Related Research Articles
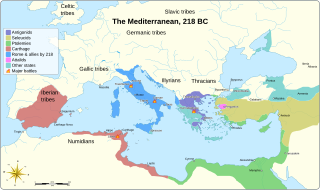
The First Macedonian War was fought by Rome, allied with the Aetolian League and Attalus I of Pergamon, against Philip V of Macedon, contemporaneously with the Second Punic War against Carthage. There were no decisive engagements, and the war ended in a stalemate.
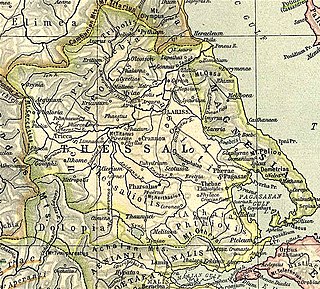
Demetrias was a Greek city in Magnesia in ancient Thessaly, situated at the head of the Pagasaean Gulf, near the modern city of Volos.

Volsinii or Vulsinii, is the name of two ancient cities of Etruria, one situated on the shore of Lacus Volsiniensis, and the other on the Via Clodia, between Clusium (Chiusi) and Forum Cassii (Vetralla). The latter was Etruscan and was destroyed by the Romans in 264 BC following an attempted revolt by its slaves, while the former was founded by the Romans using the remainder of the Etruscan population rescued from the razed city.

Valerius Antias was an ancient Roman annalist whom Livy mentions as a source. No complete works of his survive but from the sixty-five fragments said to be his in the works of other authors it has been deduced that he wrote a chronicle of ancient Rome in at least seventy-five books. The latest dateable event in the fragments is mention of the heirs of the orator, Lucius Licinius Crassus, who died in 91 BC. Of the seventy references to Antias in classical literature sixty-one mention him as an authority on Roman legendary history.
Elaea was an ancient city of Aeolis, Asia, the port of Pergamum. According to the Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World, it was located near the modern town of Zeytindağ, İzmir Province, Turkey. The ruins of the silted port's breakwater can be seen on satellite maps at 38°56'35.54"N 27°2'16.34"E.

Pythion or Pythium, also Pythoion (Πύθοιον) was a city and polis (city-state) of Perrhaebia in ancient Thessaly, situated at the foot of Mount Olympus, and forming a Tripolis with the two neighbouring towns of Azorus and Doliche. Pythion derived its name from a temple of Apollo Pythius situated on one of the summits of Olympus, as we learn from an epigram of Xeinagoras, a Greek mathematician, who measured the height of Olympus from these parts. Games were also celebrated here in honour of Apollo.
Selinus or Selinous was a port-town on the west coast of ancient Cilicia and later of Isauria, at the mouth of a small river of the same name, now called Musa Çay. This town is memorable in history as the place where the emperor Trajan is said by some authors to have died in 117 CE. After this event the place for a time bore the name of Trajanopolis or Traianopolis; but its bishops afterwards are called bishops of Selinus. Basil of Seleucia describes the place as reduced to a state of insignificance in his time, though it had once been a great commercial town. Selinus was situated on a precipitous rock, surrounded on almost every side by the sea, by which position it was rendered almost impregnable. The whole of the rock, however, was not included in the ancient line of fortifications; inside the walls there still are many traces of houses, but on the outside, and between the foot of the hill and the river, the remains of some large buildings are yet standing, which appear to be a mausoleum, an agora, a theatre, an aqueduct, and some tombs. No longer a residential bishopric, it remains a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church.
Cypsela or Kypsela, was an ancient Greek town on the river Hebrus in ancient Thrace, which was once an important place on the Via Egnatia. Antiochus besieged Cypsela and its citizens surrendered and became allies with Antiochus.
Daedala or Daidala was a city of the Rhodian Peraea in ancient Caria, or a small place, as Stephanus of Byzantium says, on the authority of Strabo.
Sinda was an ancient town mentioned to have been situated on the western frontier of ancient Pisidia, in the neighbourhood of Cibyra and the river Caularis. Stephanus of Byzantium, who spoke of a Sindia as a town of Lycia, was thought to have alluded to the same place. Some writers have confounded Sinda with Isionda, which is the more surprising, as Livy mentions the two as different towns in the same chapter; modern scholars treat them as separate places.

Canae was, in classical antiquity, a city in ancient Aeolis, on the island of Argennusa in the Aegean Sea off the modern Dikili Peninsula on the coast of modern-day Turkey, near the modern village of Bademli. Today Argennusa has joined the mainland as the Kane Promontory off the Dikili Peninsula. Canae is famous as the site of the Battle of Arginusae in 406 B.C.
Metropolis was an ancient town in the southern part of Phrygia, belonging to the conventus of Apamea. That this town is different from the more northerly town of the name in northern Phrygia, is quite evident, even independently of the fact that Stephanus of Byzantium mentions two towns of the name of Metropolis in Phrygia, and that Hierocles. and the Notitiae speak of a town of this name in two different provinces of Phrygia. In Roman times, it was assigned to the province of Pisidia, where it became a bishopric. No longer a residential see, it remains, under the name Metropolis in Pisidia, a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church.
Pygela or Phygela (Φύγελα) was a small town of ancient Ionia, on the coast of the Caystrian Bay, a little to the south of Ephesus. According to Greek mythology, it was said to have been founded by Agamemnon, and to have been peopled with the remnants of his army; it contained a temple of Artemis Munychia. Dioscorides commends the wine of this town. It was a polis (city-state) and a member of the Delian League. Silver and bronze coins dated to the 4th century BCE bearing the legends «ΦΥΓΑΛΕΩΝ» or «ΦΥΓ» are attributed to the town.
Tendeba was a town of ancient Caria in the territory of Stratonicea. It commanded a strong position and was a point of contest between the Rhodians and Macedonians in their war
Astragon was a town of ancient Caria in the territory of Stratonicea. It was a point of contest between the Rhodians and Macedonians in their war
Casystes or Kasystes was a port town of ancient Ionia, near Erythrae. Strabo, whose description proceeds from south to north, after describing Teos, says, "before you come to Erythrae, first is Erae, a small city of the Teians, then Corycus, a lofty mountain, and a harbour under it, Casystes; and another harbour called Erythras." It is probably the Cyssus of Livy, the port to which the fleet of Antiochus III sailed (191 BCE) before the naval engagement in which the king was defeated by Eumenes II and the Romans.
Nephelis was a small town of ancient Cilicia, situated, according to Ptolemy, between Antioch and Anemurium; but if, as some suppose, it be the same place as the Zephelium or Zephelion (Ζεφέλιον) mentioned in the Stadiasmus Maris Magni, it ought to be looked for between Selinus and Celenderis. Near the place was a promontory of the same name, where, according to Livy, the fleet of Antiochus the Great was stationed, when, after reducing the towns of Cilicia as far as Selinus, he was engaged in the siege of Coracesium, and where he received the ambassadors of the Rhodians.
Orthosia was a town of ancient Caria, inhabited during Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine times. It was not far from Alabanda, on the left bank of the Maeander River, and apparently on or near a hill of the same name. Near this town the Rhodians gained a victory over the Carians. It was the seat of a bishop from an early date, and, while no longer a residential bishopric, it remains under the name Orthosias in Caria a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church.
Beudos, also known as Palaion Beudos or Beudos Vetus, was a town of ancient Phrygia, inhabited during Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine times. Livy, when describing the march of Manlius, places five Roman miles from Synnada, and between Synnada and Anabura.
Lysinia or Lysinoe (Λυσινόη) was a town in the north of ancient Pisidia and later assigned to Pamphylia. Hierocles has the name as Lysenara (Λυσήναρα). It was located on the south of the Ascania Lacus, and west of Sagalassus.
References
- ↑ Livy. Ab Urbe Condita Libri (History of Rome). 38.15.
- ↑ Richard Talbert, ed. (2000). Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World . Princeton University Press. p. 62, and directory notes accompanying.
![]()
| This article about a location in ancient Phrygia is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |