Timeline
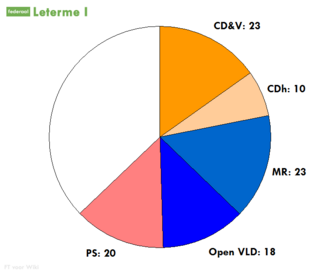
The 2007–2008 Belgian government formation followed the general election of 10 June 2007, and comprised a period of negotiation in which the Flemish parties Flemish Liberal Democratic, Christian Democratic and Flemish (CD&V) and New Flemish Alliance (N-VA), and the French-speaking parties Reformist Movement (MR), Democratic Front of Francophones (FDF) and Humanist Democratic Centre (CdH) negotiated to form a government coalition. The negotiations were characterized by the disagreement between the Dutch- and French-speaking parties about the need for and nature of a constitutional reform. According to some, this political conflict could have led to a partition of Belgium. The Verhofstadt III government was an interim Belgian government inaugurated on December 21, 2007 and lasting until 23 March 2008. It was led by Belgian Prime Minister Guy Verhofstadt government and contained representatives from the Open Flemish Liberals and Democrats, Flemish Christian Democrats (CD&V), the Francophone Socialists (PS), the Francophone Liberals (MR) and Francophone Christian Democrats (CDH). |
See also
 The area within Belgium known as Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde encompasses the bilingual Brussels-Capital Region, which coincides with the arrondissement of Brussels-Capital and the surrounding Dutch-speaking area of Halle-Vilvoorde, which in turn coincides with the arrondissement of Halle-Vilvoorde. Halle-Vilvoorde contains several municipalities with language facilities, i.e. municipalities where French-speaking people form a considerable part of the population and therefore have special language rights.  The partition of Belgium is a hypothetical situation which has been discussed by both Belgian and international media envisioning a split of the country along linguistic divisions, with each of the Flemish Community (Flanders) and the French-speaking Community (Wallonia) either becoming independent states or joining, respectively, The Netherlands and France. Both communities currently have a large degree of autonomy within the Belgian federation.  The term State reform in the Belgian context refers to the ongoing process of seeking and finding constitutional and legal solutions to the problems and tensions that exist among the different segments of the Belgian population, mostly between the Dutch-speakers of Flanders and the French-speakers of Wallonia. In general, Belgium has evolved from a unitary state to a federal state with communities, regions, and language areas. |
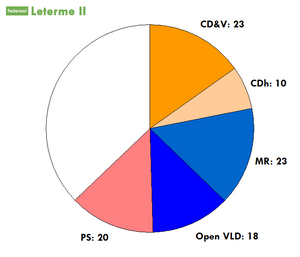
The Leterme II Government was the federal government of Belgium from 25 November 2009 to 26 April 2010, and the caretaker government until 6 December 2011. It took office when the Flemish Christian Democrat Yves Leterme (CD&V) was sworn in as Prime Minister. [1] It followed the Van Rompuy I Government which ended when Herman Van Rompuy became the first President of the European Council. It comprised five parties: the Dutch-speaking Christian Democratic and Flemish (CD&V), the Dutch-speaking Open Flemish Liberals and Democrats (Open VLD), the French-speaking liberal Reformist Movement (MR), the French-speaking Socialist Party (PS) and the French-speaking Humanist Democratic Centre (CDH).

Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Western Europe. It is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the southwest, and the North Sea to the northwest. It covers an area of 30,688 square kilometres (11,849 sq mi) and has a population of more than 11.4 million. The capital and largest city is Brussels; other major cities are Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi and Liège.
A caretaker government is a government that rules on a temporary basis, due to the loss of election or a pending transition of power.

Yves Camille Désiré Leterme is a Belgian politician, a leader of the Christian Democratic and Flemish party (CD&V). He was the 48th Prime Minister of Belgium, from November 2009 to December 2011.