
Italy has a well developed transport infrastructure. The Italian rail network is extensive, especially in the north, and it includes a high-speed rail network that joins the major cities of Italy from Naples through northern cities such as Milan and Turin. The Florence–Rome high-speed railway was the first high-speed line opened in Europe when more than half of it opened in 1977. Italy has 2,507 people and 12.46 km2 per kilometer of rail track, giving Italy the world's 13th largest rail network. The Italian rail network is operated by state-owned Ferrovie dello Stato, while the rail tracks and infrastructure are managed by Rete Ferroviaria Italiana.

The Italian railway system is one of the most important parts of the infrastructure of Italy, with a total length of 24,227 km (15,054 mi) of which active lines are 16,723 km. The network has recently grown with the construction of the new high-speed rail network. Italy is a member of the International Union of Railways (UIC). The UIC Country Code for Italy is 83.

Ferrovie dello Stato Italiane S.p.A. is Italy's national state-owned railway holding company that manages transport, infrastructure, real estate services and other services in Italy and other European countries.

Colico is a town and comune in the province of Lecco, in Lombardy in northern Italy. It is situated on the northern arm of Lake Como, where the river Adda enters the lake. Colico is the largest town in the northern part of Lake Como, which is often identified as its Colico branch.

The Italian Istituto Poligrafico e Zecca dello Stato (IPZS), founded in 1928, is situated at the via Salaria 691 in Rome. As well as producing coins, passports, and postage stamps for Italy, it serves the micro-states of the Vatican City, San Marino, and the Sovereign Military Order of Malta. It also publishes books under the imprint Libreria dello Stato. The O.C.V. and traditional productions factory, the multimedial production institute and the Mint are also located in the capital. Other factories are located in Verrès, Val d'Aosta, and Foggia, Apulia. Banknotes are produced by the Bank of Italy.

The Vatican Railway was opened in 1934 to serve Vatican City and its only station, Vatican City. The main rail tracks are standard gauge and 300 metres (980 ft) long, with two freight sidings, making it the shortest national railway system in the world. Access to the Italian rail network is over a viaduct to Roma San Pietro railway station, and is guaranteed by the Lateran Treaty dating from 1929. The tracks and station were constructed during the reign of Pope Pius XI, shortly after the treaty.

The Central Archives of the State is the national archives of Italy which keeps the archives and documents produced after the Unification of Italy (1861) by the central bodies of the Kingdom of Italy and of the present Italian Republic, as well as by public bodies of national importance and by selected private individuals.

The Florence–Rome high-speed railway line is a link in the Italian high-speed rail network. It is known as the ferrovia direttissima Firenze-Roma in Italian—meaning "most direct Florence–Rome railway" ; this name reflects the naming of the Rome–Formia–Naples Direttissima opened in 1927 and the Bologna–Florence Direttissima opened in 1934. The line was the first high-speed line opened in Europe when more than half of it opened on 24 February 1977. It was completed on 26 May 1992, reducing the time of the fastest trains between the two cities to 1 hour and 20 minutes. The old line is referred to by Ferrovie dello Stato as the Linea Lenta to distinguish it from the parallel high-speed line.

Torino Porta Nuova railway station is the main railway station of Turin, northern Italy. It is the third busiest station in Italy after Rome Termini and Milan Central, with about 192,000 journeys per day and 70 million travellers a year and a total of about 350 trains per day. Porta Nuova is a terminal station, with trains arriving perpendicularly to the facade. The station is located in Corso Vittorio Emanuele II, right in front of Piazza Carlo Felice.

The Domodossola–Milan railway line is a major Italian railway route and an important part of the European rail network. It is one of Italy's busiest lines for both passenger and freight trains. The line connects Milan and Domodossola with Brig, an important Swiss railway junction, via the Simplon Tunnel. Direct passenger trains ran from Brig to Paris and Brussels and Luxembourg via Basel. The line runs through lower Varese Province, the valley of Ossola and along the shore of Lake Maggiore.

The Pisa–Rome railway is one of the trunk lines of the Italian railway network. It connects Italy’s northwest with its south, running along the Tyrrhenian coast between the Italian regions of Tuscany and Lazio, through the provinces of Livorno, Grosseto, Viterbo and Rome. The line is double track and is fully electrified at 3,000 V DC. Passenger traffic is managed by Trenitalia.

The Brenner Railway is a major line connecting the Austrian and Italian railways from Innsbruck to Verona, climbing up the Wipptal, passing over the Brenner Pass, descending down the Eisacktal to Bolzano/Bozen, then further down the Adige Valley to Rovereto/Rofreit, and along the section of the Adige Valley, called in Italian the “Vallagarina”, to Verona. This railway line is part of the Line 1 of Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T). It is considered a "fundamental" line by the state railways Ferrovie dello Stato (FS).

Grandi Stazioni S.p.A. is a member company of Italy's Ferrovie dello Stato group. It was created to rehabilitate and manage, even commercially, the 13 biggest Italian railway stations.

Biella San Paolo railway station is the main station serving the town and comune of Biella, in the Piedmont region, northwestern Italy. It is the junction of the Biella–Novara and Santhià–Biella railways.

The Melide causeway crosses across Lake Lugano in the Swiss canton of Ticino, connecting the communities of Melide and Bissone, and provides the only domestic land connection between the southern section of Ticino, around Mendrisio and Chiasso, and the rest of Switzerland.

The Alessandria–Novara–Arona railway is a railway line in Italy that connects Alessandria to Arona on Lake Maggiore, passing through Novara.

FS Class 103 was a class of 2-2-2 steam locomotives of the Italian State Railways (FS), originally built for the Strade Ferrate dello Stato Piemontese (SFSP).
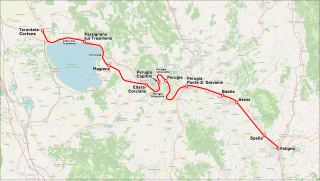
The Terontola–Foligno railway is an electrified, standard-gauge Italian railway that connects the Florence–Rome railway in Terontola-Cortona with the Rome–Ancona railway in Foligno, passing through Perugia and Assisi.



















