Related Research Articles
Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) is a control system architecture comprising computers, networked data communications and graphical user interfaces for high-level supervision of machines and processes. It also covers sensors and other devices, such as programmable logic controllers, which interface with process plant or machinery.

An intelligent transportation system (ITS) is an advanced application which aims to provide innovative services relating to different modes of transport and traffic management and enable users to be better informed and make safer, more coordinated, and 'smarter' use of transport networks.
Zigbee is an IEEE 802.15.4-based specification for a suite of high-level communication protocols used to create personal area networks with small, low-power digital radios, such as for home automation, medical device data collection, and other low-power low-bandwidth needs, designed for small scale projects which need wireless connection. Hence, Zigbee is a low-power, low data rate, and close proximity wireless ad hoc network.
Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) is an extension to the Internet Protocol and to the Transmission Control Protocol and is defined in RFC 3168 (2001). ECN allows end-to-end notification of network congestion without dropping packets. ECN is an optional feature that may be used between two ECN-enabled endpoints when the underlying network infrastructure also supports it.
Deep packet inspection (DPI) is a type of data processing that inspects in detail the data being sent over a computer network, and may take actions such as alerting, blocking, re-routing, or logging it accordingly. Deep packet inspection is often used to baseline application behavior, analyze network usage, troubleshoot network performance, ensure that data is in the correct format, check for malicious code, eavesdropping, and internet censorship, among other purposes. There are multiple headers for IP packets; network equipment only needs to use the first of these for normal operation, but use of the second header is normally considered to be shallow packet inspection despite this definition.

NetFlow is a feature that was introduced on Cisco routers around 1996 that provides the ability to collect IP network traffic as it enters or exits an interface. By analyzing the data provided by NetFlow, a network administrator can determine things such as the source and destination of traffic, class of service, and the causes of congestion. A typical flow monitoring setup consists of three main components:

A security alarm is a system designed to detect intrusion, such as unauthorized entry, into a building or other areas such as a home or school. Security alarms used in residential, commercial, industrial, and military properties protect against burglary (theft) or property damage, as well as personal protection against intruders. Security alerts in neighborhoods show a connection with diminished robbery. Car alarms likewise help protect vehicles and their contents. Prisons also use security systems for the control of inmates.
The concept of the "sensor web" is a type of sensor network that is especially well suited for environmental monitoring. The phrase the "sensor web" is also associated with a sensing system which heavily utilizes the World Wide Web. OGC's Sensor Web Enablement (SWE) framework defines a suite of web service interfaces and communication protocols abstracting from the heterogeneity of sensor (network) communication.
The next-generation network (NGN) is a body of key architectural changes in telecommunication core and access networks. The general idea behind the NGN is that one network transports all information and services by encapsulating these into IP packets, similar to those used on the Internet. NGNs are commonly built around the Internet Protocol, and therefore the term all IP is also sometimes used to describe the transformation of formerly telephone-centric networks toward NGN.
A network tap is a system that monitors events on a local network. A tap is typically a dedicated hardware device, which provides a way to access the data flowing across a computer network.
In computer networks, network traffic measurement is the process of measuring the amount and type of traffic on a particular network. This is especially important with regard to effective bandwidth management.
Autonomic Networking follows the concept of Autonomic Computing, an initiative started by IBM in 2001. Its ultimate aim is to create self-managing networks to overcome the rapidly growing complexity of the Internet and other networks and to enable their further growth, far beyond the size of today.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) recording is a subset of telephone recording or voice logging, first used by call centers and now being used by all types of businesses. There are many reasons for recording Voice over IP call traffic such as: reducing company vulnerability to lawsuits by maintaining recorded evidence, complying with telephone call recording laws, increasing security, employee training and performance reviews, enhancing employee control and alignment, verifying data, sharing data as well as customer satisfaction and enhancing call center agent morale.
In computing, Microsoft's Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 introduced in 2007/2008 a new networking stack named Next Generation TCP/IP stack, to improve on the previous stack in several ways. The stack includes native implementation of IPv6, as well as a complete overhaul of IPv4. The new TCP/IP stack uses a new method to store configuration settings that enables more dynamic control and does not require a computer restart after a change in settings. The new stack, implemented as a dual-stack model, depends on a strong host-model and features an infrastructure to enable more modular components that one can dynamically insert and remove.
Named Data Networking (NDN) is a proposed Future Internet architecture inspired by years of empirical research into network usage and a growing awareness of unsolved problems in contemporary internet architectures like IP. NDN has its roots in an earlier project, Content-Centric Networking (CCN), which Van Jacobson first publicly presented in 2006. The NDN project is investigating Jacobson's proposed evolution from today's host-centric network architecture IP to a data-centric network architecture (NDN). The belief is that this conceptually simple shift will have far-reaching implications for how people design, develop, deploy, and use networks and applications.
The Internet of things (IoT) describes physical objects that are embedded with sensors, processing ability, software, and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other communications networks. Internet of Things has been considered a misnomer because devices do not need to be connected to the public internet, they only need to be connected to a network and be individually addressable.
Dust Networks, Inc. is an American company specializing in the design and manufacture of wireless sensor networks for industrial applications including process monitoring, condition monitoring, asset management, Environment, Health and Safety (EHS) monitoring and power management. They were acquired by Linear Technology, Inc in December 2011, which in turn was acquired by Analog Devices, Inc in 2017. The Dust Networks product team operates in the IoT Networking Platforms group of Analog Devices.

The unattended ground sensor (UGS) is under development as part of the United States Army's Future Combat Systems Program. For information on currently fielded UGS systems, refer to the Current Force UGS Program or CF UGS.
Flowmon is a name for monitoring probe which is the result of academic research activity on CESNET and also a name for a commercial product which is marketed by university spin-off company Flowmon Networks.
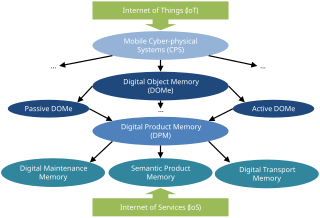
A digital object memory (DOMe) is a digital storage space intended to keep permanently all related information about a concrete physical object instance that is collected during the lifespan of this object and thus forms a basic building block for the Internet of Things (IoT) by connecting digital information with physical objects.
References
- ↑ Welcome to LOBSTER!, Information Society Technologies
- ↑ "Taking stock of LOBSTER" (press release), 17 May 2007
- ↑ M. Polychronakis et al. (2004), "Design of an Application Programming Interface for IP Network Monitoring"
- ↑ APPMON Archived 2012-12-18 at archive.today
- ↑ Stager, UNINETT.AS
- ↑ ABW [ permanent dead link ]