
Paragliding is the recreational and competitive adventure sport of flying paragliders: lightweight, free-flying, foot-launched glider aircraft with no rigid primary structure. The pilot sits in a harness or in a cocoon-like 'pod' suspended below a fabric wing. Wing shape is maintained by the suspension lines, the pressure of air entering vents in the front of the wing, and the aerodynamic forces of the air flowing over the outside.

Flight instruments are the instruments in the cockpit of an aircraft that provide the pilot with data about the flight situation of that aircraft, such as altitude, airspeed, vertical speed, heading and much more other crucial information in flight. They improve safety by allowing the pilot to fly the aircraft in level flight, and make turns, without a reference outside the aircraft such as the horizon. Visual flight rules (VFR) require an airspeed indicator, an altimeter, and a compass or other suitable magnetic direction indicator. Instrument flight rules (IFR) additionally require a gyroscopic pitch-bank, direction and rate of turn indicator, plus a slip-skid indicator, adjustable altimeter, and a clock. Flight into instrument meteorological conditions (IMC) require radio navigation instruments for precise takeoffs and landings.

Takeoff is the phase of flight in which an aerospace vehicle leaves the ground and becomes airborne. For aircraft traveling vertically, this is known as liftoff.

Landing is the last part of a flight, where a flying animal, aircraft, or spacecraft returns to the ground. When the flying object returns to water, the process is called alighting, although it is commonly called "landing", "touchdown"a or "splashdown" as well. A normal aircraft flight would include several parts of flight including taxi, takeoff, climb, cruise, descent and landing.
In aviation, a go-around is an aborted landing of an aircraft that is on final approach or has already touched down. A go-around can either be initiated by the pilot flying or requested by air traffic control for various reasons, such as an unstabilized approach or an obstruction on the runway.

An autopilot is a system used to control the path of an aircraft, marine craft or spacecraft without requiring constant manual control by a human operator. Autopilots do not replace human operators. Instead, the autopilot assists the operator's control of the vehicle, allowing the operator to focus on broader aspects of operations.

Landing gear is the undercarriage of an aircraft or spacecraft that is used for taxiing, takeoff or landing. For aircraft it is generally needed for both. It was also formerly called alighting gear by some manufacturers, such as the Glenn L. Martin Company. For aircraft, Stinton makes the terminology distinction undercarriage (British) = landing gear (US).

Wingsuit flying is the sport of skydiving using a webbing-sleeved jumpsuit called a wingsuit to add webbed area to the diver's body and generate increased lift, which allows extended air time by gliding flight rather than just free falling. The modern wingsuit, first developed in the late 1990s, uses a pair of fabric membranes stretched flat between the arms and flanks/thighs to imitate an airfoil, and often also between the legs to function as a tail and allow some aerial steering.

Thrust reversal, also called reverse thrust, is the temporary diversion of an aircraft engine's thrust for it to act against the forward travel of the aircraft, providing deceleration. Thrust reverser systems are featured on many jet aircraft to help slow down just after touch-down, reducing wear on the brakes and enabling shorter landing distances. Such devices affect the aircraft significantly and are considered important for safe operations by airlines. There have been accidents involving thrust reversal systems, including fatal ones.

A slip is an aerodynamic state where an aircraft is moving somewhat sideways as well as forward relative to the oncoming airflow or relative wind. In other words, for a conventional aircraft, the nose will be pointing in the opposite direction to the bank of the wing(s). The aircraft is not in coordinated flight and therefore is flying inefficiently.

A powered parachute, often abbreviated PPC, and also called a motorized parachute or paraplane, is a type of aircraft that consists of a parafoil with a motor and wheels.

The Ryan X-13 Vertijet was an experimental tail-sitting vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) jet aircraft built by Ryan Aeronautical and flown in the United States in the 1950s. The main objective of the project was to demonstrate the ability of a pure jet to vertically take off, hover, transition to horizontal forward flight, and vertically land.

The vortex ring state (VRS) is a dangerous aerodynamic condition that may arise in helicopter flight, when a vortex ring system engulfs the rotor, causing severe loss of lift. Often the term settling with power is used as a synonym, e.g., in Australia, the UK, and the US, but not in Canada, which uses the latter term for a different phenomenon.

The Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA) is a former NASA training vehicle that duplicated the Space Shuttle's approach profile and handling qualities, allowing pilots to simulate Shuttle landings under controlled conditions before attempting the task on board the orbiter. The STA was also flown to assess weather conditions just prior to Space Shuttle launches and landings.

Human senses are not naturally geared for the in-flight environment. Pilots may experience disorientation and loss of perspective, creating illusions that range from false horizons to sensory conflict with instrument readings or the misjudging of altitude over water.

P-factor, also known as asymmetric blade effect and asymmetric disc effect, is an aerodynamic phenomenon experienced by a moving propeller, wherein the propeller's center of thrust moves off-center when the aircraft is at a high angle of attack. This shift in the location of the center of thrust will exert a yawing moment on the aircraft, causing it to yaw slightly to one side. A rudder input is required to counteract the yawing tendency.
The center of gravity (CG) of an aircraft is the point over which the aircraft would balance. Its position is calculated after supporting the aircraft on at least two sets of weighing scales or load cells and noting the weight shown on each set of scales or load cells. The center of gravity affects the stability of the aircraft. To ensure the aircraft is safe to fly, the center of gravity must fall within specified limits established by the aircraft manufacturer.
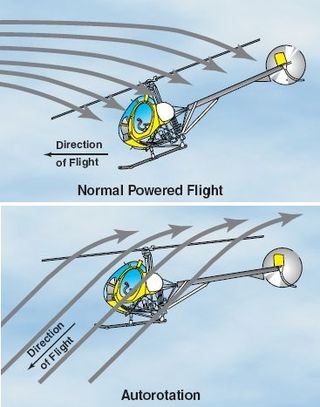
Autorotation is a state of flight in which the main rotor system of a helicopter or other rotary-wing aircraft turns by the action of air moving up through the rotor, as with an autogyro, rather than engine power driving the rotor. The term autorotation dates to a period of early helicopter development between 1915 and 1920, and refers to the rotors turning without the engine. It is analogous to the gliding flight of a fixed-wing aircraft. Some trees have seeds that have evolved wing-like structures that enable the seed to spin to the ground in autorotation, which helps the seeds to disseminate over a wider area.
Aircraft have different ways to take off and land. Conventional airplanes accelerate along the ground until reaching a speed that is sufficient for the airplane to takeoff and climb at a safe speed. Some airplanes can take off at low speed, this being a short takeoff. Some aircraft such as helicopters and Harrier jump jets can take off and land vertically. Rockets also usually take off vertically, but some designs can land horizontally.

A drop test is a method of testing the in-flight characteristics of prototype or experimental aircraft and spacecraft by raising the test vehicle to a specific altitude and then releasing it. Test flights involving powered aircraft, particularly rocket-powered aircraft, may be referred to as drop launches due to the launch of the aircraft's rockets after release from its carrier aircraft.


















