
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Hepatitis is acute if it resolves within six months, and chronic if it lasts longer than six months. Acute hepatitis can resolve on its own, progress to chronic hepatitis, or (rarely) result in acute liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may progress to scarring of the liver (cirrhosis), liver failure, and liver cancer.

Forrest Gump is a 1994 American comedy-drama film directed by Robert Zemeckis and written by Eric Roth. It is based on the 1986 novel of the same name by Winston Groom and stars Tom Hanks, Robin Wright, Gary Sinise, Mykelti Williamson and Sally Field. The story depicts several decades in the life of Forrest Gump (Hanks), a slow-witted and kindhearted man from Alabama who witnesses and unwittingly influences several defining historical events in the 20th-century United States. The film differs substantially from the novel.

Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and yellow tinged skin occurs. The virus persists in the liver in about 75% to 85% of those initially infected. Early on chronic infection typically has no symptoms. Over many years however, it often leads to liver disease and occasionally cirrhosis. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop serious complications such as liver failure, liver cancer, or dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and stomach.

Hepatology is the branch of medicine that incorporates the study of liver, gallbladder, biliary tree, and pancreas as well as management of their disorders. Although traditionally considered a sub-specialty of gastroenterology, rapid expansion has led in some countries to doctors specializing solely on this area, who are called hepatologists.
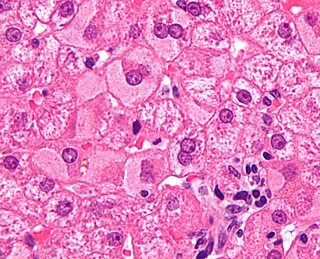
Viral hepatitis is liver inflammation due to a viral infection. It may present in acute form as a recent infection with relatively rapid onset, or in chronic form.

Chiron Corporation was an American multinational biotechnology firm founded in 1981, based in Emeryville, California, that was acquired by Novartis on April 20, 2006. It had offices and facilities in eighteen countries on five continents. Chiron's business and research was in three main areas: biopharmaceuticals, vaccines, and blood testing. Chiron's vaccines and blood testing units were combined to form Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics, while Chiron BioPharmaceuticals was integrated into Novartis Pharmaceuticals. In 2014, Novartis completed the sale of its blood transfusion diagnostics unit to Grifols and announced agreements for the sale of its vaccines unit to GlaxoSmithKline.
An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming retroviruses in the 1950–60s, when the term "oncornaviruses" was used to denote their RNA virus origin. With the letters "RNA" removed, it now refers to any virus with a DNA or RNA genome causing cancer and is synonymous with "tumor virus" or "cancer virus". The vast majority of human and animal viruses do not cause cancer, probably because of longstanding co-evolution between the virus and its host. Oncoviruses have been important not only in epidemiology, but also in investigations of cell cycle control mechanisms such as the retinoblastoma protein.

Harvey James Alter is an American medical researcher, virologist, physician and Nobel Prize laureate, who is best known for his work that led to the discovery of the hepatitis C virus. Alter is the former chief of the infectious disease section and the associate director for research of the Department of Transfusion Medicine at the Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center in the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in Bethesda, Maryland. In the mid-1970s, Alter and his research team demonstrated that most post-transfusion hepatitis cases were not due to hepatitis A or hepatitis B viruses. Working independently, Alter and Edward Tabor, a scientist at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, proved through transmission studies in chimpanzees that a new form of hepatitis, initially called "non-A, non-B hepatitis" caused the infections, and that the causative agent was probably a virus. This work eventually led to the discovery of the hepatitis C virus in 1988, for which he shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2020 along with Michael Houghton and Charles M. Rice.

The history of virology – the scientific study of viruses and the infections they cause – began in the closing years of the 19th century. Although Louis Pasteur and Edward Jenner developed the first vaccines to protect against viral infections, they did not know that viruses existed. The first evidence of the existence of viruses came from experiments with filters that had pores small enough to retain bacteria. In 1892, Dmitri Ivanovsky used one of these filters to show that sap from a diseased tobacco plant remained infectious to healthy tobacco plants despite having been filtered. Martinus Beijerinck called the filtered, infectious substance a "virus" and this discovery is considered to be the beginning of virology.
The Freedom Forum is a nonprofit organization that runs the First Amendment Center and the Newseum Institute at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tennessee. The Freedom Forum is also the creator of the Newseum in Washington, D.C., which it sold to Johns Hopkins University in 2019.

Sir Michael Houghton is a British scientist and Nobel Prize laureate. Along with Qui-Lim Choo, George Kuo and Daniel W. Bradley, he co-discovered Hepatitis C in 1989. He also co-discovered the Hepatitis D genome in 1986. The discovery of the Hepatitis C virus (HCV) led to the rapid development of diagnostic reagents to detect HCV in blood supplies, which has reduced the risk of acquiring HCV through blood transfusion from one in three to about one in two million. It is estimated that antibody testing has prevented at least 40,000 new infections per year in the US alone and many more worldwide.
Qui-Lim Choo is a Singapore-born scientist, who along with Michael Houghton, George Kuo and Daniel W. Bradley, co-discovered and cloned Hepatitis C in 1989. He also co-discovered the Hepatitis D genome in 1986. The discovery of Hepatitis C led to the rapid development of diagnostic reagents to detect Hepatitis C virus in blood supplies which has reduced the risk of acquiring hepatitis C through blood transfusion from one in three to about one in two million. It is estimated that antibody testing has prevented at least 40,000 new infections per year in the US alone and many more worldwide.
Daniel W. Bradley is an important American virologist who, along with Michael Houghton, Qui-Lim Choo and George Kuo at Chiron Corporation, worked to help isolate the Hepatitis C virus in 1989. He graduated from San José State University in 1964 before going on to receive a master's degree in biochemistry from the University of California and a doctorate from the University of Arizona. He worked for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention starting in 1971. He received the Karl Landsteiner Memorial Award of the American Association of Blood Banks in 1992, the Robert Koch Prize in 1993, and the Gairdner Foundation International Award in 2013.
George Ching-Hung Kuo is a Taiwanese-born scientist, who along with Michael Houghton, Qui-Lim Choo and Daniel W. Bradley, co-discovered and cloned the hepatitis C virus in 1989.
Stephen Mark Feinstone is a virologist who, together with Albert Kapikian and Robert Purcell, co-identified the Hepatitis A virus (HAV) in 1973.

Robert Harry Purcell is an American virologist and former co-chief of the Laboratory of Infectious Diseases at the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease. He is known for his work on hepatitis viruses, and was involved in identifying hepatitis A virus, hepatitis D virus, and hepatitis E virus, developing an animal model for hepatitis B, and developing the hepatitis A vaccine.
The Karl Landsteiner Memorial Award is a scientific award given by the American Association of Blood Banks (AABB) to scientists with "an international reputation in transfusion medicine or cellular therapies" "whose original research resulted in an important contribution to the body of scientific knowledge". Recipients give a lecture at the AABB Annual Meeting and receive a $7,500 honorarium. The prize was initiated in 1954 to honor Karl Landsteiner, whose research laid the foundation for modern blood transfusion therapy.

Charles Moen Rice is an American virologist and Nobel Prize laureate whose main area of research is the Hepatitis C virus. He is a professor of virology at the Rockefeller University in New York City and an adjunct professor at Cornell University and Washington University School of Medicine. At the time of the award he was a faculty at Rockefeller.

Edward Charles Holmes is an evolutionary biologist and virologist, and since 2012 a National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Australia Fellow and professor at the University of Sydney. He is also an Honorary Visiting Professor at Fudan University, Shanghai, China (2019–present)













