Related Research Articles

In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis.

The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as mice, cats, birds and dogs, but not in whales, or most reptiles.

The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is a ligament in each knee of humans and various other animals. It works as a counterpart to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). It connects the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia to the medial condyle of the femur. This configuration allows the PCL to resist forces pushing the tibia posteriorly relative to the femur.
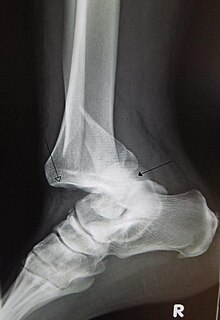
A joint dislocation, also called luxation, occurs when there is an abnormal separation in the joint, where two or more bones meet. A partial dislocation is referred to as a subluxation. Dislocations are often caused by sudden trauma on the joint like an impact or fall. A joint dislocation can cause damage to the surrounding ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves. Dislocations can occur in any joint major or minor. The most common joint dislocation is a shoulder dislocation.

Chondromalacia patellae is an inflammation of the underside of the patella and softening of the cartilage.

Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction is a surgical tissue graft replacement of the anterior cruciate ligament, located in the knee, to restore its function after an injury. The torn ligament can either be removed from the knee, or preserved before reconstruction an arthroscopic procedure. ACL repair is also a surgical option. This involves repairing the ACL by re-attaching it, instead of performing a reconstruction. Theoretical advantages of repair include faster recovery and a lack of donor site morbidity, but randomised controlled trials and long-term data regarding re-rupture rates using contemporary surgical techniques are lacking.

Patellar tendinitis, also known as jumper's knee, is an overuse injury of the tendon that straightens the knee. Symptoms include pain in the front of the knee. Typically the pain and tenderness is at the lower part of the kneecap, though the upper part may also be affected. Generally there is no pain when the person is at rest. Complications may include patellar tendon rupture.
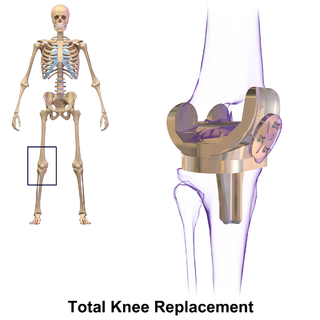
Knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace the weight-bearing surfaces of the knee joint to relieve pain and disability, most commonly offered when joint pain is not diminished by conservative sources and also for other knee diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. In patients with severe deformity from advanced rheumatoid arthritis, trauma, or long-standing osteoarthritis, the surgery may be more complicated and carry higher risk. Osteoporosis does not typically cause knee pain, deformity, or inflammation and is not a reason to perform knee replacement.
A meniscus transplant or meniscal transplant is a transplant of the meniscus of the knee, which separates the thigh bone (femur) from the lower leg bone (tibia). The worn or damaged meniscus is removed and is replaced with a new one from a donor. The meniscus to be transplanted is taken from a cadaver, and, as such, is known as an allograft. Meniscal transplantation is technically difficult, as it must be sized accurately for each person, positioned properly and secured to the tibial plateau. As of 2012, only a few surgeons have significant volume of experience in meniscus transplantation worldwide.
Articular cartilage, most notably that which is found in the knee joint, is generally characterized by very low friction, high wear resistance, and poor regenerative qualities. It is responsible for much of the compressive resistance and load bearing qualities of the knee joint and, without it, walking is painful to impossible. Osteoarthritis is a common condition of cartilage failure that can lead to limited range of motion, bone damage and invariably, pain. Due to a combination of acute stress and chronic fatigue, osteoarthritis directly manifests itself in a wearing away of the articular surface and, in extreme cases, bone can be exposed in the joint. Some additional examples of cartilage failure mechanisms include cellular matrix linkage rupture, chondrocyte protein synthesis inhibition, and chondrocyte apoptosis. There are several different repair options available for cartilage damage or failure.

Knee taping is a procedure performed by physiotherapists or physicians to alleviate the symptoms of patellofemoral pain. Though knee taping has been shown to offer short-term pain relief, its long-term efficacy is confounded by several studies. The mechanism of action by which it alleviates pain is unknown, though it has been suggested by physicians that it could correct patella position, facilitate/inhibit quadriceps components or bear stress associated with peripatellar tissues or patellar compression. Evidence for these suggestions, however, has been contradictory or absent.

The patellar tendon is the distal portion of the common tendon of the quadriceps femoris, which is continued from the patella to the tibial tuberosity. It is also sometimes called the patellar ligament as it forms a bone to bone connection when the patella is fully ossified.

In human anatomy, the quadriceps tendon works with the quadriceps muscle to extend the leg. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle attach to the shin via the patella, where the quadriceps tendon becomes the patellar ligament. It attaches the quadriceps to the top of the patella, which in turn is connected to the shin from its bottom by the patellar ligament. A tendon connects muscle to bone, while a ligament connects bone to bone.

Patellofemoral pain syndrome is knee pain as a result of problems between the kneecap and the femur. The pain is generally in the front of the knee and comes on gradually. Pain may worsen with sitting, excessive use, or climbing and descending stairs.
Patellar subluxation syndrome, is an injury that is concerned with the kneecap. Patellar subluxation is more common than patellar dislocation and is just as disabling.

A patellar dislocation is a knee injury in which the patella (kneecap) slips out of its normal position. Often the knee is partly bent, painful and swollen. The patella is also often felt and seen out of place. Complications may include a patella fracture or arthritis.

Knee pain is pain in or around the knee.

In medicine, Clarke's test is a component of knee examination which may be used to test for patellofemoral pain syndrome, chondromalacia patellae, patellofemoral arthritis, or anterior knee pain. It is not a standard part of the knee examination but is used to diagnose anterior knee pain where the history indicates this as the likely pathology. The patient is asked to actively contract the quadriceps muscle while the examiner's hand exerts pressure on the superior pole of the patella, so trying to prevent the proximal movement of the patella. While it can produce some discomfort even in normal people, the reproduction of the symptoms suggest pain of patellofemoral origin.
The Latarjet operation, also known as the Latarjet-Bristow procedure, is a surgical procedure used to treat recurrent shoulder dislocations, typically caused by bone loss or a fracture of the glenoid. The procedure was first described by French surgeon Dr. Michel Latarjet in 1954.
Dr. Jeremy Bruce is an Orthopaedic Surgeon at Erlanger Hospital in Chattanooga, Tennessee. He is also a Program Director and Director of Sports Medicine for the Orthopedic Residency program at The University of Tennessee College of Medicine in Chattanooga. He is a ringside physician that has covered UFC fights, Bellator fights, Ringside World Boxing championship, USA Boxing events and is a member of the USA Boxing Medical Commission. Dr. Bruce was a member of the USA Bobsled and Skeleton Team and competed alongside future Olympic gold medalist Jim Shea in the North American Skeleton Championship in Calgary, AL (1994).
References
- ↑ Fithian, D. C.; Paxton, E. W.; Post, W. R.; Panni, A. S.; International Patellofemoral Study Group (2004). "Lateral retinacular release: A survey of the international patellofemoral study group". Arthroscopy. 20 (5): 463–468. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2004.03.002. PMID 15122135.
- Panni AS, Tartarone M, Patricola A, Paxton EW, Fithian DC (May 2005). "Long-term results of lateral retinacular release". Arthroscopy. 21 (5): 526–31. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2005.01.007. PMID 15891716.
- Ricchetti ET, Mehta S, Sennett BJ, Huffman GR (May 2007). "Comparison of lateral release versus lateral release with medial soft-tissue realignment for the treatment of recurrent patellar instability: a systematic review". Arthroscopy. 23 (5): 463–8. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2007.01.007. PMID 17478275.
- Lattermann C, Toth J, Bach BR (Jun 2007). "The role of lateral retinacular release in the treatment of patellar instability". Sports Med Arthrosc. 15 (2): 57–60. doi:10.1097/JSA.0b013e318042af30. PMID 17505318. S2CID 9661859.
- Gerbino PG, Zurakowski D, Soto R, Griffin E, Reig TS, Micheli LJ (Jan–Feb 2008). "Long-term functional outcome after lateral patellar retinacular release in adolescents: an observational cohort study with minimum 5-year follow-up". J Pediatr Orthop. 28 (1): 118–23. doi:10.1097/bpo.0b013e31815b4dcf. PMID 18157056. S2CID 21906406.
- Fithian DC, Paxton EW, Post WR, Panni AS, International Patellofemoral Study Group (May 2004). "Lateral retinacular release: a survey of the International Patellofemoral Study Group". Arthroscopy. 20 (5): 463–8. doi:10.1016/j.arthro.2004.03.002. PMID 15122135.