
The zebu, sometimes known in the plural as indicine cattle, Camel cow or humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of domestic cattle originating in South Asia. Zebu, like many Sanga cattle breeds, differs from taurine cattle by a fatty hump on their shoulders, a large dewlap, and sometimes drooping ears. They are well adapted to withstanding high temperatures and are farmed throughout the tropics.

The Texas Longhorn is an American breed of beef cattle, characterized by its long horns, which can span more than 8 ft (2.4 m) from tip to tip. It derives from cattle brought from the Iberian Peninsula to the Americas by Spanish conquistadores from the time of the Second Voyage of Christopher Columbus until about 1512. For hundreds of years the cattle lived a semi-feral existence on the rangelands; they have a higher tolerance of heat and drought than most European breeds. It can be of any color or mix of colors. In some 40% of the cattle it is some shade of red, often a light red; the only shade of red not seen is the deep color typical of the Hereford.

Lake Chad is a freshwater lake located at the junction of Nigeria, Niger, Chad and Cameroon in central and western Africa. It is also an important wetland ecosystem in West Africa. The catchment area of Lake Chad is 1 million square kilometers. It used to be a large lake with an area of 28,000 square kilometers in the 19th century. However, due to climate change and human water diversion, Lake Chad has been greatly reduced since the mid-1970s, and its area has fluctuated between 2,000 and 5,000 square kilometers.

The Highland is a Scottish breed of rustic cattle. It originated in the Scottish Highlands and the Western Islands of Scotland and has long horns and a long shaggy coat. It is a hardy breed, able to withstand the intemperate conditions in the region. The first herd-book dates from 1885; two types – a smaller island type, usually black, and a larger mainland type, usually dun – were registered as a single breed. It is reared primarily for beef, and has been exported to several other countries.

The Longhorn or British Longhorn is a British breed of beef cattle characterised by long curving horns. It originated in northern England, in the counties of Lancashire, Westmorland and Yorkshire, and later spread to the English Midlands and to Ireland. It was originally a slow heavy draught animal; cows gave a little milk, although high in fat. In the eighteenth century Robert Bakewell applied his methods of selective breeding to these cattle, which for a short time became the predominant British breed. Both the numbers and the quality of the breed declined throughout the nineteenth century and for much of the twentieth. A breed society was formed in 1878, and a herd-book published in that year.

The Nguni is a cattle breed indigenous to Southern Africa. A hybrid of different Indian and later European cattle breeds, they were introduced by pastoralist tribes ancestral to modern Nguni people to Southern Africa during their migration from the North of the continent.
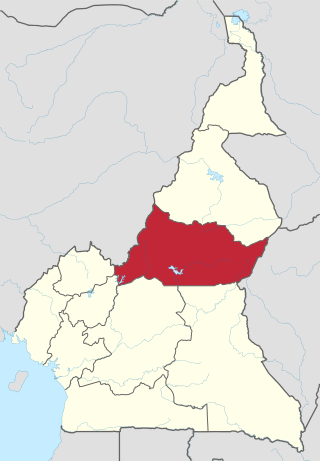
The Adamawa Region is a constituent region of the Republic of Cameroon. It borders the Centre and East regions to the south, the Northwest and West regions to the southwest, Nigeria to the west, the Central African Republic (CAR) to the east, and the North Region to the north.
The Zaghawa people, also called Beri or Zakhawa, are an ethnic group primarily residing in southwestern Libya, northeastern Chad, and western Sudan, including Darfur.

The Sukuma are a Bantu ethnic group from the southeastern African Great Lakes region. They are the largest ethnic group in Tanzania, with an estimated 10 million members or 16 percent of the country's total population. Sukuma means "north" and refers to "people of the north." The Sukuma refer to themselves as Basukuma (plural) and Nsukuma (singular).

A bovid hybrid is the hybrid offspring of members of two different species of the bovid family. There are 143 extant species of bovid, and the widespread domestication of several species has led to an interest in hybridisation for the purpose of encouraging traits useful to humans, and to preserve declining populations. Bovid hybrids may occur naturally through undirected interbreeding, traditional pastoral practices, or may be the result of modern interventions, sometimes bringing together species from different parts of the world.
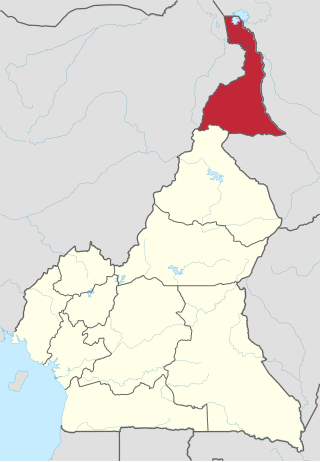
The Far North Region, also known as the Extreme North Region, is the northernmost and most populous constituent province of the Republic of Cameroon. It borders the North Region to the south, Chad to the east, and Nigeria to the west. The capital is Maroua.

The Ennedi Plateau is located in the northeast of Chad, in the regions of Ennedi-Ouest and Ennedi-Est. It is considered a part of the group of mountains known as the Ennedi Massif found in Chad, which is one of the nine countries that make up the Sahelian belt that spans the Atlantic Ocean to Sudan. The Ennedi is a sandstone bulwark in the middle of the Sahara, which was formed by erosion from wind and temperature. Many people occupied this area, such as hunters-gatherers and pastoralists. The Ennedi area is also known for its large collection of rock art depicting mainly cattle, as these animals had the greatest financial, environmental, and cultural impact. This art dates back nearly 7,000 years ago. Today, two semi-nomadic groups, mainly Muslim, live in the Ennedi during the rainy months and pass through the area during the dry season. They rely on their herds of camels, donkeys, sheep, and goats to survive.
The Buduma are an ethnic group of Chad, Cameroon, and Nigeria who inhabit many of the islands of Lake Chad. They are predominantly fishers and cattle-herders. In the past, the Buduma carried out violent raids on the cattle herds of their neighbors. They were feared villains with aggressive reputations; thus, they were respected and left alone for many years, protected by their own habitat of water and reeds.
Baggara cattle are an autochthonous Sudanese breed part of the shorthorned Zebu group of breeds of eastern Africa. Baggara cattle are smaller and thinner than the Boran breed of Kenya and Ethiopia. They are named for the Baggara people of western Sudan and central Chad, who raise Baggara cattle primarily for beef. Baggara means cattle people in the Shuwa Arabic language of these people. The related Butana and Kenana breeds of the Nile Valley are dairy breeds and need much more feed and water than the Baggara.
The Dufuna canoe is a dugout canoe discovered in 1987 by a Fulani cattle herdsman a few kilometers from the village of Dufuna in the Fune Local Government Area, not far from the Komadugu Gana River, in Yobe State, Nigeria. Radiocarbon dating of a sample of charcoal found near the site dates the canoe at 8,500 to 8,000 years old, linking the site to Lake Chad. The canoe is 8.4 metres (28 ft) long and is 0.5 metres tall at it largest point. It is currently located in Damaturu, Nigeria.

Sanga cattle is the collective name for indigenous cattle of sub-Saharan Africa. They are sometimes identified as a subspecies with the scientific name Bos taurus africanus. Their history of domestication and their origins in relation to taurine cattle, zebu cattle, and native African varieties of the ancestral aurochs are a matter of debate.

The Red Fulani is an African breed of cattle found from Mali across Niger and northern Nigeria to Chad and Cameroon.
Miniature cattle are found in various parts of the world. Some, such as the Dexter of Ireland and the Vechur of Kerala, India, are traditional breeds; others have been created by selective breeding. The Australian Lowline was the unexpected result of a scientific experiment. Some, but not all, miniature breeds display achondroplasia, or dwarfism.
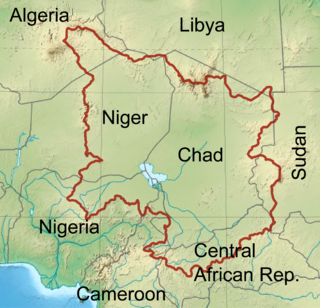
The Chad Basin is the largest endorheic basin in Africa, centered approximately on Lake Chad. It has no outlet to the sea and contains large areas of semi-arid desert and savanna. The drainage basin is approximately coterminous with the sedimentary basin of the same name, but extends further to the northeast and east.
The Kalahari Debate is a series of back and forth arguments that began in the 1980s amongst anthropologists, archaeologists, and historians about how the San people and hunter-gatherer societies in southern Africa have lived in the past. On one side of the debate were scholars led by Richard Borshay Lee and Irven DeVore, considered traditionalists or "isolationists." On the other side of the debate were scholars led by Edwin Wilmsen and James Denbow, considered revisionists or "integrationists."














