Related Research Articles

GW-BASIC is a dialect of the BASIC programming language developed by Microsoft from IBM BASICA. Functionally identical to BASICA, its BASIC interpreter is a fully self-contained executable and does not need the Cassette BASIC ROM found in the original IBM PC. It was bundled with MS-DOS operating systems on IBM PC compatibles by Microsoft.

PKZIP is a file archiving computer program, notable for introducing the popular ZIP file format. PKZIP was first introduced for MS-DOS on the IBM-PC compatible platform in 1989. Since then versions have been released for a number of other architectures and operating systems. PKZIP was originally written by Phil Katz and marketed by his company PKWARE, Inc, with both of them bearing his initials: 'PK'.
In computing, tar is a computer software utility for collecting many files into one archive file, often referred to as a tarball, for distribution or backup purposes. The name is derived from "tape archive", as it was originally developed to write data to sequential I/O devices with no file system of their own. The archive data sets created by tar contain various file system parameters, such as name, timestamps, ownership, file-access permissions, and directory organization. POSIX abandoned tar in favor of pax, yet tar sees continued widespread use.
ZIP is an archive file format that supports lossless data compression. A ZIP file may contain one or more files or directories that may have been compressed. The ZIP file format permits a number of compression algorithms, though DEFLATE is the most common. This format was originally created in 1989 and was first implemented in PKWARE, Inc.'s PKZIP utility, as a replacement for the previous ARC compression format by Thom Henderson. The ZIP format was then quickly supported by many software utilities other than PKZIP. Microsoft has included built-in ZIP support in versions of Microsoft Windows since 1998 via the "Windows Plus!" addon for Windows 98. Native support was added as of the year 2000 in Windows ME. Apple has included built-in ZIP support in Mac OS X 10.3 and later. Most free operating systems have built in support for ZIP in similar manners to Windows and Mac OS X.

A JAR is a package file format typically used to aggregate many Java class files and associated metadata and resources into one file for distribution.

In computing, configuration files are files used to configure the parameters and initial settings for some computer programs. They are used for user applications, server processes and operating system settings.
.exe is a common filename extension denoting an executable file for Microsoft Windows.
A fat binary is a computer executable program or library which has been expanded with code native to multiple instruction sets which can consequently be run on multiple processor types. This results in a file larger than a normal one-architecture binary file, thus the name.

LHA or LZH is a freeware compression utility and associated file format. It was created in 1988 by Haruyasu Yoshizaki, a doctor and originally named LHarc. A complete rewrite of LHarc, tentatively named LHx, was eventually released as LH. It was then renamed to LHA to avoid conflicting with the then-new MS-DOS 5.0 LH command. The original LHA and its Windows port, LHA32, are no longer in development because Yoshizaki is busy at work.
FILE_ID.DIZ is a plain-text file containing a brief description of the content of archive to which it belongs. Such files were originally used in archives distributed through bulletin board systems (BBSes) and is still used in the warez scene. FILE_ID stands for "file identification". DIZ stands for "description in zipfile".
ARC is a lossless data compression and archival format by System Enhancement Associates (SEA). The file format and the program were both called ARC. The format is known as the subject of controversy in the 1980s, part of important debates over what would later be known as open formats.
In computing, an archive file is a computer file that is composed of one or more files along with metadata. Archive files are used to collect multiple data files together into a single file for easier portability and storage, or simply to compress files to use less storage space. Archive files often store directory structures, error detection and correction information, arbitrary comments, and sometimes use built-in encryption.
Amiga Disk File (ADF) is a file format used by Amiga computers and emulators to store images of floppy disks. It has been around almost as long as the Amiga itself, although it was not initially called by any particular name. Before it was known as ADF, it was used in commercial game production, backup and disk virtualization. ADF is a track-by-track dump of the disk data as read by the Amiga operating system, and so the "format" is really fixed-width AmigaDOS data tracks appended one after another and held in a file. This file would, typically, be formatted, like the disk, in Amiga Old File System (OFS).
A source-to-source translator, source-to-source compiler, transcompiler, or transpiler is a type of translator that takes the source code of a program written in a programming language as its input and produces an equivalent source code in the same or a different programming language. A source-to-source translator converts between programming languages that operate at approximately the same level of abstraction, while a traditional compiler translates from a higher level programming language to a lower level programming language. For example, a source-to-source translator may perform a translation of a program from Python to JavaScript, while a traditional compiler translates from a language like C to assembler or Java to bytecode. An automatic parallelizing compiler will frequently take in a high level language program as an input and then transform the code and annotate it with parallel code annotations or language constructs.
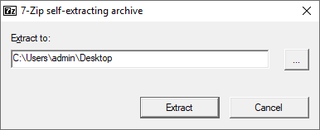
A self-extracting archive is a computer executable program which contains compressed data in an archive file combined with machine-executable program instructions to extract this information on a compatible operating system and without the necessity for a suitable extractor to be already installed on the target computer. The executable part of the file is known as a decompressor stub.
SQ (squeeze) is a computer program, devised by Richard (Dick) Greenlaw circa 1981, which was used in the early 1980s on both DOS and CP/M computer systems to compress files so they use less space.

DOS is a platform-independent acronym for "disk operating system" that later became a common shorthand for disk-based operating systems on IBM PC compatibles. DOS primarily consists of Microsoft's MS-DOS and a rebranded version under the name IBM PC DOS, both of which were introduced in 1981. Later compatible systems from other manufacturers include DR DOS (1988), ROM-DOS (1989), PTS-DOS (1993), and FreeDOS (1998). MS-DOS dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995.