Related Research Articles
A boot sector is the sector of a persistent data storage device which contains machine code to be loaded into random-access memory (RAM) and then executed by a computer system's built-in firmware.
Disk formatting is the process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard disk drive, solid-state drive, floppy disk, memory card or USB flash drive for initial use. In some cases, the formatting operation may also create one or more new file systems. The first part of the formatting process that performs basic medium preparation is often referred to as "low-level formatting". Partitioning is the common term for the second part of the process, dividing the device into several sub-devices and, in some cases, writing information to the device allowing an operating system to be booted from it. The third part of the process, usually termed "high-level formatting" most often refers to the process of generating a new file system. In some operating systems all or parts of these three processes can be combined or repeated at different levels and the term "format" is understood to mean an operation in which a new disk medium is fully prepared to store files. Some formatting utilities allow distinguishing between a quick format, which does not erase all existing data and a long option that does erase all existing data.

CIH, also known as Chernobyl or Spacefiller, is a Microsoft Windows 9x computer virus that first emerged in 1998. Its payload is highly destructive to vulnerable systems, overwriting critical information on infected system drives and, in some cases, destroying the system BIOS. Chen Ing-hau, a student at Tatung University in Taiwan, created the virus. It was believed to have infected sixty million computers internationally, resulting in an estimated US$1 billion in commercial damages.
Logical block addressing (LBA) is a common scheme used for specifying the location of blocks of data stored on computer storage devices, generally secondary storage systems such as hard disk drives. LBA is a particularly simple linear addressing scheme; blocks are located by an integer index, with the first block being LBA 0, the second LBA 1, and so on.
The SCA virus is the first computer virus created for the Amiga and one of the first to gain public notoriety. It appeared in November 1987. The SCA virus is a boot sector virus. It features a line of text that appears at every 15th copy after a warm reboot:
Something wonderful has happened Your AMIGA is alive !!! and, even better...
Some of your disks are infected by a VIRUS !!! Another masterpiece of The Mega-Mighty SCA !!
dd is a command-line utility for Unix, Plan 9, Inferno, and Unix-like operating systems and beyond, the primary purpose of which is to convert and copy files. On Unix, device drivers for hardware and special device files appear in the file system just like normal files; dd can also read and/or write from/to these files, provided that function is implemented in their respective driver. As a result, dd can be used for tasks such as backing up the boot sector of a hard drive, and obtaining a fixed amount of random data. The dd program can also perform conversions on the data as it is copied, including byte order swapping and conversion to and from the ASCII and EBCDIC text encodings.
Files-11 is the file system used by Digital Equipment Corporation OpenVMS operating system, and also by the older RSX-11. It is a hierarchical file system, with support for access control lists, record-oriented I/O, remote network access, and file versioning.
The Amiga Fast File System is a file system used on the Amiga personal computer. The previous Amiga filesystem was never given a specific name and known originally simply as "DOS" or AmigaDOS. Upon the release of FFS, the original filesystem became known as Amiga Old File System (OFS). OFS, which was primarily designed for use with floppy disks, had been proving slow to keep up with hard drives of the era. FFS was designed as a full replacement for the original Amiga filesystem. FFS differs from its predecessor mainly in the removal of redundant information. Data blocks contain nothing but data, allowing the filesystem to manage the transfer of large chunks of data directly from the host adapter to the final destination.
On the Amiga, the Old File System was the filesystem for AmigaOS before the Amiga Fast File System. Even though it used 512-byte blocks, it reserved the first small portion of each block for metadata, leaving an actual data block capacity of 488 bytes per block. It wasn't very suitable for anything except floppy disks, and it was soon replaced.

Cylinder-head-sector (CHS) is an early method for giving addresses to each physical block of data on a hard disk drive.
An Option ROM for the PC platform is a piece of firmware that resides in ROM on an expansion card, which gets executed to initialize the device and (optionally) add support for the device to the BIOS. In its usual use, it is essentially a driver that interfaces between the BIOS API and hardware. Technically, an option ROM is firmware that is executed by the BIOS after POST and before the BIOS boot process, gaining complete control of the system and being generally unrestricted in what it can do. The BIOS relies on each option ROM to return control to the BIOS so that it can either call the next option ROM or commence the boot process. For this reason, it is possible for an option ROM to keep control and preempt the BIOS boot process. The BIOS generally scans for and initializes option ROMs in ascending address order at 2 KB address intervals within two different address ranges above address C0000h in the conventional (20-bit) memory address space; later systems may also scan additional address ranges in the 24-bit or 32-bit extended address space.
Byte Bandit is a boot sector computer virus created for the Amiga personal computer. It first appeared in January 1988.
Jerusalem is a logic bomb DOS virus first detected at Hebrew University of Jerusalem, in October 1987. On infection, the Jerusalem virus becomes memory resident, and then infects every executable file run, except for COMMAND.COM. COM files grow by 1,813 bytes when infected by Jerusalem and are not re-infected. Executable files grow by 1,808 to 1,823 bytes each time they are infected, and are then re-infected each time the files are loaded until they are too large to load into memory. Some .EXE files are infected but do not grow because several overlays follow the genuine .EXE file in the same file. Sometimes .EXE files are incorrectly infected, causing the program to fail to run as soon as it is executed.
Ontario is a family of computer viruses, named after its point of isolation, the Canadian province of Ontario. This family of computer virus consists of Ontario.1024, Ontario.512 and Ontario.2048. The first variant Ontario.512 was discovered in July 1990. Because Ontario.1024 was also discovered in Ontario, it is likely that both viruses originate from within the province. By the Ontario.2048 variant, the author had adopted "Ontario" as the family's name and even included the name "Ontario-3" in the virus code.
Apple Partition Map (APM) is a partition scheme used to define the low-level organization of data on disks formatted for use with 68k and PowerPC Macintosh computers. It was introduced with the Macintosh II.

Stoned is a boot sector computer virus created in 1987. It is one of the first viruses and is thought to have been written by a student in Wellington, New Zealand. By 1989 it had spread widely in New Zealand and Australia, and variants became very common worldwide in the early 1990s.

The Ping-Pong virus is a boot sector virus discovered on March 1, 1988, at the Politecnico di Torino in Italy. It was likely the most common and best known boot sector virus until outnumbered by the Stoned virus.

AmigaOS is a family of proprietary native operating systems of the Amiga and AmigaOne personal computers. It was developed first by Commodore International and introduced with the launch of the first Amiga, the Amiga 1000, in 1985. Early versions of AmigaOS required the Motorola 68000 series of 16-bit and 32-bit microprocessors. Later versions were developed by Haage & Partner and then Hyperion Entertainment. A PowerPC microprocessor is required for the most recent release, AmigaOS 4.

A computer virus is a type of computer program that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and inserting its own code into those programs. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a computer virus, a metaphor derived from biological viruses.
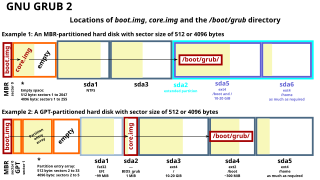
A master boot record (MBR) is a special type of boot sector at the very beginning of partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept of MBRs was publicly introduced in 1983 with PC DOS 2.0.