
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.

Pillow lavas are lavas that contain characteristic pillow-shaped structures that are attributed to the extrusion of the lava underwater, or subaqueous extrusion. Pillow lavas in volcanic rock are characterized by thick sequences of discontinuous pillow-shaped masses, commonly up to one meter in diameter. They form the upper part of Layer 2 of normal oceanic crust.

A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and periodic intervals of explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions, although some have collapsed summit craters called calderas. The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and hardens before spreading far, due to high viscosity. The magma forming this lava is often felsic, having high to intermediate levels of silica, with lesser amounts of less viscous mafic magma. Extensive felsic lava flows are uncommon, but have travelled as far as 15 km (9 mi).

Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic landforms. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and size of the fragments ejected during the eruption. Types of volcanic cones include stratocones, spatter cones, tuff cones, and cinder cones.
Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as their creating process, shape, elevation, slope, orientation, rock exposure, and soil type.

The Lassen volcanic area presents a geological record of sedimentation and volcanic activity in and around Lassen Volcanic National Park in Northern California, U.S. The park is located in the southernmost part of the Cascade Mountain Range in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. Pacific Oceanic tectonic plates have plunged below the North American Plate in this part of North America for hundreds of millions of years. Heat and molten rock from these subducting plates has fed scores of volcanoes in California, Oregon, Washington and British Columbia over at least the past 30 million years, including these in the Lassen volcanic areas.

Medicine Lake Volcano is a large shield volcano in northeastern California about 30 mi (50 km) northeast of Mount Shasta. The volcano is located in a zone of east-west crustal extension east of the main axis of the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the Cascade Range. The 0.6 mi (1 km) thick shield is 22 mi (35 km) from east to west and 28 to 31 mi from north to south, and covers more than 770 sq mi (2,000 km2). The underlying rock has downwarped by 0.3 mi (0.5 km) under the center of the volcano. The volcano is primarily composed of basalt and basaltic andesite lava flows, and has a 4.3 by 7.5 mi caldera at the center.

In geology, a dike or dyke is a sheet of rock that is formed in a fracture of a pre-existing rock body. Dikes can be either magmatic or sedimentary in origin. Magmatic dikes form when magma flows into a crack then solidifies as a sheet intrusion, either cutting across layers of rock or through a contiguous mass of rock. Clastic dikes are formed when sediment fills a pre-existing crack.

A flood basalt is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reaching the surface of the earth via a mantle plume. Flood basalt provinces such as the Deccan Traps of India are often called traps, after the Swedish word trappa, due to the characteristic stairstep geomorphology of many associated landscapes.

Alba Mons is a volcano located in the northern Tharsis region of the planet Mars. It is the biggest volcano on Mars in terms of surface area, with volcanic flow fields that extend for at least 1,350 km (840 mi) from its summit. Although the volcano has a span comparable to that of the United States, it reaches an elevation of only 6.8 km (22,000 ft) at its highest point. This is about one-third the height of Olympus Mons, the tallest volcano on the planet. The flanks of Alba Mons have very gentle slopes. The average slope along the volcano's northern flank is 0.5°, which is over five times lower than the slopes on the other large Tharsis volcanoes. In broad profile, Alba Mons resembles a vast but barely raised welt on the planet's surface. It is a unique volcanic structure with no counterpart on Earth or elsewhere on Mars.

Puʻu ʻŌʻō is a volcanic cone on the eastern rift zone of Kīlauea volcano in the Hawaiian Islands. The eruption that created Puʻu ʻŌʻō began on January 3, 1983, and continued nearly continuously until April 30, 2018, making it the longest-lived rift-zone eruption of the last two centuries.

Parinacota, Parina Quta or Parinaquta is a dormant stratovolcano on the border of Bolivia and Chile. Together with Pomerape it forms the Nevados de Payachata volcanic chain. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, its summit reaches an elevation of 6,380 metres (20,930 ft) above sea level. The symmetrical cone is capped by a summit crater with widths of 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) or 500 metres (1,600 ft). Farther down on the southern slopes lie three parasitic centres known as the Ajata cones. These cones have generated lava flows. The volcano overlies a platform formed by lava domes and andesitic lava flows.

Submarine volcanoes are underwater vents or fissures in the Earth's surface from which magma can erupt. Many submarine volcanoes are located near areas of tectonic plate formation, known as mid-ocean ridges. The volcanoes at mid-ocean ridges alone are estimated to account for 75% of the magma output on Earth. Although most submarine volcanoes are located in the depths of seas and oceans, some also exist in shallow water, and these can discharge material into the atmosphere during an eruption. The total number of submarine volcanoes is estimated to be over one million of which some 75,000 rise more than 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) above the seabed. Only 119 submarine volcanoes in Earth's oceans and seas are known to have erupted during the last 11,700 years.

Nevado de Longaví is a volcano in the Andes of central Chile. The 3,242 m (10,636 ft) high volcano lies in the Linares Province, which is part of the Maule Region. It features a summit crater and several parasitic vents. The volcano is constructed principally from lava flows. Two collapses of the edifice have carved collapse scars into the volcano, one on the eastern slope known as Lomas Limpias and another on the southwestern slope known as Los Bueye. The volcano features a glacier and the Achibueno and Blanco rivers originate on the mountain.
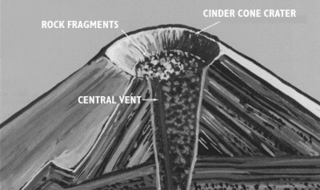
A cinder cone is a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments, such as volcanic clinkers, volcanic ash, or scoria that has been built around a volcanic vent. The pyroclastic fragments are formed by explosive eruptions or lava fountains from a single, typically cylindrical, vent. As the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall as either cinders, clinkers, or scoria around the vent to form a cone that often is symmetrical; with slopes between 30 and 40°; and a nearly circular ground plan. Most cinder cones have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit.

A volcanic plateau is a plateau produced by volcanic activity. There are two main types: lava plateaus and pyroclastic plateaus.

A lava cave is any cave formed in volcanic rock, though it typically means caves formed by volcanic processes, which are more properly termed volcanic caves. Sea caves, and other sorts of erosional and crevice caves, may be formed in volcanic rocks, but through non-volcanic processes and usually long after the volcanic rock was emplaced.

Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or underwater, usually at temperatures from 800 to 1,200 °C. The volcanic rock resulting from subsequent cooling is also often called lava.

Cerro Chao is a lava flow complex associated with the Cerro del León volcano in the Andes. It is the largest known Quaternary silicic volcano body and part of the most recent phase of activity in the Altiplano–Puna volcanic complex.

A fissure is a long, narrow crack opening along the surface of Earth. The term is derived from the Latin word fissura, which means 'cleft' or 'crack'. Fissures emerge in Earth's crust, on ice sheets and glaciers, and on volcanoes.



















