
Leopold Hoesch (born 13 January 1820 in Düren, died 21 April 1899 in Düren) was a German entrepreneur. In 1871 he founded the Eisen-und Stahlwerk Hoesch AG, later the Westfalenhütte in Dortmund, Westphalia. [1] [2] [3]

Leopold Hoesch (born 13 January 1820 in Düren, died 21 April 1899 in Düren) was a German entrepreneur. In 1871 he founded the Eisen-und Stahlwerk Hoesch AG, later the Westfalenhütte in Dortmund, Westphalia. [1] [2] [3]

In 1846, Hoesch's father expanded the family business, founding a rolling mill in Eschweiler and acquiring ten additional mine fields. On October 1, 1846, the company "Gebrüder Eberhard and Wilhelm Hoesch" (named after Leopold's father and uncle) went on to operate under the name "Eberhard Hoesch & Söhne."
After the death of his uncle Eberhard on 21 April 1852, Leopold became the new head of the company.
During the 1860s, Hoesch moved the company's headquarters to the Ruhr area in order to benefit from low freight costs and the proximity to the coal mines.
Together with his sons Wilhelm (1845-1923) and Albert (1847-1898), as well as with the sons of his uncle Eberhard, Viktor and Eberhard Hoesch, on 1 September 1871 he founded the "Eisen- und Stahlwerk Hoesch" in Dortmund. The company was initially an OHG and was transformed into a public limited company two years later, the shares of which remained family-owned and which has since been operating under the name "Hoesch AG". The new company set up its own company health insurance fund, and later a death benefit fund. [4] [5]

The Krupp family is a prominent 400-year-old German dynasty from Essen, noted for its production of steel, artillery, ammunition and other armaments. The family business, known as Friedrich Krupp AG, was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century, and was the premier weapons manufacturer for Germany in both world wars. Starting from the Thirty Years' War until the end of the Second World War, it produced battleships, U-boats, tanks, howitzers, guns, utilities, and hundreds of other commodities.

Leopold V, known as the Virtuous was a member of the House of Babenberg who reigned as Duke of Austria from 1177 and Duke of Styria within the Holy Roman Empire from 1192 until his death. The Georgenberg Pact resulted in Leopold being enfeoffed with Styria by Roman-German Emperor Frederick Barbarossa in 1193, which would lead to the eventual creation of modern Austria. Leopold was also known for his involvement in the Third Crusade where he fought in the Siege of Acre in 1191 and of his imprisonment of King Richard I in 1193 at Dürnstein Castle.

Düren is a town in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, between Aachen and Cologne, on the river Rur.

Georg Wilhelm von Siemens was a German telecommunications industrialist of the Siemens family.
Estel was a steel company formed by the merging of Koninklijke Hoogovens IJmuiden steel plant and Hoesch's main steel plant in Dortmund. The company existed from 1972 to 1982 until de-merged.
The Vereinigte Stahlwerke AG was a German industrial conglomerate producing coal, iron, and steel in the interbellum and during World War II.

Zeche Carl is a cultural centre set up by Essen Council in a former coal mine.

Hoesch AG was an important steel and mining company with locations in the Ruhr area and Siegen.
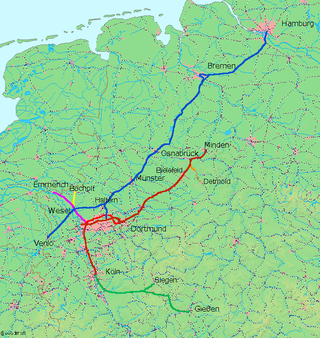
The Cologne-Minden Railway Company was along with the Bergisch-Märkische Railway Company and the Rhenish Railway Company one of the railway companies that in the mid-19th century built the first railways in the Ruhr and large parts of today's North Rhine-Westphalia.
Events from the year 1871 in Germany.

The Düsseldorf tramway network is a network of tramways serving Düsseldorf, the capital city of the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. In combination with the Düsseldorf Stadtbahn and Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn, it forms the backbone of the public transport system in Düsseldorf.

Dortmund-Barop station is on Barop Marktplatz in the Hombruch district of the city of Dortmund in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia on the Elberfeld–Dortmund line. The station is currently classified as a category 5 station. It is served by regional services and Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn line S 5.

Leybold GmbH, based in Cologne, is part of the Swedish industry group Atlas Copco. The company’s core competencies are based on the development of components and systems for the generation of vacuum and gas management engineering.

David Ostrowski is a German painter. He studied at Kunstakademie Düsseldorf with Albert Oehlen. He lives and works in Cologne, Germany. He is the grandson of Krystyna Żywulska.

The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Dortmund, Germany.

The proclamation of the German Empire, also known as the Deutsche Reichsgründung, took place in January 1871 after the joint victory of the German states in the Franco-Prussian War. As a result of the November Treaties of 1870, the southern German states of Baden, Hesse-Darmstadt, with their territories south of the Main line, Württemberg and Bavaria, joined the Prussian-dominated "North German Confederation" on 1 January 1871. On the same day, the new Constitution of the German Confederation came into force, thereby significantly extending the federal German lands to the newly created German Empire. The Day of the founding of the German Empire, January 18, became a day of celebration, marking when the Prussian King William I was proclaimed German Emperor at the Palace of Versailles.
Hermann Claasen was a German photographer.

Industrialization in Germany was the phase of the breakthrough of industrialization in Germany, beginning at the time from around 1815 to 1835. This period was preceded by the periods of pre-industrialization and early industrialization. In general, the decades between the 1830s and 1873 are considered the phase of industrial take off. The Industrial Revolution was followed by the phase of high industrialization during the German Empire. The (catch-up) Industrial Revolution in Germany differed from that of the pioneering country of Great Britain in that the key industries became not the textile industry but coal production, steel production and railroad construction.

Carl Gehrts, also Karl Gehrts, complete name Karl Heinrich Julius Gehrts was a German painter, illustrator and academic scholar. As a professor, he taught at the Kunstakademie Düsseldorf.
Peter Klöckner was a German businessman and industrialist.