
Dakshin Gangotri was the first scientific base station of India situated in Antarctica, part of the Indian Antarctic Programme. It is located at a distance of 2,500 kilometres (1,600 mi) from the South Pole. It is currently being used as a supply base and transit camp. The base is named after Dakshin Gangotri Glacier.

Maitri also known as Friendship Research Centre, is India's second permanent research station in Antarctica as part of the Indian Antarctic Programme. The name was suggested by then-Prime Minister Indira Gandhi. Work on the station was first started by the Indian Expedition which arrived the end of December 1984, with a team led by Dr. B. B. Bhattacharya. Squadron Leader D. P. Joshi, the surgeon of the team, was the first camp commander of the tentage at camp Maitri. The first huts were started by the IV Antarctica Expedition and completed in 1989, shortly before the first station, Dakshin Gangotri, was buried in ice and abandoned in 1990–91. Maitri is situated in the rocky mountainous region called Schirmacher Oasis. It is only 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) away from the Russian Novolazarevskaya Station.
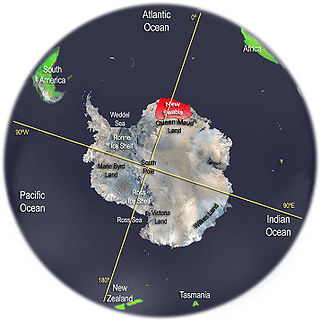
New Swabia was a disputed Antarctic claim by Nazi Germany within the Norwegian territorial claim of Queen Maud Land and is now a cartographic name sometimes given to an area of Antarctica between 20°E and 10°W in Queen Maud Land. New Swabia was explored by Germany in early 1939 and named after that expedition's ship, Schwabenland, itself named after the German region of Swabia.

Lake Fryxell is a frozen lake 4.5 kilometres (2.8 mi) long, between Canada Glacier and Commonwealth Glaciers at the lower end of Taylor Valley in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was mapped in the early 1900s and named during Operation Deep Freeze in the 1950s. There are several forms of algae living in the waters and a weather station located at the lake.

The Indian Antarctic Programme is a multi-disciplinary, multi-institutional programme under the control of the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research, Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India. It was initiated in 1981 with the first Indian expedition to Antarctica. The programme gained global acceptance with India's signing of the Antarctic Treaty and subsequent construction of the Dakshin Gangotri Antarctic research base in 1983, superseded by the Maitri base from 1989. The newest base commissioned in 2012 is Bharati, constructed out of 134 shipping containers. Under the programme, atmospheric, biological, earth, chemical, and medical sciences are studied by India, which has carried out 40 scientific expeditions to the Antarctic.

A blue ice runway is a runway constructed in Antarctic areas with no net annual snow accumulation. The density of the ice increases as air bubbles are forced out, strengthening the resultant ice surface so that aircraft landings using wheels instead of skis can be supported. Such runways simplify the transfer of materials to research stations, since wheeled aircraft can carry much heavier loads than ski-equipped aircraft.
Bunger Hills, also known as Bunger Lakes or Bunger Oasis, is a coastal range on the Knox Coast in Wilkes Land in Antarctica, consisting of a group of moderately low, rounded coastal hills, overlain by morainic drift and notably ice free throughout the year, lying south of the Highjump Archipelago. The reasoning behind the minute amount of ice in the area is still relatively unknown and remains under intense debate amongst scientists today.

Novolazarevskaya Station is a Russian, formerly Soviet, Antarctic research station. The station is located at Schirmacher Oasis, Queen Maud Land, 75 km (47 mi) from the Antarctic coast, from which it is separated by Lazarev Ice Shelf. It was opened on January 18, 1961 by the 6th Soviet Antarctic Expedition. The maximum summer population is 70.
Gangotri is a town and pilgrimage centre in Uttarakhand, India.

Lake Untersee is the largest surface freshwater lake in the interior of the Gruber Mountains of central Queen Maud Land in East Antarctica. It is situated 90 kilometres (56 mi) to the southeast of the Schirmacher Oasis. The lake is approximately 6.5 kilometres (4.0 mi) long and 2.5 kilometres (1.6 mi) wide, with a surface area of 11.4 square kilometres (4.4 sq mi), and a maximum depth of 169 metres (554 ft). The lake is permanently covered with ice and is partly bounded by glacier ice.

The Schirmacher Oasis is a 25 km (16 mi) long and up to 3 km (1.9 mi) wide ice-free plateau with more than 100 freshwater lakes. It is situated in the Schirmacher Hills on the Princess Astrid Coast in Queen Maud Land in East Antarctica and is, on average, 100 m (330 ft) above sea level. With an area of 34 km2 (13 sq mi), the Schirmacher Oasis ranks among the smallest Antarctic oases and is a typical polar desert.
Radok Lake is a meltwater lake about four miles (6.4 km) long and marked by a slender glacier tongue feeding into it from the west, lying three miles (4.8 km) south-west of Beaver Lake and 15 miles (24 km) south-east of the Aramis Range, Prince Charles Mountains. It was plotted by Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE) from air photos taken by the RAAF Antarctic Flight in 1956. The lake was named for Uwe Radok, Reader (head) of Meteorology Department at the University of Melbourne, who greatly assisted Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE)'s glaciological program. With a depth of 362 metres (1,188 ft), Radok Lake is the deepest known lake on the Antarctic continent and the only known freshwater lake to host a floating ice tongue glacier. It is drained by three-mile-long (4.8 km) Pagodroma Gorge in to Beaver Lake. Radok Lake is an isothermal and non-stratified Lake, i.e. homogeneous water body.
Schirmacher Hills is a line of low coastal hills, 11 nautical miles (20 km) long, with numerous meltwater ponds, standing 40 nautical miles (70 km) north of the Humboldt Mountains along the coast of Queen Maud Land. Discovered by the Third German Antarctic Expedition under Alfred Ritscher, 1938–39, and named for Richardheinrich Schirmacher, pilot of the Boreas, one of the expedition seaplanes.

An Antarctic oasis is a large area naturally free of snow and ice in the otherwise ice-covered continent of Antarctica.
Richard Brice Hoover is a physicist who has authored 33 volumes and 250 papers on astrobiology, extremophiles, diatoms, solar physics, X-ray/EUV optics and meteorites. He holds 11 U.S. patents and was 1992 NASA Inventor of the Year. He was employed at the United States' NASA Marshall Space Flight Center from 1966 to 2012, where he worked on astrophysics and astrobiology. He established the Astrobiology Group there in 1997 and until his retirement in late 2011 he headed their astrobiology research. He conducted research on microbial extremophiles in the Antarctic, microfossils, and chemical biomarkers in precambrian rocks and in carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. Hoover has published claims to have discovered fossilized microorganisms in a collection of select meteorites on multiple occasions.

The Russian bath (banya) of Novolazarevskaya Station, Schirmacher Oasis, Queen Maud Land is the only glued timber building in Antarctica. It is the southernmost wooden sauna in the world.
Sudipta Sengupta is a professor in structural geology in Jadavpur University, Calcutta, India, and a trained mountaineer. She is one of the first Indian women to set foot on Antarctica. She is also popularly known in India for her book Antarctica in Bengali and numerous articles and television interviews on geosciences. She has published extensively in international peer-reviewed journals of structural geology. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded her the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for her contributions to Earth, Atmosphere, Ocean and Planetary Sciences in 1991.
The 20 indian Antarctic Expedition was flagged off on-board M.V. Magdalena Oldenorff from Cape Town on 30 December 2000. The team comprising a total of 51 members was led by Shri Mervin J. D’Souza from Geological Survey of India. The 20th IAE team consisted of 51 members including 34 scientists from various scientific Organizations/Universities/Departments and 17 logistic members. After successful completion of all logistics and scientific tasks the 20th IAE team returned to India in March 2002.

The Dakshin Gangotri Glacier is a small tongue of the polar continental ice sheet impinging on the Schirmacher Oasis of central Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by the Second Indian Expedition to Antarctica in 1983, and is named after the Gangotri Glacier in the Himalayas. The first Antarctic research base of India, Dakshin Gangotri is located near to the glacier. Since then its snout, and the area around it, has been regularly monitored and it has become a valuable site for tracking the impact of global warming through changes in the movement of the Antarctic ice sheet. The site is protected under the Antarctic Treaty System as Antarctic Specially Protected Area (ASPA) No.163.

The German Antarctic Expedition (1938–1939), led by German Navy captain Alfred Ritscher (1879–1963), was the third official Antarctic expedition of the German Reich, by order of the "Commissioner for the Four Year Plan" Hermann Göring. Prussian State Councilor Helmuth Wohlthat was mandated with planning and preparation. The expedition's main objective was of economic nature, in particular the establishment of a whaling station and the acquisition of fishing grounds for a German whaling fleet in order to reduce the Reich's dependence on the import of industrial oils, fats and dietary fats. Preparations took place under strict secrecy as the enterprise was also tasked to make a feasibility assessment for a future occupation of Antarctic territory in the region between 20 ° West and 20 ° East.













