
Uxmal is an ancient Maya city of the classical period in present-day Mexico. It is considered one of the most important archaeological sites of Maya culture, along with Palenque, Chichén, and Calakmul in Mexico, Caracol and Xunantunich in Belize, and Tikal in Guatemala. It is located in the Puuc region of the eastern Yucatan Peninsula, and is considered one of the Maya cities most representative of the region's dominant architectural style. It has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in recognition of its significance.

Bolonchén or Bolonchén de Rejón is a town in the Mexican state of Campeche, about 120 km East from the state capital, Campeche, in Hopelchén Municipality. As of 2010 the town had a population of 3,975 people. A short distance to the south of Bolonchén are located the caves of Xtacunbilxunan.

The Lacandon are one of the Maya peoples who live in the jungles of the Mexican state of Chiapas, near the southern border with Guatemala. Their homeland, the Lacandon Jungle, lies along the Mexican side of the Usumacinta River and its tributaries. The Lacandon are one of the most isolated and culturally conservative of Mexico's native peoples. Almost extinct in 1943, today their population has grown significantly, yet remains small, at approximately 650 speakers of the Lacandon language.

Flores is the capital of the Petén Department, Guatemala's landlocked, northernmost department. The population is 13,700 (2003).
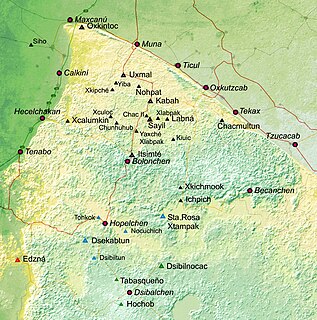
Puuc is the name of either a region in the Mexican state of Yucatán or a Maya architectural style prevalent in that region. The word "puuc" is derived from the Maya term for "hill". Since the Yucatán is relatively flat, this term was extended to encompass the large karstic range of hills in the southern portion of the state, hence, the terms Puuc region or Puuc hills. The Puuc hills extend into northern Campeche and western Quintana Roo.

Teobert Maler, later Teoberto was an explorer who devoted his energies to documenting the ruins of the Maya civilization.

Maya codices are folding books written by the pre-Columbian Maya civilization in Maya hieroglyphic script on Mesoamerican bark paper. The folding books are the products of professional scribes working under the patronage of deities such as the Tonsured Maize God and the Howler Monkey Gods. Most of the codices were destroyed by conquistadors and Catholic priests in the 16th century. The codices have been named for the cities where they eventually settled. The Dresden codex is generally considered the most important of the few that survive.

Alice Dixon Le Plongeon (1851–1910) was an English photographer, amateur archeologist, traveller, and author. She was one of the first people to excavate and study the ancient Maya sites of Chicén Itzá and Uxmal.
Na Bolom was the home of archeologist Frans Blom and his wife, Gertrude Duby Blom, the documentary photographer, journalist, environmental pioneer, and jungle adventurer. It is in San Cristóbal de las Casas, Chiapas, Mexico and today, Na Bolom operates as a hotel, museum, and research center run by Asociación Cultural Na Bolom, a non-profit organization dedicated to the protection of the Lacandon Maya and the preservation of the Chiapas rain forest.

The Lacandon Jungle is an area of rainforest which stretches from Chiapas, Mexico, into Honduras and into the southern part of the Yucatán Peninsula. The heart of this rainforest is located in the Montes Azules Biosphere Reserve in Chiapas near the border with Guatemala in the Montañas del Oriente region of the state. Although most of the jungle outside the reserve has been partially or completely destroyed and damage continues inside the Reserve, the Lacandon is still the largest montane rainforest in North America and one of the last ones left large enough to support jaguars. It contains 1,500 tree species, 33% of all Mexican bird species, 25% of all Mexican animal species, 56% of all Mexican diurnal butterflies and 16% of all Mexico's fish species.

Ancient Maya cuisine was varied and extensive. Many different types of resources were consumed, including maritime, flora, and faunal material, and food was obtained or produced through a host of strategies, such as hunting, foraging, and large-scale agricultural production. Plant domestication focused on several core foods, the most important of which was maize.

Chunchucmil was once a large, sprawling pre-Columbian Maya city located in the western part of what is now the state of Yucatán, Mexico.

Gertrude "Trudi" Duby Blom was a Swiss journalist, social anthropologist, and documentary photographer who spent five decades chronicling the Mayan cultures of Chiapas, Mexico, particularly the culture of the Lacandon Maya. In later life, she also became an environmental activist. Blom's former home Casa Na Bolom is a research and cultural center devoted to the protection and preservation of the Lacandon Maya and La Selva Lacandona rain forest.

Xpuhil Pronounced:/ʃpuχil̥/ is a Maya archaeological site located in the Mexican state of Campeche, in the vicinity of the modern-day town of Xpujil. The area surrounding Xpuhil, along Federal Highway 186, is rich with other Maya sites, including Becan and Calakmul. The name xpuhil means "cat's tail" in reference to a type of vegetation found locally.

Chichen Itza was a large pre-Columbian city built by the Maya people of the Terminal Classic period. The archaeological site is located in Tinúm Municipality, Yucatán State, Mexico.
Remote sensing techniques in archaeology are an increasingly important component of the technical and methodological tool set available in archaeological research. The use of remote sensing techniques allows archaeologists to uncover unique data that is unobtainable using traditional archaeological excavation techniques.

Palenque is a city and municipality located in the north of the state of Chiapas, Mexico. The city was named almost 200 years before the famous nearby Mayan ruins were discovered in the 18th century. The area has a significant indigenous population, mostly of the Ch'ol people, a Mayan descendent. The city is the only urban area in a municipality of over 600 communities and it is surrounded by rainforest. However, deforestation has had dramatic effects on the local environment, with howler monkeys occasionally seen in the city itself as they look for food. While most of the municipality’s population is highly marginalized economically, working in agriculture, the Palenque archeological site is one of the most important tourist attractions for both the area and the state of Chiapas. It is the poorest major city in the state of Chiapas.

Chactún is the name of an archaeological site of the Mesoamerican Maya civilization in the state of Campeche, Mexico, in the northern part of the Calakmul Biosphere Reserve. The site of approximately 54 acres is located in the lowlands of the Yucatán Peninsula, between the regions of Rio Bec and Chenes. There are some significant differences that have yet to be explained completely, which distinguish it from some of the other nearby sites.

Ian James Alastair Graham OBE was a British Mayanist whose explorations of Maya ruins in the jungles of Mexico, Guatemala, and Belize helped establish the Corpus of Maya Hieroglyphic Inscriptions published by the Peabody Museum of Harvard University. Among his related works is a biography of an early predecessor, the 19th-century British Maya explorer Alfred Maudslay.

Tamchen is an ancient Maya city, located in the Yucatán Peninsula, Mexico. It was discovered in August 2014, along with Lagunita, by Ivan Sprajc, associate professor at the Research Center of the Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts, and his team, after they reviewed aerial photographs of the area.



















