Wind power or wind energy is the use of wind to provide the mechanical power through wind turbines to turn electric generators and traditionally to do other work, like milling or pumping. Wind power is a sustainable and renewable energy, and has a much smaller impact on the environment compared to burning fossil fuels.

SSE Airtricity was founded in Ireland in 1997 and is now an energy company owned by SSE plc. It is an international wind farm developer.

A wind farm or wind park, also called a wind power station or wind power plant, is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electricity. Wind farms vary in size from a small number of turbines to several hundred wind turbines covering an extensive area. Wind farms can be either onshore or offshore.

The United Kingdom is one of the best locations for wind power in the world and is considered to be the best in Europe. Wind power contributed 18% of UK electricity generation in 2018, making up 52% of electricity generation from renewable sources .Onshore wind power has the lowest levelised cost of electricity in the United Kingdom when a carbon cost is applied to generating technologies. In 2019, a strike price was agreed during the latest CfD round for £39.65/MWh for Offshore wind projects which is lower than the expected UK wholesale electricity price, meaning that this will be the first "negative subsidy" wind farm operating n the UK. In 2016, wind power first surpassed coal in UK electricity generation, and in the first quarter of 2018 surpassed nuclear power generation for the first time.

Wind power became a significant energy source within South Australia over the first two decades of the 21st century. As of 2015, there was an installed capacity of 1,475 MW, which accounts for 34% of electricity production in the state. This represents 35% of Australia's installed wind power capacity.

The Altamont Pass wind farm is located in the Altamont Pass of the Diablo Range in Northern California. It is one of the earliest wind farms in the United States. The first wind turbines were placed on the Altamont in the early 1980s by Fayette Manufacturing Corporation on land owned by cattle rancher Joe Jess. The wind farm is composed of 4930 relatively small wind turbines of various types, making it at one time the largest wind farm in the world in terms of capacity. Altamont Pass is still one of the largest concentration of wind turbines in the world, with a capacity of 576 megawatts (MW), producing about 125 MW on average and 1.1 terawatt-hours (TWh) yearly. They were installed after the 1970s energy crisis in response to favorable tax policies for investors.

Wind power generation capacity in India has significantly increased in recent years. As of 31 December 2019 the total installed wind power capacity was 37.505 GW, the fourth largest installed wind power capacity in the world. Wind power capacity is mainly spread across the Southern, Westrn and Northern regions.

Blood Hill is a wind farm near Hemsby in Norfolk, England. It is the smallest windfarm owned by E.ON; taking up 3 hectares. It has a nameplate capacity of 2.25MW which is enough to power 1000 homes at peak. There are 10 Vestas V27-225 kW turbines which are 30 metres tall and stand on top of Blood Hill. They are visible from the villages of Hemsby and Winterton-on-Sea. Blood Hill began operating in December 1992 and was one of the first windfarms in the United Kingdom.

Wind power in Scotland is the fastest-growing renewable energy technology, with 8423 MW of installed wind power capacity as of December 2018. This included 7800 MW from onshore wind in Scotland and 623 MW of offshore wind generators.

Gwynt y Môr is a 576-megawatt (MW) offshore wind farm located off the coast of North Wales and is the fifth largest operating offshore windfarm in the world. The farm has 160 wind turbines of 150 metres (490 ft) tip height above mean sea level.

Wind power in Ohio has a long history, and as of 2016, Ohio had 545 megawatt (MW) of utility-scale wind power installations installed, responsible for 1.1% of in-state electricity generated. Over 1000 MW more were under construction or pending approval. Some installations have become tourist attractions. There has been a sudden increase in generating capacity, as total windpower generation in the state in 2010 was just 9.7 MW.

Wind power in New Zealand generates a small but growing proportion of the country's electricity. As of December 2017, wind power accounts for 690 MW of installed capacity and over 5 percent of electricity generated in the country.

Whitelee Wind Farm is a windfarm on the Eaglesham moor in Scotland. The main visitor centre is located in East Renfrewshire, but the majority of turbines are located in East Ayrshire and South Lanarkshire. It is the largest on-shore wind farm in the United Kingdom with 215 Siemens and Alstom wind turbines and a total capacity of 539 megawatts (MW), with the average of 2.5 MW per turbine. Whitelee was developed and is operated by ScottishPower Renewables, which is part of the Spanish company Iberdrola.

In 2017 France reached a total of 13,759 MW installed wind power capacity placing France at that time as the world's eighth largest wind power nation by installed capacity, behind the United Kingdom and Canada and ahead of Italy and Brazil. According to the IEA the yearly wind production was 20.2 TWh in 2015, representing almost 23% of the 88.4 TWh from renewable sources in France during that year. Furthermore wind provided for 4.3% of the country’s electricity demand out of the 18.7% provided by renewables in 2015.

Wind power in Illinois provided 6.2% of the state's generated electrical power in 2017 and 8.3% of electrical power sales. At the end of 2017, Illinois had 4,464 megawatts (MW) of wind power installed, ranking sixth among states for installed wind turbine capacity.

The Beatrice Offshore Wind Farm now known as Beatrice Offshore Windfarm Ltd (BOWL) project, is a wind farm close to the Beatrice oil field in the Moray Firth, part of the North Sea 13 km off the north east coast of Scotland.
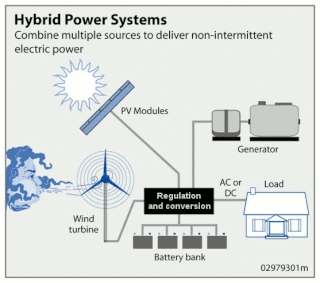
Wind hybrid power systems combines wind turbines with other storage and/or generation sources. One of the key issues with wind energy is its intermittent nature. This has led to numerous methods of storing energy.