
Motorola, Inc. was an American multinational telecommunications company based in Schaumburg, Illinois. It was founded in 1928 as Galvin Manufacturing Corporation by brothers Paul and Joseph Galvin. The company changed its name to Motorola in 1947. After having lost $4.3 billion from 2007 to 2009, the company split into two independent public companies, Motorola Mobility and Motorola Solutions, on January 4, 2011. The reorganization was structured with Motorola Solutions legally succeeding Motorola, Inc., and Motorola Mobility being spun off.

A smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card is a physical electronic authentication device, used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart cards include a pattern of metal contacts to electrically connect to the internal chip. Others are contactless, and some are both. Smart cards can provide personal identification, authentication, data storage, and application processing. Applications include identification, financial, public transit, computer security, schools, and healthcare. Smart cards may provide strong security authentication for single sign-on (SSO) within organizations. Numerous nations have deployed smart cards throughout their populations.
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics. Biometric authentication is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used to identify individuals in groups that are under surveillance.
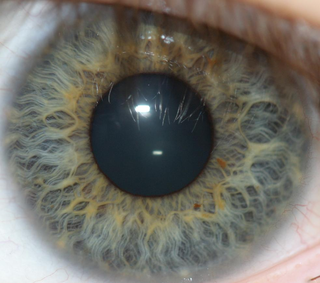
Iris recognition is an automated method of biometric identification that uses mathematical pattern-recognition techniques on video images of one or both of the irises of an individual's eyes, whose complex patterns are unique, stable, and can be seen from some distance. The discriminating powers of all biometric technologies depend on the amount of entropy they are able to encode and use in matching. Iris recognition is exceptional in this regard, enabling the avoidance of "collisions" even in cross-comparisons across massive populations. Its major limitation is that image acquisition from distances greater than a meter or two, or without cooperation, can be very difficult.

United States Visitor and Immigrant Status Indicator Technology is a U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) management system. The system involves the collection and analysis of biometric data, which are checked against a database to track individuals deemed by the United States to be terrorists, criminals, and illegal immigrants. US-VISIT is accessed by 30,000 users from federal, state, and local government agencies. Upon Presidential approval of the 2013 Continuing resolution the US-VISIT program officially became the "Office of Biometric Identity Management" (OBIM), save for portions of the agency which performed overstay analysis being transferred into U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement and biometric Entry and Exit operations which became a part of U.S. Customs and Border Protection.

A biometric passport is a traditional passport that has an embedded electronic microprocessor chip which contains biometric information that can be used to authenticate the identity of the passport holder. It uses contactless smart card technology, including a microprocessor chip and antenna embedded in the front or back cover, or centre page, of the passport. The passport's critical information is printed on the data page of the passport, repeated on the machine readable lines and stored in the chip. Public key infrastructure (PKI) is used to authenticate the data stored electronically in the passport chip, making it expensive and difficult to forge when all security mechanisms are fully and correctly implemented.
HID Global is an American manufacturer of secure identity products. The company is an independent brand of Assa Abloy, a Swedish door and access control conglomerate. Björn Lidefelt was appointed CEO on 27 January 2020. He succeeded Stefan Widing, who led HID Global for over four years.

Gemalto was an international digital security company providing software applications, secure personal devices such as smart cards and tokens, e-wallets and managed services. It was formed in June 2006 by the merger of two companies, Axalto and Gemplus International. Gemalto N.V.'s revenue in 2018 was €2.969 billion.

A Chilean passport is an identity document issued to citizens of Chile to facilitate international travel. Chilean passports are valid for worldwide travel and facilitate the access to consular services whilst abroad. They are issued by the Registro Civil e Identificación.

The Albanian passport is a travel document issued by the Ministry of Interior to Albanian citizens to enable them to travel abroad. They are also used as proof of identity within the country, along with the Albanian ID card.

Entrust Corp., formerly Entrust Datacard, provides software and hardware used to issue financial cards, e-passport production, user authentication for those looking to access secure networks or conduct financial transactions, trust certificated for websites, mobile credentials, and connected devices. The privately-held company is based in Shakopee, Minnesota and employs more than 2,500 people globally.
Extended Access Control (EAC) is a set of advanced security features for electronic passports that protects and restricts access to sensitive personal data contained in the RFID chip. In contrast to common personal data which can be protected by basic mechanisms, more sensitive data must be protected further for preventing unauthorized access and skimming. A chip protected by EAC will allow that this sensitive data is read only by an authorized passport inspection system.
Next Generation Identification (NGI) is a project of the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI). The project's goal is to expand the capabilities of the Integrated Automated Fingerprint Identification System (IAFIS), which is currently used by law enforcement to identify subjects by their fingerprints and to look up their criminal history. The NGI system will be a more modular system. It will also have more advanced lookup capabilities, incorporating palm print, iris, and facial identification. The FBI first used this system in February 2011.

The Albanian identity card (Letërnjoftim) is a national identity card issued by Albanian authorities to Albanian citizens. It is proof of identity, citizenship and residence. The current version is in ID1 format and biometric. The ID card is compulsory for citizens over 16 years of age, costs 1,500 lekë and is valid for 10 years.
IDEX Biometrics ASA, is a Norwegian biometrics company, specialising in fingerprint imaging and fingerprint recognition technology. The company was founded 1996 and is headquartered in Oslo, but its main operation is in the US, with offices in New York and Massachusetts. The company also has offices in the UK and China.
Biometrics refers to the automated recognition of individuals based on their biological and behavioral characteristics, not to be confused with statistical biometrics; which is used to analyse data in the biological sciences. Biometrics for the purposes of identification may involve DNA matching, facial recognition, fingerprints, retina and iris scanning, voice analysis, handwriting, gait, and even body odor.
This article is about Biometrics used by the South African government to combat fraud and corruption and to increase the efficiency of service delivery to the public.
IDEMIA is a multinational technology company headquartered in Courbevoie, France. It provides identity-related security services, and sells facial recognition and other biometric identification products and software to private companies and governments.
Identix Incorporated, established in August 1982, designed, developed, manufactured, and marketed user authentication solutions by capturing and/or comparing fingerprints for security applications and personal identification. Markets included corporate enterprise security, intranet, extranet, internet, wireless Web access and security, E-commerce, government, and law enforcement agencies.

Automated border control systems (ABC) or eGates are automated self-service barriers which use data stored in a chip in biometric passports along with a photo or fingerprint taken at the time of entering the eGates to verify the passport holder's identity. Travellers undergo biometric verification using facial or iris recognition, fingerprints, or a combination of modalities. After the identification process is complete and the passport holder's identity is verified, a physical barrier such as a gate or turnstile opens to permit passage. If the passport holder's identification is not verified or if the system malfunctions, then the gate or turnstile does not open and an immigration officer will meet the person. E-gates came about in the mid-2000s as an automated method of reading the then-newly ICAO mandated e-passports.











