
Naracoorte Caves National Park is a national park near Naracoorte in the Limestone Coast tourism region in the south-east of South Australia (Australia). It was officially recognised in 1994 for its extensive fossil record when the site was inscribed on the World Heritage List, along with Riversleigh. The park preserves 6 km2 of remnant vegetation, with 26 caves contained within the 3.05 km2 World Heritage Area. Out of the 28 known caves in the park, only four are open to the public. Other caves are kept away from the public eye as they are important for scientific research and also for the protection of the caves and their contents. Many of the caves contain spectacular stalactites and stalagmites.

The order Peramelemorphia includes the bandicoots and bilbies; it equates approximately to the mainstream of marsupial omnivores. All members of the order are endemic to the twin land masses of Australia-New Guinea and most have the characteristic bandicoot shape: a plump, arch-backed body with a long, delicately tapering snout, very large upright ears, relatively long, thin legs, and a thin tail. Their size varies from about 140 grams up to 4 kilograms, but most species are about one kilogram, or the weight of a half-grown kitten.

Riversleigh World Heritage Area is Australia's most famous fossil location, recognised for the series of well preserved fossils deposited from the Late Oligocene to more recent geological periods. The fossiliferous limestone system is located near the Gregory River in the north-west of Queensland, an environment that was once a very wet rainforest that became more arid as the Gondwanan land masses separated and the Australian continent moved north. The approximately 100 square kilometres (39 sq mi) area has fossil remains of ancient mammals, birds, and reptiles of the Oligocene and Miocene ages, many of which were discovered and are only known from the Riversleigh area; the species that have occurred there are known as the Riversleigh fauna.

The American cheetah is either of two feline species of the extinct genus Miracinonyx, endemic to North America during the Pleistocene epoch and morphologically similar to the modern cheetah. These cats were originally known from fragments of skeletons, but nearly complete skeletons have been recovered from Natural Trap Cave in northern Wyoming.

Cúc Phương National Park is located in Ninh Bình Province, in Vietnam's Red River Delta. Cuc Phuong was Vietnam's first national park and is the country's largest nature reserve. The park is one of the most important sites for biodiversity in Vietnam.

Bát Tràng porcelain and pottery is a type of ceramic made in the village of Bát Tràng, in the suburban outskirts of the northern Vietnamese city of Hanoi. The village is located in an area rich in clay suitable for making ceramic. Bát Tràng ceramics are considered some of the best known porcelain products in Vietnam besides those of Chu Đậu, Biên Hòa, Phù Lãng, Hương Canh, Lái Thiêu and Bầu Trúc. The history of ceramic making in this village can be traced back as far as the 14th century AD during the Ly-Tran dynasty period.

Dorothea Minola Alice Bate FGS, also known as Dorothy Bate, was a Welsh palaeontologist and pioneer of archaeozoology. Her life's work was to find fossils of recently extinct mammals with a view to understanding how and why giant and dwarf forms evolved.
The Tham Khuyen is a palaeontological formation located in Vietnam. It dates to the Jurassic period. The cave is located in Lang Son province, about 125 kilometers northeast of Hanoi.

Lạng Sơn is a province in northern Vietnam. Its capital is also called Lạng Sơn, which is a strategically important town at the border with China and is 137 kilometres (85 mi) northeast of Hanoi connected by rail and road. Lạng Sơn province is bordered by Cao Bằng province, Bắc Giang province, Bắc Kạn province, Quảng Ninh province, Thái Nguyên province, and China's Guangxi province. The province covers an area of 8310.09 square kilometres and as of 2008 it had a population of 781,655.

Tuyên Quang is a province of Vietnam, located in the northeastern part of the country to the northwest of Hanoi, at the centre of Lô River valley, a tributary of the Red River. Its capital is Tuyên Quang. The province had a population of 784,811 in 2019, with a density of 130 persons per km2 over a total land area of 5,867.3 square kilometres (2,265.4 sq mi).
Haasgat is a fossiliferous South African paleocave located in the Cradle of Humankind UNESCO World Heritage Area, approx. 20 kilometres (12 mi) northeast of the hominin-bearing sites of Sterkfontein and Swartkrans and approx. 60 kilometres (37 mi) north-northwest of the City of Johannesburg. It is located on private land and is not accessible by the public.
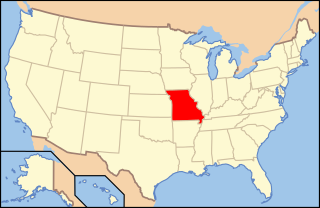
Paleontology in Missouri refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Missouri. The geologic column of Missouri spans all of geologic history from the Precambrian to present with the exception of the Permian, Triassic, and Jurassic. Brachiopods are probably the most common fossils in Missouri.
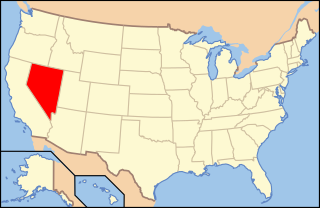
Paleontology in Nevada refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Nevada. Nevada has a rich fossil record of plants and animal life spanning the past 650 million years of time. The earliest fossils from the state are from Esmeralda County, and are Late Proterozoic in age and represent stromatolite reefs of cyanobacteria, amongst these reefs were some of the oldest known shells in the fossil record, the Cloudina-fauna. Much of the Proterozoic and Paleozoic fossil story of Nevada is that of a warm, shallow, tropical sea, with a few exceptions towards the Late Paleozoic. As such many fossils across the state are those of marine animals, such as trilobites, brachiopods, bryozoans, honeycomb corals, archaeocyaths, and horn corals.

Many areas of Vietnam are under protection. While the national reserves cover small areas of scientific significance with restricted access, the national parks also cover wetlands of Ramsar designated areas and BirdLife International inscribed bird areas. The largest of the national parks initially covered were the Cúc Phương National Park, the Cát Tiên National Park, and the Côn Đảo National Park which to start with were forest areas cum reserves or prohibited areas. The objective for creating national parks was to allow access to the reserved areas as a part of ecotourism and cultural needs with full attention to the basic approach of conservation of natural environmental resources.
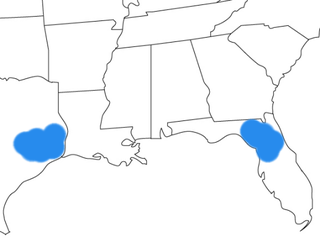
Floridachoerus olseni is an extinct peccary that lived during the Hemingfordian age of the Early Miocene, and was endemic to North America. F. olseni was in existence for approximately 4.46 million years. Remains of this extinct mammal were located at the fossil rich Thomas Farm site in Gilchrist County, Florida and Toledo Bend site, Newton County, Texas. Floridachoerus olseni was named after Stanley. J. Olsen of the Florida Geological Survey in 1962. Olsen previously worked at the site for Harvard University.
Zhiren Cave is a karstic cave in the Mulan Mountains that overlooks the Hejiang River in Chongzuo, Guangxi, China. Zhiren Cave is an early Late Pleistocene site that has yielded the fossil remains of possibly anatomically modern humans with some mixed archaic human features.
Hipposideros winsburyorum is a hipposiderid species of bat known by fossil specimens, one of the many new taxa of chiropterans discovered in the Riversleigh World Heritage Area. The species existed during the Pliocene.

Crash bandicoot is an extinct bandicoot, known from fossils located at the Riversleigh World Heritage Area in northeast Australia.

Pendlebury's roundleaf bat is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It was previously considered a subspecies of H. turpis, but has now been raised to full species level. It is endemic to Thailand and is found in limestone karst areas.














