| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 150 seats in the Chamber of Representatives 40 of 71 seats in the Senate respectively 76 and 36 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Colours denote the winning party in each electoral district, as shown in the table of results. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Timeline
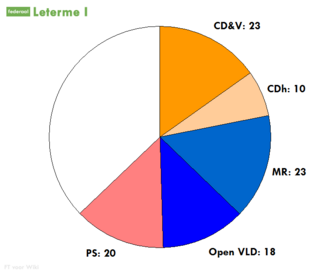
The 2007–2008 Belgian government formation followed the general election of 10 June 2007, and comprised a period of negotiation in which the Flemish parties Flemish Liberal Democratic, Christian Democratic and Flemish (CD&V) and New Flemish Alliance (N-VA), and the French-speaking parties Reformist Movement (MR), Democratic Front of Francophones (FDF) and Humanist Democratic Centre (CdH) negotiated to form a government coalition. The negotiations were characterized by the disagreement between the Dutch- and French-speaking parties about the need for and nature of a constitutional reform. According to some, this political conflict could have led to a partition of Belgium. The Verhofstadt III government was an interim Belgian government inaugurated on December 21, 2007 and lasting until 23 March 2008. It was led by Belgian Prime Minister Guy Verhofstadt government and contained representatives from the Open Flemish Liberals and Democrats, Flemish Christian Democrats (CD&V), the Francophone Socialists (PS), the Francophone Liberals (MR) and Francophone Christian Democrats (CDH). |
See also
 The area within Belgium known as Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde encompasses the bilingual Brussels-Capital Region, which coincides with the arrondissement of Brussels-Capital and the surrounding Dutch-speaking area of Halle-Vilvoorde, which in turn coincides with the arrondissement of Halle-Vilvoorde. Halle-Vilvoorde contains several municipalities with language facilities, i.e. municipalities where French-speaking people form a considerable part of the population and therefore have special language rights.  The partition of Belgium is a hypothetical situation which has been discussed by both Belgian and international media envisioning a split of the country along linguistic divisions, with each of the Flemish Community (Flanders) and the French-speaking Community (Wallonia) either becoming independent states or joining, respectively, The Netherlands and France. Both communities currently have a large degree of autonomy within the Belgian federation.  The term State reform in the Belgian context refers to the ongoing process of seeking and finding constitutional and legal solutions to the problems and tensions that exist among the different segments of the Belgian population, mostly between the Dutch-speakers of Flanders and the French-speakers of Wallonia. In general, Belgium has evolved from a unitary state to a federal state with communities, regions, and language areas. |
The 2007 Belgian federal election took place on Sunday 10 June 2007. Voters went to the polls in order to elect new members for the Chamber of Representatives and Senate.
Contents
- Background
- Parties
- Flemish parties (Dutch speaking)
- Francophone parties (French speaking)
- Issues
- Good governance
- Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde and constitutionality
- Corruption in the Walloon Region
- Armenian Genocide
- Polls
- Results
- Chamber of Representatives
- Senate
- Government formation
- See also
- References
- External links
Eligible voters were Belgian citizens 18 years and older. There was a legal electoral threshold of 5% for political parties to meet to receive representation, but in several election districts the real electoral threshold is higher than the legal, due to the small number of seats to be elected in the particular district. The 150 members of the Chamber of Representatives were elected from 11 electoral districts. The 40 Senate members were elected from the Dutch (25) and Francophone (15) electoral colleges.

Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Western Europe. It is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the southwest, and the North Sea to the northwest. It covers an area of 30,688 square kilometres (11,849 sq mi) and has a population of more than 11.4 million. The capital and largest city is Brussels; other major cities are Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi and Liège.
Of the Flemish parties, the alliance of Christian Democratic and Flemish party (CD&V) and the New-Flemish Alliance (N-VA) received an increased share of the vote from the previous election, held in 2003. The CD&V/N-VA list was headed by Yves Leterme, and became the largest political formation in Belgium, thus leading the coalition talks for a new government. [1] Flemish Interest (Vlaams Belang) received more votes than in the previous election, but lost one seat. Green! was able to return to parliament and newcomers List Dedecker (Lijst Dedecker) surprised most by immediately grabbing six seats, including one in the Senate. Prime minister Guy Verhofstadt's "purple coalition," consisting of his Open Flemish Liberals and Democrats (Open VLD) alliance list and Socialist Party – Different (SP.A/SPIRIT), was punished in the election, with the SP.A/SPIRIT alliance losing somewhat more than Verhofstadt's Open VLD alliance. The day after the election, Verhofstadt handed in the resignation of his government to King Albert II. [2] [3] SP.A leader Johan Vande Lanotte resigned from his leadership position as well that day. [4]
The Francophone situation did not mirror its Flemish counterpart. While Verhofstadt's Open VLD struggled, its Francophone sister party Mouvement Réformateur managed to defeat the long-dominant Parti Socialiste (PS), although the PS remained strong in Hainaut and Liège. The Humanist Democratic Centre brought in a positive result as well, but the biggest gains were for the environmentalist party Ecolo.
The overall outcome of the elections was that the liberal fraction (MR, VLD) became the largest group in parliament with, followed by the Christian Democrats (CD&V, Cdh) and N-VA with 40 seats. The electoral alliance between the Flemish CD&V and N-VA parties became the biggest single parliamentary grouping (25 seats for CD&V and 5 for N-VA).