
Aristid Lindenmayer was a Hungarian biologist. In 1968 he developed a type of formal language today called L-systems or Lindenmayer systems. Using those systems Lindenmayer modelled the behaviour of cells of plants. L-systems nowadays are also used to model whole plants.

The Second Boer War, also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics over the Empire's influence in Southern Africa from 1899 to 1902.

Artifacts indicating human activity dating back to the early Stone Age have been found in the Kingdom of Eswatini. The earliest known inhabitants of the region were Khoisan hunter-gatherers. Later, the population became predominantly Nguni during and after the great Bantu migrations. People speaking languages ancestral to the current Sotho and Nguni languages began settling no later than the 11th century. The country now derives its name from a later king named Mswati II. Mswati II was the greatest of the fighting kings of Eswatini, and he greatly extended the area of the country to twice its current size. The people of Eswatini largely belong to a number of clans that can be categorized as Emakhandzambili, Bemdzabu, and Emafikamuva, depending on when and how they settled in Eswatini.

Stephanus Johannes Paulus Kruger was a South African politician. He was one of the dominant political and military figures in 19th-century South Africa, and State President of the South African Republic from 1883 to 1900. Nicknamed Oom Paul, he came to international prominence as the face of the Boer cause—that of the Transvaal and its neighbour the Orange Free State—against Britain during the Second Boer War of 1899–1902. He has been called a personification of Afrikanerdom, and remains a controversial figure; admirers venerate him as a tragic folk hero.

The Anglo-Zulu War was fought in 1879 between the British Empire and the Zulu Kingdom. Following the passing of the British North America Act of 1867 forming a federation in Canada, Lord Carnarvon thought that a similar political effort, coupled with military campaigns, might succeed with the African Kingdoms, tribal areas and Boer republics in South Africa. In 1874, Sir Bartle Frere was sent to South Africa as High Commissioner for the British Empire to effect such plans, among the obstacles were the armed independent states of the South African Republic and the Kingdom of Zululand.

Pieter Arnoldus "Piet" Cronjé was a South African Boer general during the Anglo-Boer Wars of 1880–1881 and 1899–1902.

Dinuzulu kaCetshwayo was the king of the Zulu nation from 20 May 1884 until his death in 1913. He succeeded his father Cetshwayo, who was the last king of the Zulus to be officially recognised as such by the British. Zululand had been broken up into thirteen smaller territories by the British government after the Anglo-Zulu War, and Cetshwayo, and subsequently Dinuzulu, administered one of them. The British later realized the futility of breaking up Zululand into the territories and restored Cetshwayo as paramount leader of the territories. However, they left one of Cetshwayo's relatives, Usibepu (Zibhebhu), alone with his lands intact. On 22 July 1883, Usibepu attacked Cetshwayo's new kraal in Ulundi, wounding the king and causing him to flee.

Ladysmith is a city in the Uthukela District of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. It lies 230 kilometres (140 mi) north-west of Durban and 365 kilometres (227 mi) south-east of Johannesburg. Important industries in the area include food processing, textiles, and tyre production. Ladysmith is the seat for both the Alfred Duma Local Municipality and Uthukela District Municipality.

Petrus Jacobus Joubert, better known as Piet Joubert, was Commandant-General of the South African Republic from 1880 to 1900. He also served as Vice-President to Paul Kruger from May 1883 to October 1884 and from May 1896 until his death. He served in First Boer War, Second Boer War, and the Malaboch War.

Joachim Johannes Ferreira was a Boer commandant of the First Boer War. This general J. Ferreira should not be confused with general I. Ferreira.

The Battle of Spioen Kop was a military engagement between British forces and two Boer Republics, the South African Republic and the Orange Free State, during the campaign by the British to relieve the besieged city Ladysmith during the initial months of the Second Boer War. The battle was fought 23–24 January 1900 on the hilltop of Spioen Kop(1), about 38 km (24 mi) west-southwest of Ladysmith and resulted in a Boer victory.

Captain David Reginald Younger, VC was a Scottish recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces.
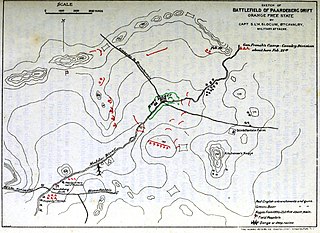
The Battle of Paardeberg or Perdeberg was a major battle during the Second Anglo-Boer War. It was fought near Paardeberg Drift on the banks of the Modder River in the Orange Free State near Kimberley.

The Battle of Magersfontein was fought on 11 December 1899, at Magersfontein, near Kimberley, South Africa, on the borders of the Cape Colony and the independent republic of the Orange Free State. British forces under Lieutenant General Lord Methuen were advancing north along the railway line from the Cape to relieve the siege of Kimberley, but their path was blocked at Magersfontein by a Boer force that was entrenched in the surrounding hills. The British had already fought a series of battles with the Boers, most recently at Modder River, where the advance was temporarily halted.

The Battle of Berg-en-dal took place in South Africa during the Second Anglo-Boer War.

The siege of Kimberley took place during the Second Boer War at Kimberley, Cape Colony, when Boer forces from the Orange Free State and the Transvaal besieged the diamond mining town. The Boers moved quickly to try to capture the area when war broke out between the British and the two Boer republics in October 1899. The town was ill-prepared, but the defenders organised an energetic and effective improvised defence that was able to prevent it from being taken.

Daniël Johannes Stephanus "Danie" Theron was a Boer Army military leader and master scout. Born in Tulbagh, Cape Colony, he was raised in Bethlehem, Orange Free State. He is best known as the driving force behind the formation of a military bicycle corps used by the Boer Army for scouting and relaying messages. Originally trained as a school teacher, he became a lawyer and notary with his own law firm in Krugersdorp, Transvaal Republic, and was made a commandant in the Boer forces during the Second Anglo-Boer War. During the course of the war, he was put in charge of a significant scouting unit, Theron se Verkenningskorps (TVK). He fought at the Battle of Spion Kop and one of his most famous feats occurred at the Battle of Paardeberg. The British Commander in Chief, Lord Roberts, called Theron: "the hardest thorn in the flesh of the British advance", put a reward of £1,000 on his head – dead or alive – and dispatched 4,000 soldiers to find and eliminate the TVK.

Richard Constant Boer was a Dutch linguist who specialized in Old Norse.

Piet Retief Commando was a light infantry regiment of the South African Army. It formed part of the South African Army Infantry Formation as well as the South African Territorial Reserve.

Lucas Johannes Meyer, was a Boer general, member of the Transvaal government and president of the Nieuwe Republiek.



















