilometres (270 mi) south of Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The Ministry of Education admits qualified students to Arba Minch University based on their score on the Ethiopian Higher Education Entrance Examination.
Gamo Zone is a zone in the South Ethiopia Regional State of Ethiopia. Gamo is bordered on the south by the Dirashe special woreda, on the southwest by Debub (South) Omo and the Basketo special woreda, on the northwest by Konta special woreda, on the north by Dawro and Wolayita, on the northeast by the Lake Abaya which separates it from the Oromia Region, and on the southeast by the Amaro special woreda. The administrative center of Gamo is Arba Minch.

Wolayita or Wolaita is an administrative zone in Ethiopia. Wolayita is bordered on the south by Gamo Zone, on the west by the Omo River which separates it from Dawro, on the northwest by Kembata Zone and Tembaro Special Woreda, on the north by Hadiya, on the northeast by the Oromia Region, on the east by the Bilate River which separates it from Sidama Region, and on the south east by the Lake Abaya which separates it from Oromia Region. The administrative centre of Wolayita is Sodo. Other major towns are Areka, Boditi, Tebela, Bale Hawassa, Gesuba, Gununo, Bedessa and Dimtu.
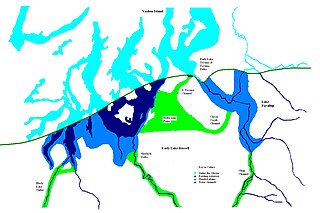
During the Vashon Glaciation a series of lakes formed along the southern margin of the Cordilleran Ice Cap. In the Puget Sound depression, a series of lakes developed, of which Lake Russell was the largest and the longest lasting. Early Lake Russell’s surface was at 160 ft (49 m) above sea level, draining across the divide at Shelton, Washington into early Glacial Lake Russell. When the ice margin receded northward, the lake expanded. When it reached the Clifton channel outlet, the water levels dropped to 120 ft (37 m) above sea level. The new longer and lower level lake is referred to as Lake Hood. The glacier continued to retreat until the northern outlet of the Hood Canal was reached as the water level equalized with Glacial Lake Russell becoming part of that body of water.
The Gidabo River is a medium-sized perennial river of south-central Ethiopia within the Great Rift Valley. The Gidabo River catchment area is one of the leading coffee production areas in Ethiopia.

The Gilgel Abay, or Lesser Abay, is a river of central Ethiopia. Rising in the mountains of Gojjam, it flows northward to empty into south-western Lake Tana at 11°48′N37°7′E. Tributaries of the Gilgel Abbay include the Ashar, Jamma, Kelti and the Koger. It was regarded as the true source of the Nile for a long time and the Jesuit priest Pedro Paez visited it in 1618. The name Gilgel Abbay means Lesser Nile, as Abbay is the name for the Blue Nile.
References
- ↑ Schütt, Brigitta, Thiemann, Stefan, Kulfo River, Southern Ethiopia:Regulator of Lake Level Changes in the Lake Abaya–Chamo Basin Archived 2018-02-07 at the Wayback Machine , Research Institute Water and Environment, Siegen University, Retrieved on June 22, 2008
- 1 2 Hanibal Lemma, and colleagues (2019). "Bedload transport measurements in the Gilgel Abay River, Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia". Journal of Hydrology. 577: 123968. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.123968. S2CID 199099061.
- ↑ Hadisa, Mamuye, Wilson, Michael, Cobblaha, Millicent, Boakyea, Daniel, (2008) Cytotaxonomy of Simulium soderense and a redescription of the ‘Kulfo’ form, International Journal of Tropical Insect Science, Cambridge University Press, Retrieved on June 22, 2008