
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from Latin clavicula 'little key' because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit.

The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus with the clavicle. Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble.
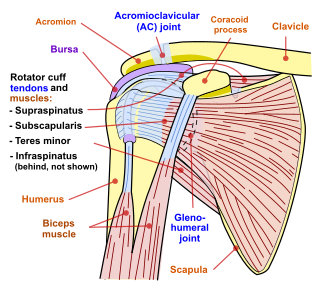
Shoulder problems including pain, are one of the more common reasons for physician visits for musculoskeletal symptoms. The shoulder is the most movable joint in the body. However, it is an unstable joint because of the range of motion allowed. This instability increases the likelihood of joint injury, often leading to a degenerative process in which tissues break down and no longer function well.

The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula, and the humerus as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons. The articulations between the bones of the shoulder make up the shoulder joints. The shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is the major joint of the shoulder, but can more broadly include the acromioclavicular joint. In human anatomy, the shoulder joint comprises the part of the body where the humerus attaches to the scapula, and the head sits in the glenoid cavity. The shoulder is the group of structures in the region of the joint.

Fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions. It owes its inflexibility and toughness to the former of these constituents, and its elasticity to the latter. It is the only type of cartilage that contains type I collagen in addition to the normal type II.

In vertebrate anatomy, hip refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.
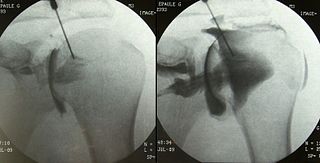
An arthrogram is a series of images of a joint after injection of a contrast medium, usually done by fluoroscopy or MRI. The injection is normally done under a local anesthetic such as Novocain or lidocaine. The radiologist or radiographer performs the study using fluoroscopy or x-ray to guide the placement of the needle into the joint and then injects around 10 ml of contrast based on age. There is some burning pain from the anesthetic and a painful bubbling feeling in the joint after the contrast is injected. This only lasts 20 – 30 hours until the Contrast is absorbed. During this time, while it is allowed, it is painful to use the limb for around 10 hours. After that the radiologist can more clearly see what is going on under your skin and can get results out within 24 to 48 hours.

The shoulder joint is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus. Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body.

The ball-and-socket joint is a type of synovial joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion around an indefinite number of axes, which have one common center. This enables the joint to move in many directions.

The shoulder girdle or pectoral girdle is the set of bones in the appendicular skeleton which connects to the arm on each side. In humans it consists of the clavicle and scapula; in those species with three bones in the shoulder, it consists of the clavicle, scapula, and coracoid. Some mammalian species have only the scapula.
Dead arm syndrome starts with repetitive motion and forces on the posterior capsule of the shoulder. The posterior capsule is a band of fibrous tissue that interconnects with tendons of the rotator cuff of the shoulder. Four muscles and their tendons make up the rotator cuff. They cover the outside of the shoulder to hold, protect and move the joint.

A SLAP tear or SLAP lesion is an injury to the glenoid labrum. SLAP is an acronym for "superior labral tear from anterior to posterior".

The glenoid fossa of the scapula or the glenoid cavity is a bone part of the shoulder. The word glenoid is pronounced or and is from Greek: gléne, "socket", reflecting the shoulder joint's ball-and-socket form. It is a shallow, pyriform articular surface, which is located on the lateral angle of the scapula. It is directed laterally and forward and articulates with the head of the humerus; it is broader below than above and its vertical diameter is the longest.
Labium is the Latin word for lip. In English, it may refer to:

The glenoid labrum is a fibrocartilaginous structure rim attached around the margin of the glenoid cavity in the shoulder blade. The shoulder joint is considered a ball and socket joint. However, in bony terms the 'socket' is quite shallow and small, covering at most only a third of the 'ball'. The socket is deepened by the glenoid labrum, stabilizing the shoulder joint.

The acetabular labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the acetabulum of the hip. The anterior portion is most vulnerable when the labrum tears.
Shoulder arthritis can be one of three types of arthritis in the glenohumeral joint of the shoulder. The glenohumeral joint is a ball and socket joint, which relies on cartilage to move smoothly and to operate normally.
Shoulder surgery is a means of treating injured shoulders. Many surgeries have been developed to repair the muscles, connective tissue, or damaged joints that can arise from traumatic or overuse injuries to the shoulder.

The capsule of the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint is the articular capsule of the shoulder. It completely surrounds the joint. It is attached above to the circumference of the glenoid cavity beyond the glenoidal labrum, and below to the anatomical neck of the humerus, approaching nearer to the articular cartilage above than in the rest of its extent.
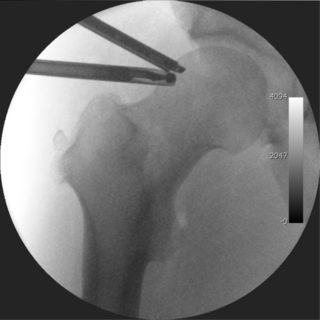
Hip arthroscopy refers to the viewing of the interior of the acetabulofemoral (hip) joint through an arthroscope and the treatment of hip pathology through a minimally invasive approach. This technique is sometimes used to help in the treatment of various joint disorders and has gained popularity because of the small incisions used and shorter recovery times when compared with conventional surgical techniques. Hip arthroscopy was not feasible until recently, new technology in both the tools used and the ability to distract the hip joint has led to a recent surge in the ability to do hip arthroscopy and the popularity of it.












