
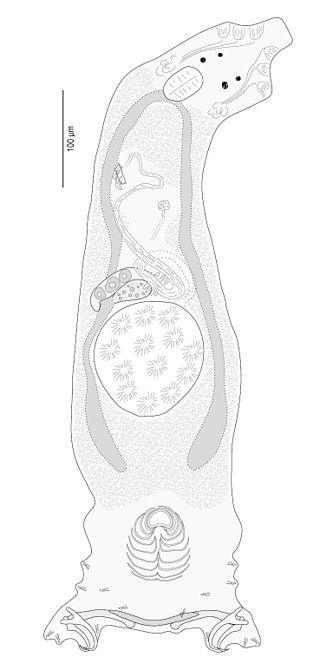
The haptor is the attachment organ of the monogeneans, a group of parasitic Platyhelminthes. The haptor is sometimes called opisthaptor to emphasize that it is located in the posterior part of the body, and to differentiate it from the prohaptor, a structure including glands located at the anterior part of the body. According to Yamaguti (1963), the chief adhesive organ of the monogeneans, the haptor, is posterior, more or less discoid, muscular, may be divided into alveoli or loculi, is usually provided with anchors, has nearly always marginal larval hooklets, or is in a reduced form with anchors. The haptor may consist of symmetrical or asymmetrical, sessile or pedunculate, muscular suckers or clamps with or without supporting sclerites; accessory adhesive organs may be present in form of armed plaques, lappets or appendices.

Pseudorhabdosynochus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, included in the family Diplectanidae. The type-species of the genus is Pseudorhabdosynochus epinepheli .

The Diplectanidae are a family of monopisthocotylean monogeneans. They are all parasitic on the gills of fish. Diplectanids are small animals, generally around 1 mm in length. As parasites, they can be extremely numerous, up to several thousand on an individual fish.
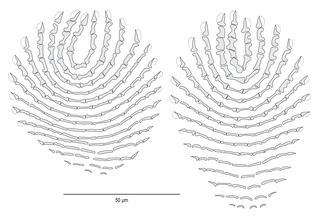
Squamodiscs are epidermal structures, which are typical of and found only in certain monogeneans of the family Diplectanidae. There are, typically, two squamodiscs, one ventral and one dorsal, located on the haptor of the monogenean. Squamodiscs are usually made up of scales embedded in the epidermis, which appear from the outside as rodlets arranged in rows.

Pseudorhabdosynochus regius is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the mottled grouper .
Calydiscoides is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, included in the family Diplectanidae.

Pseudorhabdosynochus beverleyburtonae is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the dusky grouper, Epinephelus marginatus. It has been described by Guy Oliver in 1984 as Cycloplectanum beverleyburtonae, redescribed by Oliver in 1987, transferred to the genus Pseudorhabdosynochus by Kritsky & Beverley-Burton in 1986 as Pseudorhabdosynochus beverleyburtonae, redescribed by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015, and redescribed in 2016 by Chaabane, Neifar, Gey & Justine.

Pseudorhabdosynochus marcellus is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the malabar grouper, Epinephelus malabaricus. It was described in 2007.
Lamellodiscus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Diplectanidae; all species of Lamellodiscus are small worms, parasitic on the gills of teleost fish.
Pseudorhabdosynochus amplidiscatus is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of groupers. It was described as Diplectanum amplidiscatum by Bravo-Hollis in 1954 and transferred to the genus Pseudorhabdosynochus by Kritsky and Beverley-Burton in 1986.
Pseudorhabdosynochus calathus is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the grouper Epinephelus rivulatus. It has been described in 2006.

Pseudorhabdosynochus oliveri is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the dusky grouper.
Pseudorhabdosynochus inversus is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the halfmoon grouper, Epinephelus rivulatus. It was described in 2008, from only three specimens.
Pseudorhabdosynochus quadratus is a species of diplectanid monogenean that is parasitic on the gills of the white-streaked grouper Epinephelus ongus. It was described in 2011.
Pseudorhabdosynochus exoticus is a species of diplectanid monogenean that is parasitic on the gills of the blue grouper Epinephelus cyanopodus. It was described in 2008.
Pseudorhabdosynochus hargisi is species of a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the White grouper Epinephelus aeneus. It was described in 1984 as Diplectanum hargisi and transferred to the genus Pseudorhabdosynochus by Santos, Buchmann & Gibson in 2000. Its systematic position has been clarified by Kritsky, Bakenhaster & Adams in 2015, who differentiated it from Pseudorhabdosynochus americanus.

Pseudorhabdosynochus riouxi is a species of diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of dusky grouper Mycteroperca marginata. It was described by Guy Oliver in 1986 as Cycloplectanum riouxi, then transferred to the genus Pseudorhabdosynochus by Santos, Buchmann & Gibson in 2000. The species has been redescribed by Chaabane et al. in 2017.
Pseudorhabdosynochus shenzhenensis is a species of diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the grouper Epinephelus coioides. It was described in 2005.
Monoplectanum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. All its species are parasites on fish of the family Sillaginidae.
Rhabdosynochus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae.









