
The German Confederation was an association of 39 predominantly German-speaking sovereign states in Central Europe. It was created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 as a replacement of the former Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved in 1806.
The Evangelical Lutheran Church in Thuringia was a Lutheran member church of the umbrella Protestant Church in Germany. The seat of the church was in Eisenach. The church covered those parts of the state of Thuringia that were not part of the former Province of Saxony. It was the largest Protestant denomination in this area.
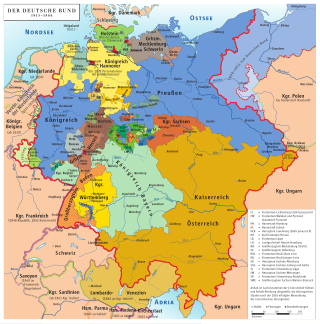
The states of the German Confederation were member states of the German Confederation, from 20 June 1815 until 24 August 1866.

Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt was a small historic state in present-day Thuringia, Germany, with its capital at Rudolstadt.

Schwarzburg-Sondershausen was a small principality in Germany, in the present day state of Thuringia, with its capital at Sondershausen.
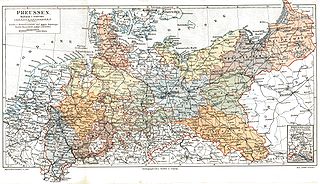
The Provinces of Prussia were the main administrative divisions of Prussia from 1815 to 1946. Prussia's province system was introduced in the Stein-Hardenberg Reforms in 1815, and were mostly organized from duchies and historical regions. Provinces were divided into several Regierungsbezirke, sub-divided into Kreise (districts), and then into Gemeinden (townships) at the lowest level. Provinces constituted the highest level of administration in the Kingdom of Prussia and Free State of Prussia until 1933, when Nazi Germany established de facto direct rule over provincial politics, and were formally abolished in 1946 following World War II. The Prussian provinces became the basis for many federal states of Germany, and the states of Brandenburg, Lower Saxony, and Schleswig-Holstein are direct successors of provinces.

Leopold III of Lippe was the sovereign of the Principality of Lippe reigning from 1851 until his death.

Leopold II of Lippe was the sovereign of the Principality of Lippe. He succeeded to the throne in 1802, and in 1820 he assumed control of the government from his mother, who had been acting as regent due to his youth at accession.

Günther Sizzo, Prince of Schwarzburg was the head of the House of Schwarzburg and pretender to the principalities of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt and Schwarzburg-Sondershausen.

Günther Victor, Prince of Schwarzburg was the final sovereign prince of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt and Schwarzburg-Sondershausen.

Georg Albert, Prince of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt was the penultimate sovereign prince of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt.

Friedrich Günther, Prince of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt was a sovereign prince of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt.
Hohenwarte is a municipality in the district Saalfeld-Rudolstadt, in Thuringia, Germany.

The German Empire consisted of 25 constituent states and an imperial territory, the largest of which was Prussia. These states, or Staaten each had votes in the Bundesrat, which gave them representation at a federal level.

Charles Gonthier, Prince of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen was the ruler of the principality of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen, a constituent state of the German Empire, and head of the House of Schwarzburg from 17 July 1880 until his death.
Events from the year 1871 in Germany.

Louis Frederick I of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt was the ruling prince of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt, Count of Hohenstein, Lord of Rudolstadt, Blankenburg and Sondershausen from 1710 until his death.
The North German Confederation Treaty was the treaty between the Kingdom of Prussia and other northern and central German states that initially created the North German Confederation, which was the forerunner to the German Empire. This treaty, and others that followed in September and October, are often described as the August treaties, although not all of them were concluded in August 1866.

Günther Friedrich Karl II of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen was the ruling Prince of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen following his father's abdication in 1835 until his own death in 1880. After Schwarzburg-Sondershausen joined the North German Confederation, he joined the Prussian Army and in 1879 became General of the Infantry.

















