Related Research Articles

The national anthem of Bolivia, also known as "Bolivianos, el Hado Propicio" and originally titled the "Canción Patriótica", was adopted in 1851. José Ignacio de Sanjinés, a signer of both the Bolivian Declaration of Independence and the first Bolivian Constitution, wrote the lyrics. The music was composed by an Italian, Leopoldo Benedetto Vincenti.

Huacho is a city in Peru, capital of the Huaura Province and capital of the Lima Region. Also is the most populated city of the Lima Region and Norte Chico. It is located 223 feet above sea level and 148 km north of the city of Lima. The city is located on the Pan-American Highway and it is close to the Lachay National Reserve, so it has extensive vegetation and wildlife.

Chorrillos is a district of the Lima Province in Peru and part of the city of Lima. It gets its name from the Spanish word for "trickle of water". The district was founded as San Pedro de los Chorrillos and served as a deluxe beach resort until the late 19th century, when it was almost completely destroyed by Chilean forces during the War of the Pacific.
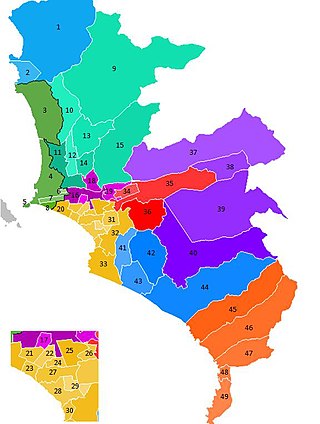
The Lima Metropolitan Area is an area formed by the conurbation of the Peruvian provinces of Lima and Callao. It is the largest of the metropolitan areas of Peru, the seventh largest in the Americas, the fourth largest in Latin America, and among the thirty largest in the world. The conurbation process started to be evident in the 1980s.

Rímac is a district in the Lima Province, Peru. It lies directly to the north of downtown Lima, to which it is connected by six bridges over the Rímac River. The district also borders the Independencia, San Martín de Porres, and San Juan de Lurigancho districts. Vestiges of Lima's colonial heyday remain today in an area of the Rímac district known as the Historic centre of Lima, which was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1988. Downtown Rímac District has, like its southern counterpart, its eastern and western sides divided by Jirón Trujillo, which connects to Lima District's Jirón de la Unión through the Puente de Piedra, the oldest bridge in the whole city. Rímac's East side features the Plaza de Acho, the most famous bullfighting arena in South America and one of the most well known in the world.

San Miguel is one of the 43 districts that are part of the Lima province and is part of the urban area of Lima, Peru. It is bordered by the districts of Bellavista and downtown Lima on the north; Pueblo Libre, Magdalena del Mar and downtown Lima on the east; the Pacific Ocean on the south; and the La Perla district on the west. It is located 20 to 30 min from the airport.

Jesús María is one of the most centrally located districts of Lima, Peru. It is an upper class, high-density district and it usually ranks in the top districts with the best quality of life in Peru with an HDI of 0.8372 (2019), only behind the districts of La Molina and Lince.
Brena District is the smallest district of the Lima Province in Peru. It is part of Lima city metropolitan area.

Pueblo Libre is a district of the Lima Province in Peru. Its name, which means Free Town or Free People, was granted by José de San Martín on April 10, 1822, as a recognition of the patriotism shown by its inhabitants during the Peruvian War of Independence. The district was created by law 9162 on November 5, 1940. Pueblo Libre is a middle-class residential community and has the most parks in Lima, although it has several branches of banks, local private universities and major corporations. The current mayor of Pueblo Libre is Mónica Rossana Tello López

The Museo Nacional de Arqueología Antropología e Historia del Perú is the largest and oldest museum in Peru, located on Plaza Bolívar in the Pueblo Libre district of Lima. The museum houses more than 100,000 artifacts spanning the entire history of human occupation in what is now Peru. Highlights include the Raimondi Stele and the Tello Obelisk from Chavín de Huantar, and an impressive scale model of the Incan citadel, Machu Picchu. The museum is currently (2023) under restoration and very few rooms are open for visitors.

Kuélap or Cuélap is a walled settlement located in the mountains near the towns of María and Tingo, in the southern part of the region of Amazonas, Peru. It was built by the Chachapoyas culture in the 6th century AD on a ridge overlooking the Utcubamba Valley.

The Huata District is the smallest of the 10 districts of the Huaylas Province in the Ancash Region of Peru. The capital of the district is the village of Huata.

The Mato District is one of 10 districts of the Huaylas Province in the Ancash Region of Peru. The capital of the district is the village of Villa Sucre.
Pueblo Libre District is one of ten districts of the province Huaylas in Peru.

The University of San Martin de Porres (USMP) is a private nonprofit university located in the city of Lima, Peru. It was founded by the Dominican Order of the Catholic Church in 1962.

Yaxcabá Municipality is one of the 106 municipalities in the Mexican state of Yucatán containing (1079 km2) of land and located roughly 80 km northeast of the city of Mérida.
The barrios of Puerto Rico are the primary legal divisions of the seventy-eight municipalities of Puerto Rico. Puerto Rico's 78 municipios are divided into geographical sections called barrios and, as of 2010, there were 902 of them. In the US Census a barrio sometimes includes a division called a comunidad or subbarrio. In Puerto Rico, barrios are composed of sectors. The types of sectors, (sectores) may vary, from normally sector to urbanización to reparto to barriada to residencial, among others.

Maunabo barrio-pueblo is a barrio and the administrative center (seat) of Maunabo, a municipality of Puerto Rico. Its population in 2010 was 317.

The Palacio de la Magdalena is a viceregal house located in the district of Pueblo Libre in Lima. It is located near the Plaza de los Libertadores, and is also known as the Quinta de los Libertadores. The building was declared a national monument in 1972.
References
- 1 2 Municipalidad de Pueblo Libre (2010). Plan de Desarrollo Concertado de Pueblo Libre 2010–2021, p. 36. Retrieved 12 October 2018 (in Spanish).
- ↑ Candamo, José Agustín Puente (2008). Pueblo Libre: historia, cultura y tradición, p. 50. Universidad Alas Peruanas. ISBN 9972210707 (in Spanish)