
The Laird LC-DW300 and LC-DW500 Super Solution aka "Sky Buzzard" was a racing biplane built in the early 1930s by Matty Laird for the Cleveland Speed Foundation, Laird was already famous in the air racing circuit. It had a large radial engine and an extremely faired windshield. Other than being a biplane, it was similar in appearance to the Gee Bee, a more famous racer from the period. It was an advanced design for the time because of the relatively clean aerodynamic construction and tight engine cowling.

Katherine Stinson was an American aviation pioneer who, in 1912, became the fourth woman in the United States to earn the FAI pilot certificate. She set flying records for aerobatic maneuvers, distance, and endurance. She was the first female pilot employed by the U.S. Postal Service and the first civilian pilot to fly the mail in Canada. She was also one of the first pilots to ever fly at night and the first female pilot to fly in Canada and Japan.

The Blériot XI is a French aircraft from the pioneer era of aviation. The first example was used by Louis Blériot to make the first flight across the English Channel in a heavier-than-air aircraft, on 25 July 1909. This is one of the most famous accomplishments of the pioneer era of aviation, and not only won Blériot a lasting place in history but also assured the future of his aircraft manufacturing business. The event caused a major reappraisal of the importance of aviation; the English newspaper The Daily Express led its story of the flight with the headline "Britain is no longer an Island".
The Talleres Nacionales de Construcciones Aeronáuticas (TNCA) was an aircraft manufacturer established outside Mexico City in 1915. TNCA closed in 1930, was briefly revived in 1941 under the name Talleres Generales de Aeronáutica (TGA) and again in 1947.

The Cessna Model A is a 1920s American high-wing four-seat tourer built by the Cessna Aircraft Company, the first in a long line of high-wing single-engined monoplanes.

The Anzani 10 was a 1913 10-cylinder air-cooled radial aircraft engine. It powered several experimental aircraft and also the later production versions of the Caudron G.3 reconnaissance aircraft, the Caudron G.4 bomber/trainer and the first production Cessna, the Model AA.

The Travel Air 2000/3000/4000 (originally, the Model A, Model B and Model BH were open-cockpit biplane aircraft produced in the United States in the late 1920s by the Travel Air Manufacturing Company. During the period from 1924–1929, Travel Air produced more aircraft than any other American manufacturer, including over 1,000 biplanes. While an exact number is almost impossible to ascertain due to the number of conversions and rebuilds, some estimates for Travel Air as a whole range from 1,200 to nearly 2,000 aircraft.
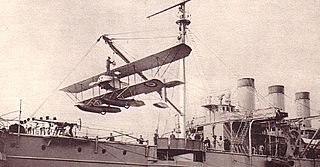
The Caudron J Marine was an amphibious, two-seat, biplane equipped with floats and wheels, similar to the earlier Caudron J floatplane.

The Driggs Dart was an American-built light sporting aircraft of the late 1920s.

The Bristol Scout E and F were a British single-seat biplane fighters built in 1916 to use newer and more powerful engines. It was initially powered by the Sunbeam Arab, but the third prototype was used as a testbed for the Cosmos Mercury, marking the start of Roy Fedden's association with the Bristol Aeroplane Company. The Armistice ended hopes of production.

The Ford Flivver is a single-seat aircraft introduced by Henry Ford as the "Model T of the Air". After a fatal crash of a prototype into the ocean off Melbourne, Florida, production plans were halted.

Emil Matthew Laird was a pioneering American aircraft designer, builder, pilot, and businessman. He put the first commercial aircraft into production at his E. M. Laird Aviation Company.

The Mann & Grimmer M.1 was a British prototype two-seat fighter aircraft of the First World War. It was a single-engined biplane with a radial engine in the aircraft's nose driving two pusher propellers, which was hoped to give a good field of fire for the gunner and high performance. Only one example was built, with no production following.

The Caudron Type A was the first successful aircraft built by René Caudron and his brother Gaston. During 1910 the Caudron brothers were briefly associated with the Société Anonyme Français d'Aviation (S.A.F.A.), and an example of the type was exhibited at the 1910 Paris Aero Salon as the S.A.F.A. Biplane.

The Potez VIII was a French training aircraft which first flew in 1920. Originally it had a very unusual vertical inline engine and a four-wheeled undercarriage, though the production version was more conventional.

The Caudron Type F was a French single seat biplane produced just before World War I. A dozen were bought by China and at least two other examples, with different engines, competed in 1913, coming first and second in the biplane category of the cross-country race at Reims. Flown by Pierre Chanteloup, one was the first biplane to loop-the-loop.

The Raab-Katzenstein RK.9 Grasmücke (Hedge-sparrow) was a 1920s German two-seat touring, advertising and training biplane. It was one of many designs from several countries aiming to provide low cost flying and was quite successful, with about twenty built.

The Rearwin Ken-Royce was an American three-seat sport/touring biplane built by Rearwin Airplanes first in Salina, Kansas then Kansas City. It was the first airplane built by the company.

The Caproni Ca.12 was a two-seater single-engine monoplane built by Caproni in the early 1910s.
TNCA Series A was a utility biplane made in Mexico by Talleres Nacionales de Construcciones Aeronáuticas (TNCA).


















