
Urology, also known as genitourinary surgery, is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of the male and female urinary-tract system and the male reproductive organs. Organs under the domain of urology include the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, and the male reproductive organs.
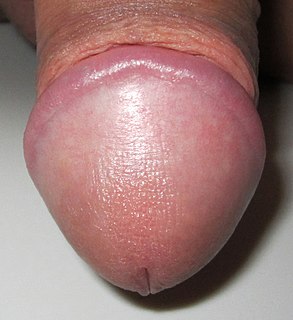
The glans penis, more commonly referred to as the glans, is a structure at the distal end of the penis in male mammals. It is the sensitive bulbous structure at the end of the human penis, and is anatomically homologous to the clitoral glans of the human female. The glans penis may be smooth, spiny, elongated, or divided in other mammals.

Hypospadias is a common variation in fetal development of the penis in which the urethra does not open from its usual location in the head of the penis. It is the second-most common birth abnormality of the male reproductive system, affecting about one of every 250 males at birth. Roughly 90% of cases are the less serious distal hypospadias, in which the urethral opening is on or near the head of the penis (glans). The remainder have proximal hypospadias, in which the meatus is all the way back on the shaft of the penis, near or within the scrotum. Shiny tissue that should have made the urethra extends from the meatus to the tip of the glans; this tissue is called the urethral plate.

Intersex medical interventions, also known as intersex genital mutilations (IGM) are surgical, hormonal and other medical interventions performed to modify atypical or ambiguous genitalia and other sex characteristics, primarily for the purposes of making a person's appearance more typical and to reduce the likelihood of future problems. The history of intersex surgery has been characterized by controversy due to reports that surgery can compromise sexual function and sensation, and create lifelong health issues. Timing, evidence, necessity and indications for surgeries in infancy, adolescence or adult age have been controversial, associated with issues of consent.

The history of intersex surgery is intertwined with the development of the specialities of pediatric surgery, pediatric urology, and pediatric endocrinology, with our increasingly refined understanding of sexual differentiation, with the development of political advocacy groups united by a human qualified analysis, and in the last decade by doubts as to efficacy, and controversy over when and even whether some procedures should be performed.
Anogenital distance (AGD) is the distance from the midpoint of the anus to the genitalia, the underside of the scrotum or the vagina. It is considered medically significant for a number of reasons, in both humans and animals, including sex determination and as a marker of endocrine disruptor exposure. It is regulated by dihydrotestosterone, which can be disrupted by phthalates common in plastics. Such endocrine disruption may affect the development of the brain.

The prostatic utricle is a small indentation in the prostatic urethra, at the apex of the urethral crest, on the seminal colliculus (verumontanum), laterally flanked by openings of the ejaculatory ducts. It is also known as the vagina masculina or uterus masculinus or vesicula prostatica.

Ashutosh K. Tewari is the chairman of urology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City. He is a board certified American urologist, oncologist, and principal investigator. Before moving to the Icahn School of Medicine in 2013, he was the founding director of both the Center for Prostate Cancer at Weill Cornell Medical College and the LeFrak Center for Robotic Surgery at NewYork–Presbyterian Hospital. Dr. Tewari was the Ronald P. Lynch endowed Chair of Urologic Oncology and the hospital's Director of Robotic Prostatectomy, treating patients with prostate, urinary bladder and other urological cancers. He is a world leading urological surgeon, and has performed over 9,000 robotically assisted procedures using the da Vinci Surgical System. Academically, he is recognized as a world-renowned expert on urologic oncology with over 250 peer reviewed published papers to his credit; he is on such lists as America's Top Doctors, New York Magazine's Best Doctors, and Who's Who in the World. In 2012, he was given the American Urological Association Gold Cystoscope Award for "outstanding contributions to the field of urologic oncology, most notably the treatment of prostate cancer and the development of novel techniques to improve the outcomes of robotic prostatectomy."

Diphallia, penile duplication (PD), diphallic terata, or diphallasparatus, is an extremely rare developmental abnormality in which a person is born with two penises. The first reported case was by Johannes Jacob Wecker in 1609. Its occurrence is 1 in 5.5 million boys in the United States.

Gary J. Alter is an American plastic surgeon. His specialties include sex reassignment surgery, genital reconstruction surgery and facial feminization surgery. He appeared in two episodes of the reality television series, Dr. 90210. PRNewswire reported on June 5, 2015 that Dr. Gary J. Alter performed the body work plastic surgery on Caitlyn Jenner. He has a practice in Beverly Hills, CA.
Labial fusion is a medical condition of the female genital anatomy where the labia minora become fused together. It is generally a pediatric condition.
Jaakko Oskari Elo was a Finnish urologist, surgeon and medical historian.
Emily Jane Willingham is a US journalist and scientist. Her writing focuses on neuroscience, genetics, psychology, health and medicine, and occasionally on evolution and ecology.
Reed Miller Nesbit was an American urologist, surgeon, and professor. He was Head of the Urology Section of the Department of Surgery at the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor, Michigan, from 1930–1967. Nesbit was a pioneer of transurethral resection of the prostate. He devised the ‘Nesbit operation’ for treating Peyronie's disease, and he made prominent contributions to pediatric urology, most notably the Cabot-Nesbit style orchiopexy.

Warren Snodgrass is a pediatric urologist specializing in the repair of hypospadias, the second most common birth defect. In 1994 he described the tubularized incised plate (TIP) repair of hypospadias, which has become known as the Snodgrass repair and has become the most common approach to repairing most forms of hypospadias. Together with Dr. Nicol Bush, he also developed the STAG repair for severe hypospadias and the Snodbush repair used mainly for reoperations after unsuccessful surgery. Snodgrass is internationally known for his advocacy of evidence-based surgery, and was the editor of a textbook on pediatric urology. He is in private practice near Dallas, Texas.

Lev Elterman, immigrated with his family in 1989 to the United States where he attended Rush Medical College. He graduated at the top of his class with a number of awards and then went on to urological residency at Rush University Medical Center.
Genitoplasty is plastic surgery to the genitals. Genitoplasties may be reconstructive to repair injuries, and damage arising from cancer treatment, or congenital disorders, endocrine conditions, or they may be cosmetic.
Miroslav Djordjevic is a Serbian surgeon specializing in sex reassignment surgery, and an assistant professor of urology at the School of Medicine, University of Belgrade, Serbia.

Intersex people in the United States have some of the same rights as other people, but with significant gaps, particularly in protection from non-consensual cosmetic medical interventions and violence, and protection from discrimination. Actions by intersex civil society organizations aim to eliminate harmful practices, promote social acceptance, and equality. In recent years, intersex activists have also secured some forms of legal recognition.

Jay Y. Gillenwater is professor emeritus at the University of Virginia. He is former chair of the Department of Urology at the School of Medicine of the University of Virginia, was president of the American Urological Association, editor of the Journal of Urology, member of the NIH Advisory Council of Diabetes, Digestive, and Kidney Diseases, and president of the American Foundation for Urologic Diseases. He is the author of Adult and Pediatric Urology.












