Related Research Articles
Canada is divided into 10 provinces and three territories. The majority of Canada's population is concentrated in the areas close to the Canada–US border. Its four largest provinces by area are also its most populous; together they account for 86.5% of the country's population. The territories account for over a third of Canada's area but are home to only 0.32% of its population, which skews the national population density value.
French Canadians, or Franco-Canadians, refeirs to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to French colonists who settled in Canada beginning in the 17th century or to French-speaking or Francophone Canadians of any ethnic origin.

The Quebec sovereignty movement is a political movement whose objective is to achieve the sovereignty of Quebec, a province of Canada since 1867, including in all matters related to any provision of Quebec's public order that is applicable on its territory. Sovereignists suggest that the people of Quebec make use of their right to self-determination – a principle that includes the possibility of choosing between integration with a third state, political association with another state or independence – so that Quebecois, collectively and by democratic means, give themselves a sovereign state with its own independent constitution.

Quebec nationalism or Québécois nationalism is a feeling and a political doctrine that prioritizes cultural belonging to, the defence of the interests of, and the recognition of the political legitimacy of the Québécois nation. It has been a movement and a central issue in Quebec politics since the beginning of the 19th century. Québécois nationalism has seen several political, ideological and partisan variations and incarnations over the years.

Quebec was first called Canada between 1534 and 1763. It was the most developed colony of New France as well as New France's centre, responsible for a variety of dependencies. Common themes in Quebec's early history as Canada include the fur trade -because it was the main industry- as well as the exploration of North America, war against the English, and alliances or war with Native American groups.
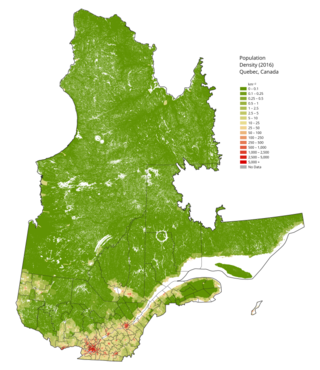
The demographics of Quebec constitutes a complex and sensitive issue, especially as it relates to the National question. Quebec is the only province in Canada to feature a francophone (French-speaking) majority, and where anglophones (English-speakers) constitute an officially recognized minority group. According to the 2011 census, French is spoken by more than 85.5% of the population while this number rises to 88% for children under 15 years old. According to the 2011 census, 95% of Quebec are able to conduct a conversation in French, with less than 5% of the population not able to speak French.
The Quebec diaspora consists of Quebec immigrants and their descendants dispersed over the North American continent and historically concentrated in the New England region of the United States, Ontario, and the Canadian Prairies. The mass emigration out of Quebec occurred in the period between 1840 and the Great Depression of the 1930s.
This article presents the current language demographics of the Canadian province of Quebec.
Francization or Francisation, Frenchification, or Gallicization is the expansion of French language use—either through willful adoption or coercion—by more and more social groups who had not before used the language as a common means of expression in daily life. As a linguistic concept, known usually as gallicization, it is the practice of modifying foreign words, names, and phrases to make them easier to spell, pronounce, or understand in French.
The Demographics of Montreal concern population growth and structure for Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The information is analyzed by Statistics Canada and compiled every five years, with the most recent census having taken place in 2016.

The official languages of Canada are English and French, which "have equality of status and equal rights and privileges as to their use in all institutions of the Parliament and Government of Canada," according to Canada's constitution. "Official bilingualism" is the term used in Canada to collectively describe the policies, constitutional provisions, and laws that ensure legal equality of English and French in the Parliament and courts of Canada, protect the linguistic rights of English- and French-speaking minorities in different provinces, and ensure a level of government services in both languages across Canada.

Franco-Columbians are French Canadians or Canadian francophones living in the province of British Columbia. According to the 2016 Canadian Census, 71,705 residents of the province stated that French is their mother tongue. In the same census, 388,815 British Columbians claimed full or partial French ancestry.

French Americans or Franco-Americans, are citizens or nationals of the United States who identify themselves with having full or partial French or French-Canadian heritage, ethnicity and/or ancestral ties. They include French-Canadian Americans, whose experience and identity differ from the broader community.
Quebec English encompasses the English dialects of the predominantly French-speaking Canadian province of Quebec. There are few distinctive phonological features and very few restricted lexical features common among English-speaking Quebecers. The native English speakers in Quebec generally align to Standard Canadian English, one of the largest and most relatively homogeneous dialects in North America. This standard English accent is common in Montreal, where the vast majority of Quebec's native English speakers live. English-speaking Montrealers have, however, established ethnic groups that retain certain lexical features: Irish, Jewish, Italian, and Greek communities that all speak discernible varieties of English. Isolated fishing villages on the Basse-Côte-Nord of Quebec speak Newfoundland English, and many Gaspesian English-speakers use Maritime English. Francophone speakers of Quebec also have their own second-language English that incorporates French accent features, vocabulary, etc. Finally, the Kahnawake Mohawks of south shore Montreal and the Cree and Inuit of Northern Quebec speak English with their own distinctive accents, usage, and expressions from their indigenous languages.
Canadian identity refers to the unique culture, characteristics and condition of being Canadian, as well as the many symbols and expressions that set Canada and Canadians apart from other peoples and cultures of the world. Primary influences on the Canadian identity trace back to the arrival, beginning in the early seventeenth century, of French settlers in Acadia and the St. Lawrence River Valley, and of English, Scottish and Irish settlers in Newfoundland and the Maritimes, the British conquest of New France in 1759, the migration of United Empire Loyalists to Upper Canada and New Brunswick, and the ensuing dominance of French and British culture in the gradual development of both an imperial and national identity.

New Brunswick is one of Canada's three provinces of the Maritimes, and the only officially bilingual province in the country. The provincial Department of Finance estimates that the province's population in 2006 was 729,997 of which the majority is English-speaking but with a substantial French-speaking minority of mostly Acadian origin.
The French term pure laine, refers to Québécois people of French-Canadian ancestry, especially those descended from the original settlers of New France who arrived during the 17th and 18th centuries. Terms with a similar meaning include de souche and old stock as in "Old Stock Canadians".
Quebecers or Quebeckers are people associated with Quebec. The term is most often used in reference to descendants of the French settlers in Quebec but it can also be used to describe people of any ethnicity who live in the province.

Interprovincial migration in Canada is the movement by people from one Canadian province or territory to another with the intention of settling, permanently or temporarily, in the new province or territory; it is more-or-less stable over time. In fiscal year 2019–20, 278,316 Canadians migrated province, representing 0.729% of the population.
English-speaking Quebecers, also known as Anglo-Quebecers, English Quebecers, or Anglophone Quebecers or simply Anglos in a Quebec context, are a linguistic minority in the francophone province of Quebec. According to the 2011 Canadian census, 599,225 people in Quebec declare English as a mother tongue. When asked, 834,950 people reported using English the most at home.
References
- ↑ Colombo's Canadian References, Oxford University Press, 1976, p.444.