
Chinese checkers (US) or Chinese chequers (UK), known as Sternhalma in German, is a strategy board game of German origin that can be played by two, three, four, or six people, playing individually or with partners. The game is a modern and simplified variation of the game Halma.

Checkers, also known as draughts, is a group of strategy board games for two players which involve forward movements of uniform game pieces and mandatory captures by jumping over opponent pieces. Checkers is developed from alquerque. The term "checkers" derives from the checkered board which the game is played on, whereas "draughts" derives from the verb "to draw" or "to move".
Mak-yek is a two-player abstract strategy board game played in Thailand and Myanmar. Players move their pieces as in the rook in chess and attempt to capture their opponent's pieces through custodian and intervention capture. The game may have been first described in literature by Captain James Low a writing contributor in the 1839 work Asiatic Researches; or, Transactions of the Society, Instituted in Bengal, For Inquiring into The History, The Antiquities, The Arts and Sciences, and Literature of Asian, Second Part of the Twentieth Volume in which he wrote chapter X On Siamese Literature and documented the game as Maak yék. Another early description of the game is by H.J.R. Murray in his 1913 work A History of Chess, and the game was written as Maak-yek.
Fox games are a category of asymmetric board games for two players, where one player attempts to catch the opponent's pieces, while that player moves their pieces to either trap the fox or reach a destination on the board. In one variant, fox and hounds, a single fox tries to evade the other player's hounds.

English draughts or checkers, also called straight checkers or simply draughts, is a form of the strategy board game checkers. It is played on an 8×8 checkerboard with 12 pieces per side. The pieces move and capture diagonally forward, until they reach the opposite end of the board, when they are crowned and can thereafter move and capture both backward and forward.

Turkish draughts (Armenian: շաշկի)(Arabic: دامە)(Kurmanji: Dame) is a variant of draughts (checkers) played in Turkey, Greece, Egypt, Kuwait, Lebanon, Syria, Jordan and several other locations around the Mediterranean Sea and Middle East.

Kōnane is a two-player strategy board game from Hawaii which was invented by the ancient Hawaiian Polynesians. The game is played on a rectangular board and begins with black and white counters filling the board in an alternating pattern. Players then hop over one another's pieces, capturing them similar to checkers. The first player unable to capture is the loser.
Ming mang is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Tibet. Ming mang is also a general term for the word "boardgame" in Tibet. The correct name and spelling of the game may actually be Mig mang(s), but pronounced Ming mang or Mi Mang. The term mig mang is also applied to Tibetan go with both games using exactly the same board which is a 17 x 17 square board, and black and white pieces. Mig is in reference to the chart of the board, and Mangs refers to the notion that the more charts are used on the board, the more pieces are needed to play the game, but some state that it means "many eyes". The game may also be known as Gundru. The game was popular among some Tibetan monks before the Chinese invasion of Tibet in 1950, and the uprising in 1959, and among aristocratic families.
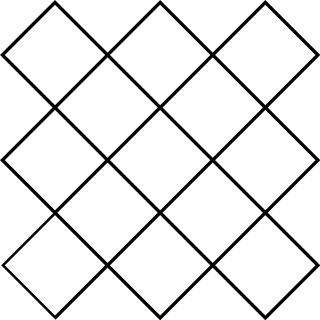
Liberian Queah is a two-player abstract strategy game from Liberia. It is specifically from the Mamba, Queah and Bassa tribes. The game is played on a slanted or diagonal square board with only 13 spaces. Pieces move "orthogonally" along these slanted or diagonal square boards. Another unique feature is that each player must have maximum four pieces on the board. Player's captured piece may resupplied with a piece from their reserve.
Zamma is a two-player abstract strategy game from Africa. It is especially played in Mauritania. The game is similar to alquerque and draughts. Board sizes vary, but they are square boards, such as 5x5 or 9x9 square grids with left and right diagonal lines running through several intersection points of the board. One could think of the 5x5 board as a standard alquerque board, but with additional diagonal lines, and the 9x9 board as four standard alquerque boards combined, but no additional diagonal lines are added. The initial setup is also similar to alquerque, where every space on the board is filled with each player's pieces except for the middle point of the board. Furthermore, each player's pieces are also set up on their respective half of the board. The game specifically resembles draughts in that pieces must move in the forward directions until they are crowned "Mullah" which is the equivalent of the king in draughts. The Edhayam can move in any direction. In Mauritania, the black pieces are referred to as men, and the white pieces as women. In the Sahara, short sticks represent the men, and camel dung represent the women.
Dablo is a family of two-player strategy board games of the Sámi people. Different variants of the game have been played in different parts of Sápmi.
High jump is a two-player strategy board game from Somalia. It is related to draughts and alquerque as pieces hop over one another for capture; however, pieces move and capture orthogonally and not diagonally. Moreover, the game is played on a 5×5 square board. A feature of high jump is that the central square offers a kind of sanctuary; a piece occupying the central square cannot be hopped over and captured. The same board is used in the game Seega.

Armenian draughts, or Tama, is a variant of draughts played in Armenia. The rules are similar to Dama. Armenian draughts, however, allows for diagonal movement.
Kotu Ellima is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Sri Lanka played by the Sinhalese people. The game was documented by Henry Parker in Ancient Ceylon: An Account of the Aborigines and of Part of the Early Civilisation (1909); the game was printed as "Kotu Ellima" which is actually a misspelling because his source for the game was Leopold Ludovici's Journal of the Ceylon Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society (1873), and specifically in the chapter entitled "The Sports and Games of the Singhalese", and Ludovici wrote the name of the game as Kotu Ellime or Taking of the Castles. The game is similar to draughts (checkers) and Alquerque as players hop over one another's pieces to capture them; it is more similar to Alquerque between the two since it uses a standard Alquerque board. However, unlike draughts and standard Alquerque, the game is played on an expanded Alquerque board consisting of four triangular boards attached to the four sides of a standard Alquerque board. It closely resembles peralikatuma and sixteen soldiers which are also played in Sri Lanka and other parts of the Indian subcontinent with the only difference being the number of pieces. In sixteen soldiers, each player has 16 pieces hence the name of the game. In peralikatuma, each player has 23 pieces. In Kotu Ellima, each player has 24 pieces, and at the beginning of the game the whole board is covered with them except the central point reminiscent of standard alquerque.
Sua ghin gnua is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Thailand, formerly known as Siam. Another name for the game is tigers and oxen. It is a hunt game played on a 5x5 square grid with only orthogonal lines. One player plays the three tigers, and the other player plays the twelve oxen. The board is empty in the beginning. Players first drop their pieces onto the board, and then are able to move them. The tigers can capture the oxen by the short leap as in draughts and alquerque, but the oxen attempt to elude and at the same time hem in the tiger. Sua Ghin Gnua most resembles the tiger hunt games such as bagh-chal, rimau-rimau, main tapal empat, catch the hare, and adugo since they all use a 5 x 5 square grid. But tiger games technically consist of a standard alquerque board which is a 5 x 5 square grid with several diagonal lines criss-crossing through it which are completely missing in sua ghin gnua. There are however some variants of catch the hare which have missing diagonal lines also. Another game that resembles sua ghin gnua is from Myanmar, called tiger and buffaloes, which is a hunt game consisting of a 4 x 4 square grid with no diagonal lines. Myanmar happens to border Thailand geographically so there might be a historical connection between the two games. Another game from Myanmar is lay gwet kyah that is presumed to be similar to sua ghin gnua. Sua ghin gnua was briefly described by Stewart Culin, in his book Chess and Playing Cards: Catalogue of Games and Implements for Divination Exhibited by the United States National Museum in Connection with the Department of Archaeology and Paleontology of the University of Pennsylvania at the Cotton States and International Exposition, Atlanta, Georgia 1895 (1898). It's also briefly mentioned by H.J.R. Murray in his book A History of Chess (1913). It was also described by R.C. Bell, in his book Board and Table Games from Many Civilizations (1969).
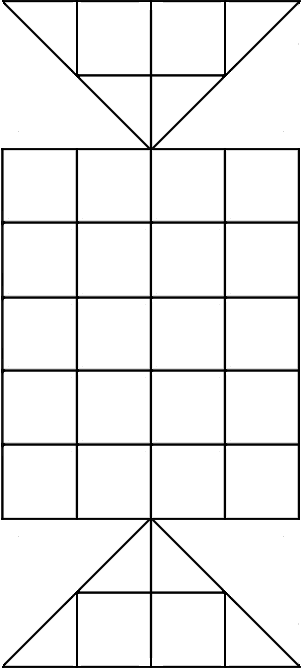
Astar is a two-player abstract strategy board game from Kyrgyzstan. It is a game similar to draughts and Alquerque as players hop over one another's pieces when capturing. However, unlike draughts and Alquerqe, Astar is played on 5×6 square grid with two triangular boards attached on two opposite sides of the grid. The board somewhat resembles those of kotu ellima, sixteen soldiers, and peralikatuma, all of which are games related to astar. However, these three games use an expanded alquerque board with a 5×5 square grid with diagonal lines. Astar uses a 5×6 grid with no diagonal lines.

Dameo is an abstract strategy board game for two players invented by Christian Freeling in 2000. It is a variant of the game draughts and is played on an 8×8 checkered gameboard.

Tobit is a draughts game that resembles Turkish and Armenian draughts in that pieces move orthogonally. It especially resembles Turkish draughts in that pieces only move orthogonally.
Keny is a draughts game played in the Caucasus and nearby areas of Turkey. Keny is actually the Ossetian name for the game as it is most popular in Ossetia, a region in the Caucasus. In Armenia, it is called Vayut tama. The game is also known as Caucasian checkers. There may be slight variations of the game, but the rules described here are from Nikita Sokolov from his article "It's been a while since we took checkers into our hands..." (2005).







