
The Lombards or Longobards were a Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774.

Romagna is an Italian historical region that approximately corresponds to the south-eastern portion of present-day Emilia-Romagna, North Italy. Traditionally, it is limited by the Apennines to the south-west, the Adriatic to the east, and the rivers Reno and Sillaro to the north and west. The region's major cities include Cesena, Faenza, Forlì, Imola, Ravenna, Rimini and City of San Marino. The region has been recently formally expanded with the transfer from the Marche region of nine comuni where the Romagnol language is spoken.
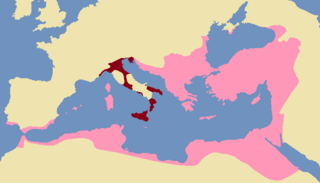
The Exarchate of Ravenna, also known as the Exarchate of Italy, was a lordship of the Eastern Roman Empire in Italy, from 584 to 751, when the last exarch was put to death by the Lombards. It was one of two exarchates established following the western reconquests under Emperor Justinian to more effectively administer the territories, along with the Exarchate of Africa.

The Duchy of Spoleto was a Lombard territory founded about 570 in central Italy by the Lombard dux Faroald. Its capital was the city of Spoleto.

The Duchy of Benevento was the southernmost Lombard duchy in the Italian Peninsula that was centred on Benevento, a city in Southern Italy. Lombard dukes ruled Benevento from 571 to 1077, when it was conquered by the Normans for four years before it was given to the Pope. Being cut off from the rest of the Lombard possessions by the papal Duchy of Rome, Benevento was practically independent from the start. Only during the reigns of Grimoald and the kings from Liutprand on was the duchy closely tied to the Kingdom of the Lombards. After the fall of the kingdom in 774, the duchy became the sole Lombard territory which continued to exist as a rump state, maintaining its de facto independence for nearly 300 years, although it was divided after 849. Benevento dwindled in size in the early 11th century, and was completely captured by the Norman Robert Guiscard in 1053.

The province of Pavia is a province in the region of Lombardy, in northern Italy; its capital is Pavia. As of 2015, the province has a population of 548,722 inhabitants and an area of 2,968.64 square kilometres (1,146.20 sq mi); the town of Pavia has a population of 72,205.

Liutprand was the king of the Lombards from 712 to 744 and is chiefly remembered for his multiple phases of law-giving, in fifteen separate sessions from 713 to 735 inclusive, and his long reign, which brought him into a series of conflicts, mostly successful, with most of Italy. He is often regarded as the most successful Lombard monarch, notable for the Donation of Sutri in 728, which was the first accolade of sovereign territory to the Papacy.

Northern Italy is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. The Italian National Institute of Statistics defines the region as encompassing the four northwestern regions of Piedmont, Aosta Valley, Liguria and Lombardy in addition to the four northeastern regions of Trentino-Alto Adige, Veneto, Friuli Venezia Giulia and Emilia-Romagna.

The Donation of Sutri was an agreement reached at Sutri by Liutprand, King of the Lombards and Pope Gregory II in 728. At Sutri, the two reached an agreement by which the city and some hill towns in Latium were given to the Papacy, "as a gift to the blessed Apostles Peter and Paul" according to the Liber Pontificalis. The pact formed the first extension of papal territory beyond the confines of the Duchy of Rome and was the first of two land transfers from Liutprand to the Church of Rome.

The Kingdom of Italy, also called Imperial Italy, was one of the constituent kingdoms of the Holy Roman Empire, along with the kingdoms of Germany, Bohemia, and Burgundy. It originally comprised large parts of northern and central Italy. Its original capital was Pavia until the 11th century.

Langobardia Minor was the name that, in the Early Middle Ages, was given to the Lombard domains in central and southern Italy, corresponding to the duchies of Spoleto and Benevento. After the conquest of the Lombard kingdom by Charlemagne in 774, it remained under Lombard control.

The Kingdom of the Lombards, also known as the Lombard Kingdom and later as the Kingdom of all Italy, was an early medieval state established by the Lombards, a Germanic people, on the Italian Peninsula in the latter part of the 6th century. The king was traditionally elected by the very highest-ranking aristocrats, the dukes, as several attempts to establish a hereditary dynasty failed. The kingdom was subdivided into a varying number of duchies, ruled by semi-autonomous dukes, which were in turn subdivided into gastaldates at the municipal level. The capital of the kingdom and the center of its political life was Pavia in the modern northern Italian region of Lombardy.

The Duchy of Friuli was a Lombard duchy in present-day Friuli, the first to be established after the conquest of the Italian peninsula in 568. It was one of the largest domains in Langobardia Major and an important buffer between the Lombard kingdom and the Slavs, Avars, and the Byzantine Empire. The original chief city in the province was Roman Aquileia, but the Lombard capital of Friuli was Forum Julii, modern Cividale.
Langobardia or Longobardia may refer to:
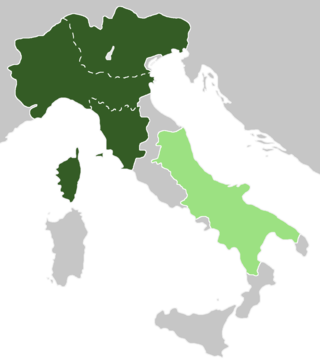
Austria was, according to the early medieval geographical classification, the eastern portion of Langobardia Major, the north-central part of the Lombard Kingdom, extended from the Adda to Friuli and opposite to Neustria. The partition had not only been territorial, but also implied significant cultural and political differences.

Neustria was, according to the early medieval geographical classification, the western portion of Langobardia Major, the north-central part of the Lombard Kingdom, extended from the Adda (river) to the Western Alps and opposite to Austria. The partition had not only been territorial, but also implied significant cultural and political differences.
Among the Lombards, the duke or dux was the man who acted as political and military commander of a set of "military families", irrespective of any territorial appropriation.

Lombard architecture refers to the architecture of the Kingdom of the Lombards, which lasted from 568 to 774 and which was commissioned by Lombard kings and dukes.

Longobards in Italy: Places of Power is seven groups of historic buildings that reflect the achievements of the Germanic tribe of the Lombards, who settled in Italy during the sixth century and established a Lombard Kingdom which ended in 774 A.D.

The coinage of the Lombards refers to the autonomous productions of coins by the Lombards. It constitutes part of the coinage produced by Germanic peoples occupying the former territory of the Roman Empire during the Migration Period. All known Lombard coinage was produced after their settlement of Italy. The coinage originates from two distinct areas, in Langobardia Major between the last decades of the sixth century and 774, and in Langobardia Minor, in the duchy of Benevento, between approximately 680 and the end of the 9th century.














