Lee Feigon | |
|---|---|
| Born | Lee Feigon |
| Nationality | American |
| Alma mater | University of California, Berkeley, University of Chicago, University of Wisconsin-Madison |
| Occupation(s) | Historian, Sinologist |
| Known for | Mao: A Reinterpretation |
Lee Feigon is an American historian who specialized in the study of 20th-century Chinese history.
In 2002 he published Mao: A Reinterpretation , a work of historical revisionism that sought to highlight what Feigon saw as the positive aspects of Mao Zedong's political leadership. He subsequently used that book as a basis for a documentary, The Passion of the Mao.
He has written for such U.S. publications as The Wall Street Journal , Barron's , The Nation , The Chicago Tribune , The Atlantic , and The Boston Globe .
| Title | Year | Publisher | ISBN |
|---|---|---|---|
| China Rising: The Meaning of Tiananmen | 1990 | Ivan R. Dee | 978-0929587301 |
| Chen Duxiu: Founder of the Chinese Communist Party | 1992 | Princeton University Press | 978-0691053936 |
| Demystifying Tibet: Unlocking the Secrets of the Land of the Snows | 1995 | Ivan R. Dee | 978-1566630894 |
| Mao: A Reinterpretation | 2002 | Ivan R. Dee | 978-1566635226 |

The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victorious in the Chinese Civil War against the Kuomintang. In 1949, Mao proclaimed the establishment of the People's Republic of China. Since then, the CCP has governed China and has sole control over the People's Liberation Army (PLA). Each successive leader of the CCP has added their own theories to the party's constitution, which outlines the ideology of the party, collectively referred to as socialism with Chinese characteristics. As of 2023, the CCP has more than 98 million members, making it the second largest political party by membership in the world after India's Bharatiya Janata Party.

Mao Zedong, also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese politician, communist philosopher, military strategist, poet and revolutionary who was the founder of the People's Republic of China (PRC), which he led as the chairman of the Chinese Communist Party from the establishment of the PRC in 1949 until his death in 1976. Ideologically a Marxist–Leninist, his theories, military strategies, and political policies are collectively known as Maoism.

The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a sociopolitical movement in the People's Republic of China (PRC) launched by Mao Zedong in 1966 and that lasted until his death in 1976. Its stated goal was to preserve Chinese communism by purging remnants of capitalist and traditional elements from Chinese society. The Revolution marked the effective commanding return of Mao—who was still the chairman of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP)—to the centre of power, after a period of self-abstention and ceding to less radical leadership in the aftermath of the Mao-led Great Leap Forward debacle and the Great Chinese Famine (1959–1961). The Revolution failed to achieve its main goals.

Maoism, officially called the Mao Zedong Thought by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), is a variety of Marxism–Leninism that Mao Zedong developed to realize a socialist revolution in the agricultural, pre-industrial society of the Republic of China and later the People's Republic of China. The philosophical difference between Maoism and traditional Marxism–Leninism is that a united front of progressive forces in class society would lead the revolutionary vanguard in pre-industrial societies rather than communist revolutionaries alone. This updating and adaptation of Marxism–Leninism to Chinese conditions in which revolutionary praxis is primary and ideological orthodoxy is secondary represents urban Marxism–Leninism adapted to pre-industrial China. Later theoreticians expanded on the idea that Mao had adapted Marxism–Leninism to Chinese conditions, arguing that he had in fact updated it fundamentally and that Maoism could be applied universally throughout the world. This ideology is often referred to as Marxism–Leninism–Maoism to distinguish it from the original ideas of Mao.

Chen Duxiu was a Chinese revolutionary socialist, educator, philosopher and author, who co-founded the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) with Li Dazhao in 1921. From 1921 to 1927, he served as the Communist Party's first general secretary. Chen was a leading figure in both the Xinhai Revolution that overthrew the Qing dynasty and the May Fourth Movement for scientific and democratic developments in the early Republic of China. After his expulsion from the CCP in 1929, Chen was for a time the leader of China's Trotskyist movement.

Hua Guofeng was a Chinese politician who served as Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party and Premier of the People's Republic of China. The designated successor of Mao Zedong, Hua held the top offices of the government, party, and the military after the deaths of Mao and Premier Zhou Enlai, but was gradually forced out of supreme power by a coalition of party leaders between December 1978 and June 1981, and subsequently retreated from the political limelight, though still remaining a member of the Central Committee until 2002.

Lin Biao was a Chinese politician and Marshal of the People's Republic of China who was pivotal in the Communist victory during the Chinese Civil War, especially in Northeast China from 1946 to 1949. Lin was the general who commanded the decisive Liaoshen and Pingjin campaigns, in which he co-led the Manchurian Field Army to victory and led the People's Liberation Army into Beijing. He crossed the Yangtze River in 1949, decisively defeated the Kuomintang and took control of the coastal provinces in Southeast China. He ranked third among the Ten Marshals. Zhu De and Peng Dehuai were considered senior to Lin, and Lin ranked directly ahead of He Long and Liu Bocheng.

Edgar Parks Snow was an American journalist known for his books and articles on Communism in China and the Chinese Communist revolution. He was the first Western journalist to give an account of the history of the Chinese Communist Party following the Long March, and he was also the first Western journalist to interview many of its leaders, including Mao Zedong. He is best known for his book, Red Star Over China (1937), an account of the Chinese Communist movement from its foundation until the late 1930s.

Isaac Mao is a Chinese software architect, and social media researcher. He is doing research in social learning and for developing the philosophy of Sharism.

Yáng Kāihuì was the second wife of Mao Zedong, whom he married in 1920. She had three children with Mao Zedong: Mao Anying, Mao Anqing, and Mao Anlong. Her father was Yang Changji, the head of the Hunan First Normal School and one of Mao's favorite teachers.

He Zizhen was the third wife of Chairman Mao Zedong from 1928 to 1937. She was one of the few female soldiers in the First Front Red Army that went on the Long March.

Red Star Over China is a 1937 book by Edgar Snow. It is an account of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) that was written when it was a guerrilla army and still obscure to Westerners.

The First United Front, also known as the KMT–CCP Alliance, of the Kuomintang (KMT) and the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), was formed in 1924 as an alliance to end warlordism in China. Together they formed the National Revolutionary Army and set out in 1926 on the Northern Expedition. The CCP joined the KMT as individuals, making use of KMT's superiority in numbers to help spread communism. The KMT, on the other hand, wanted to control the communists from within. Both parties had their own aims and the Front was unsustainable. In 1927, KMT leader Chiang Kai-shek purged the Communists from the Front while the Northern Expedition was still half-complete. This initiated a civil war between the two parties that lasted until the Second United Front was formed in 1936 to prepare for the coming Second Sino-Japanese War.
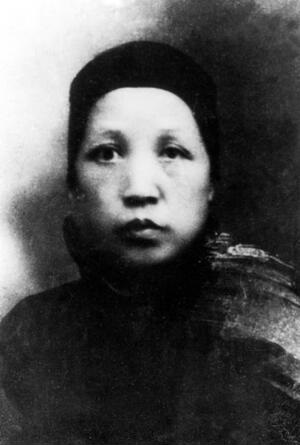
Wen Qimei was the mother of Mao Zedong.
Luo Yixiu, a Han Chinese woman, was the first wife of the later Chinese communist revolutionary and political leader Mao Zedong, to whom she was married from 1908 until her death. Coming from the area around Shaoshan, Hunan, in south central China – the same region as Mao – her family were impoverished local landowners.

Tibet came under the control of People's Republic of China (PRC) after the Government of Tibet signed the Seventeen Point Agreement which the 14th Dalai Lama ratified on 24 October 1951, but later repudiated on the grounds that he had rendered his approval for the agreement while under duress. This occurred after attempts by the Tibetan Government to gain international recognition, efforts to modernize its military, negotiations between the Government of Tibet and the PRC, and a military conflict in the Chamdo area of western Kham in October 1950. The series of events came to be called the "Peaceful Liberation of Tibet" by the Chinese government, and the "Chinese invasion of Tibet" by the Central Tibetan Administration and the Tibetan diaspora.

Mao: A Reinterpretation is a biography of the Chinese communist revolutionary and politician Mao Zedong written by Lee Feigon, an American historian of China then working at Colby College. It was first published by Ivan R. Dee in 2002, and would form the basis of Feigon's 2006 documentary Passion of the Mao.

Mao Yichang or Mao Rensheng was a Chinese farmer and grain merchant who achieved notability as the father of Mao Zedong. The nineteenth generation of the Mao clan, he was born and lived his life in the rural village of Shaoshanchong in Shaoshan, Hunan Province.

The early life of Chinese revolutionary and politician Mao Zedong covered the first 27 years of his life, from 1893 to 1919. Born in Shaoshanchong, Shaoshan in Hunan province, Mao grew up as the son of Mao Yichang, a wealthy farmer and landowner. Sent to the local Shaoshan Primary School, Mao was brought up in an environment of Confucianism, but reacted against this from an early age, developing political ideas from modern literature. Aged 13 his father organised a marriage for him with Luo Yigu, the daughter of another land-owning family, but Mao denounced the marriage and moved away from home.
Juli Feigon is a Distinguished Professor of Biochemistry at the University of California, Los Angeles, where she has been a faculty member since 1985. She was elected to the United States National Academy of Sciences in 2009. Her research focuses on structural studies of nucleic acids by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy along with other biophysical techniques.