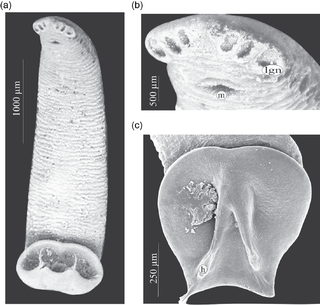
Monocotylidae is a family of monogenean flatworms.

Pseudorhabdosynochus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, included in the family Diplectanidae. The type-species of the genus is Pseudorhabdosynochus epinepheli .

The Diplectanidae are a family of monopisthocotylean monogeneans. They are all parasitic on the gills of fish. Diplectanids are small animals, generally around 1 mm in length. As parasites, they can be extremely numerous, up to several thousand on an individual fish.
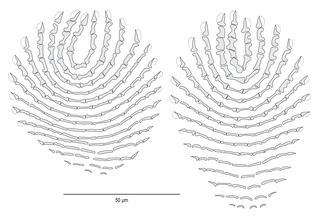
Squamodiscs are epidermal structures, which are typical of and found only in certain monogeneans of the family Diplectanidae. There are, typically, two squamodiscs, one ventral and one dorsal, located on the haptor of the monogenean. Squamodiscs are usually made up of scales embedded in the epidermis, which appear from the outside as rodlets arranged in rows.
Calydiscoides is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, included in the family Diplectanidae.

Louis Euzet was a French parasitologist.

Pseudorhabdosynochus beverleyburtonae is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the dusky grouper, Epinephelus marginatus. It has been described by Guy Oliver in 1984 as Cycloplectanum beverleyburtonae, redescribed by Oliver in 1987, transferred to the genus Pseudorhabdosynochus by Kritsky & Beverley-Burton in 1986 as Pseudorhabdosynochus beverleyburtonae, redescribed by Kritsky, Bakenhaster and Adams in 2015, and redescribed in 2016 by Chaabane, Neifar, Gey & Justine.

Echinoplectanum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Diplectanidae. All its species are parasites on the gills of fish; hosts recorded to date are all groupers, including coralgroupers and the Dusky grouper. So far, species of Echinoplectanum have been recorded only from fish caught off Australia, New Caledonia and in the Mediterranean Sea.

Pseudorhabdosynochus hayet is a diplectanid monogenean parasitic on the gills of the mottled grouper .
Plectanocotylidae is a family of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans. All the species in this family are parasitic on the gills of marine fish.

Ancyrocephalidae is a family of monogenean flatworms. The family is considered as a "temporary name" in WorMS but includes a large number of genera and species.
Acleotrema is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Diplectanidae. All its species are parasites on fish. The type-species is Acleotrema girellaeJohnston & Tiegs, 1922.
Delane C. Kritsky is an American parasitologist who specialised on the Monogenea, a class of parasitic flatworms which are important ectoparasites of fishes. His research was mainly in the fields of taxonomy, faunistics, and phylogeny of the Monogenea.

Sparicotyle chrysophrii is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of the marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. Its type-host is the gilt-head seabream.
Murraytrema is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. Species of this genus are parasitic on the gills of marine fish of the families Sciaenidae and Sparidae.

Neodiplectanum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. According to Mizelle & Blatz (1941), the genus Neodiplectanum "differs from DiplectanumDiesing, 1858, its closest relative, by the presence of two, instead of three, cuticular bars on the haptor". Oliver (1987) thought that the two genera were synonyms, but Neodiplectanum was resurrected later.
Pseudodiplectanum is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, belonging to the family Diplectanidae. Species of Pseudodiplectanum are parasites of marine teleost fish.
Microcotyle erythrini is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. This species was described by Van Beneden & Hesse in 1863 and redescribed by Parona & Perugia in 1890.
Protolamellodiscus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Diplectanidae. All species of Protolamellodiscus are parasites of marine perciform fishes of the families Lethrinidae, Nemipteridae, Serranidae and Sparidae.
Plectanocotyle is a genus of monogeneans in the family Plectanocotylidae. All its members are parasites on the gills of fish. It includes four species:










