
The IBM Personal Computer is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team of engineers and designers at International Business Machines (IBM), directed by William C. Lowe and Philip Don Estridge in Boca Raton, Florida.

CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc. CP/M is a disk operating system and its purpose is to organize files on a magnetic storage medium, and to load and run programs stored on a disk. Initially confined to single-tasking on 8-bit processors and no more than 64 kilobytes of memory, later versions of CP/M added multi-user variations and were migrated to 16-bit processors.

An IBM PC compatible is any personal computer that is hardware- and software-compatible with the IBM Personal Computer and its subsequent models. Like the original IBM PC, an IBM PC–compatible computer uses an x86-based central processing unit, sourced either from Intel or a second source like AMD, Cyrix or other vendors such as Texas Instruments, Fujitsu, OKI, Mitsubishi or NEC and is capable of using interchangeable commodity hardware such as expansion cards. Initially such computers were referred to as PC clones, IBM clones or IBM PC clones, but the term "IBM PC compatible" is now a historical description only, as the vast majority of microcomputers produced since the 1990s are IBM compatible. IBM itself no longer sells personal computers, having sold its division to Lenovo in 2005. "Wintel" is a similar description that is more commonly used for modern computers.

Xenix is a discontinued Unix operating system for various microcomputer platforms, licensed by Microsoft from AT&T Corporation. The first version was released in 1980, and Xenix would eventually become the most common Unix variant, measured according to the number of machines on which it was installed, in the mid-to-late 1980s. The Santa Cruz Operation (SCO) later acquired exclusive rights to the software, and eventually replaced it with SCO UNIX, later known as OpenServer, with the final Xenix version released in 1991.

Digital Research, Inc. was a privately held American software company created by Gary Kildall to market and develop his CP/M operating system and related 8-bit, 16-bit and 32-bit systems like MP/M, Concurrent DOS, FlexOS, Multiuser DOS, DOS Plus, DR DOS and GEM. It was the first large software company in the microcomputer world. Digital Research was originally based in Pacific Grove, California, later in Monterey, California.

CP/M-86 is a discontinued version of the CP/M operating system that Digital Research (DR) made for the Intel 8086 and Intel 8088. The system commands are the same as in CP/M-80. Executable files used the relocatable .CMD file format. Digital Research also produced a multi-user multitasking operating system compatible with CP/M-86, MP/M-86, which later evolved into Concurrent CP/M-86. When an emulator was added to provide PC DOS compatibility, the system was renamed Concurrent DOS, which later became Multiuser DOS, of which REAL/32 is the latest incarnation. The FlexOS, DOS Plus, and DR DOS families of operating systems started as derivations of Concurrent DOS as well.
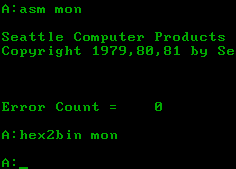
86-DOS is a discontinued operating system developed and marketed by Seattle Computer Products (SCP) for its Intel 8086-based computer kit.

In DOS memory management, expanded memory is a system of bank switching that provided additional memory to DOS programs beyond the limit of conventional memory (640 KiB).
DataFlex is an object-oriented high-level programming language and a fourth generation visual tool for developing Windows, web and mobile software applications on one framework-based platform. It was introduced and developed by Data Access Corporation beginning in 1982.

PC Magazine is an American computer magazine published by Ziff Davis. A print edition was published from 1982 to January 2009. Publication of online editions started in late 1994 and continues as of 2025.
Merge is a software system which allows a user to run DOS/Windows 3.1 on SCO UNIX, in an 8086 virtual machine.

Venix is a discontinued version of the Unix operating system for low-end computers, developed by VenturCom, a "company that specialises in the skinniest implementations of Unix".
Interactive Systems Corporation was a US-based software company and the first vendor of the Unix operating system outside AT&T, operating from Santa Monica, California. It was founded in 1977 by Peter G. Weiner, a RAND Corporation researcher who had previously founded the Yale University computer science department and had been the Ph.D. advisor to Brian Kernighan, one of Unix's developers at AT&T. Weiner was joined by Heinz Lycklama, also a veteran of AT&T and previously the author of a Version 6 Unix port to the LSI-11 computer.
A source-to-source translator, source-to-source compiler, transcompiler, or transpiler is a type of translator that takes the source code of a program written in a programming language as its input and produces an equivalent source code in the same or a different programming language. A source-to-source translator converts between programming languages that operate at approximately the same level of abstraction, while a traditional compiler translates from a higher level programming language to a lower level programming language. For example, a source-to-source translator may perform a translation of a program from Python to JavaScript, while a traditional compiler translates from a language like C to assembly or Java to bytecode. An automatic parallelizing compiler will frequently take in a high level language program as an input and then transform the code and annotate it with parallel code annotations or language constructs.

The IBM 3270 PC, is a personal computer developed by IBM and released in October 1983. Although its hardware is mostly identical to the IBM PC XT, the 3270 contains additional components that, in combination with software, can emulate the behavior of an IBM 3270 terminal. Therefore, it can be used both as a standalone computer, and as a terminal to a mainframe.

Following the introduction of the IBM Personal Computer in 1981, many other personal computer architectures became extinct within just a few years. It led to a wave of IBM PC compatible systems being released.
This article presents a timeline of events in the history of 16-bit x86 DOS-family disk operating systems from 1980 to present. Non-x86 operating systems named "DOS" are not part of the scope of this timeline.
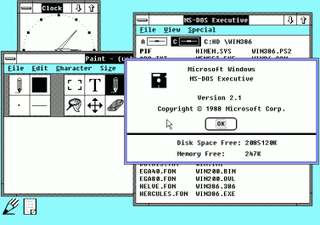
Windows 2.1 is a release of Microsoft Windows. It was released to manufacturing on May 27, 1988, as a successor to Windows 2.0.
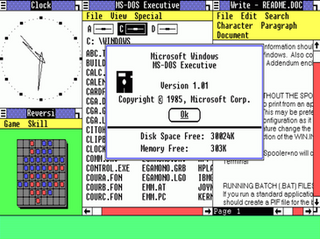
Windows 1.0 is the first major release of Microsoft Windows, a family of graphical operating systems for personal computers developed by Microsoft. It was first released to manufacturing in the United States on November 20, 1985, while the European version was released as Windows 1.02 in May 1986.
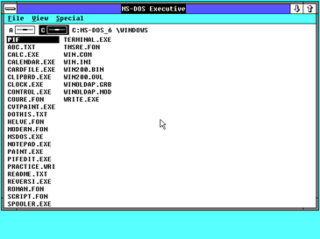
Windows 2.0 is a major release of Microsoft Windows, a family of graphical operating systems for personal computers developed by Microsoft. It was released to manufacturing on December 9, 1987, as a successor to Windows 1.0.














