Related Research Articles

Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada. Situated in the country's Atlantic region, it is composed of the insular region of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador to the northwest, with a combined area of 405,212 square kilometres (156,500 sq mi). In 2018, the province's population was estimated at 525,073. About 92% of the province's population lives on the island of Newfoundland, of whom more than half live on the Avalon Peninsula.
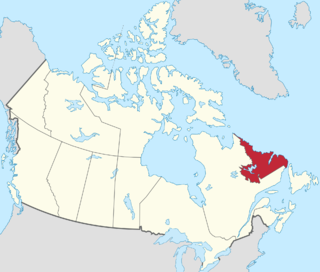
Labrador is a geographic and cultural region within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is the continental portion of the province and constitutes 71% of the province's area but is home to only 6% of the province's population. It is separated from the island of Newfoundland by the Strait of Belle Isle. It is the largest and northernmost geographical region in Atlantic Canada.

The flag of Newfoundland and Labrador was introduced in 1980 and was designed by Newfoundland artist Christopher Pratt. The flag design was approved by the House of Assembly of the province of Newfoundland, Canada, on May 28, 1980. It was flown for the first time on Discovery Day, June 24, 1980. The name of the province was changed to Newfoundland and Labrador by an amendment to the constitution of Canada in December 2001. This was at the request of the provincial legislature.
Edward Moxon Roberts is a Canadian politician and the 11th Lieutenant Governor of Newfoundland and Labrador.

Newfoundland was a British dominion from 1907 to 1934. The dominion, situated in northeastern North America along the Atlantic coast, comprised the island of Newfoundland as well as Labrador on the continental mainland. Before attaining dominion status, Newfoundland was a British colony, self-governing from 1855.

Same-sex marriage in Newfoundland and Labrador has been legal since December 21, 2004, when the province was ordered to issue marriage licences to same-sex couples.

The Newfoundland pony is a breed of pony originating in Newfoundland, Canada. They are sturdy and muscular ponies, found in many colors, including the relatively rare white coloration. The Newfoundland developed from a mix of English, Irish and Scottish pony breeds brought to Newfoundland by settlers over a period of four centuries. Initially free-roaming, they crossbred to produce the modern type. They were used by settlers as draft and multi-purpose ponies until the mid-20th century, when they were brought almost to the point of extinction by mechanization and slaughter. The population rebounded slightly after the formation of a breed registry in 1980, but still remains low. In 1997, the Newfoundland pony was declared a heritage breed of Newfoundland and Labrador, which afforded it protection under the law, but the breed has not yet been recognized under the Canadian federal Animal Pedigree Act. As of 2008, there were 248 registered ponies of breeding age, out of a total population of 361. In 2013, the widely dispersed breeding population is still estimated at between 200 and 250 animals.

The London and Bristol Company came about in the early 17th century when English merchants had begun to express an interest in the Newfoundland fishery. Financed by a syndicate of investors John Guy, himself a Bristol merchant, visited Newfoundland in 1608 to locate a favourable site for a colony. Upon his return to England 40 people applied for incorporation as the Tresurer and the Companye of Adventurers and planter of the Cittye of london and Bristoll for the Collonye or plantacon in Newfoundland. The company was known as the London and Bristol Company or simply the Newfoundland Company.

The Court of Appeal of Newfoundland and Labrador is at the top of the hierarchy of courts for the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. The Court of Appeal derives its powers and jurisdiction from the Court of Appeal Act.

The Newfoundland and Labrador Federation of Labour is the Newfoundland and Labrador provincial trade union federation for the Canadian Labour Congress. It was founded in 1937, and has a membership of 65,000.

The first brief European contact with Newfoundland and Labrador came c. AD 1000 when the Vikings briefly settled in L'Anse aux Meadows. In 1497, European explorers and fishermen from England, Portugal, Netherlands, France, and Spain began exploration. Fishing expeditions came seasonally; the first small permanent settlements appeared around 1630. Catholic-Protestant religious tensions were high but mellowed after 1860. The British colony voted against joining Canada in 1869 and became an independent dominion in the early 20th century. Fishing was always the dominant industry, but the economy collapsed in the Great Depression of the 1930s and the people voluntarily relinquished their independence to become a British colony again. Prosperity and self-confidence returned during the Second World War, and after the intense debate, the people voted to join Canada in 1949.

The Supreme Court of Newfoundland and Labrador is the superior court for the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. The Supreme Court has jurisdiction to hear appeals in both criminal and civil matters from the Provincial Court and designated boards and administrative tribunals. The court also hear serious criminal cases in the first instances, matters of probate, and family law matters.

The Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador is governed by a unicameral legislature, the House of Assembly, which operates under the Westminster model of government. The executive function of government is formed by the Lieutenant Governor, the premier and his or her cabinet. The politics of Newfoundland and Labrador is defined by a long history, liberal democratic political institutions and a unique political culture.

Franco-Newfoundlanders, also known as Franco-Terreneuvians in English or Franco-Terreneuviens in French, are francophone and/or French Canadian residents of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. The name Franco-Terreneuvian derives from Terre-Neuve, the French name of Newfoundland.

Newfoundland is a large island off the east coast of the North American mainland, and the most populous part of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It has 29 percent of the province's land area. The island is separated from the Labrador Peninsula by the Strait of Belle Isle and from Cape Breton Island by the Cabot Strait. It blocks the mouth of the Saint Lawrence River, creating the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, the world's largest estuary. Newfoundland's nearest neighbour is the French overseas community of Saint-Pierre and Miquelon.

Andrew Parsons is a Canadian politician and Lawyer, who was elected to the Newfoundland and Labrador House of Assembly in the 2011 provincial election.
Malcolm H. Rowe is a Puisne Justice of the Supreme Court of Canada. Rowe is the first judge from Newfoundland and Labrador to sit on the Supreme Court.

Chesley Furneaux "Ches" Crosbie, Q.C. is a Canadian lawyer and politician who currently serves as the Leader of the Opposition in the Newfoundland and Labrador House of Assembly. Crosbie was elected leader of the Progressive Conservative Party of Newfoundland and Labrador on April 28, 2018. On September 20, 2018 he was elected as MHA for Windsor Lake, and therefore became Leader of the Official Opposition upon being sworn in on October 12, 2018.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Newfoundland and Labrador.
References
- ↑ Dr. Melvin Baker. "History of Newfoundland and Labrador Summary Chronology of Events" (PDF). Royal Commission on Renewing and Strengthening Our Place in Canada. p. 7. Retrieved June 10, 2020.