
An electoral college is a set of electors who are selected to elect a candidate to a particular office. Often these represent different organizations, political parties, or entities, with each organization, political party or entity represented by a particular number of electors or with votes weighted in a particular way. The system can ignore the wishes of a general membership.

The Parliament of Australia is the legislative branch of the government of Australia. It consists of three elements: the Crown, the Senate and the House of Representatives. The combination of two elected chambers, in which the members of the Senate represent the states and territories while the members of the House represent electoral divisions according to population, is modelled on the United States Congress. Through both chambers, however, there is a fused executive, drawn from the Westminster system.

The New Zealand Parliament is the legislature of New Zealand, consisting of the Queen of New Zealand (Queen-in-Parliament) and the New Zealand House of Representatives. The Queen is usually represented by a governor-general. Before 1951, there was an upper chamber, the New Zealand Legislative Council. The Parliament was established in 1854 and is one of the oldest continuously functioning legislatures in the world.

The Michigan Legislature is the legislature of the U.S. state of Michigan. It is organized as a bicameral body composed of an upper chamber, the Senate, and a lower chamber, the House of Representatives. Article IV of the Michigan Constitution, adopted in 1963, defines the role of the Legislature and how it is to be constituted. The primary purpose of the Legislature is to enact new laws and amend or repeal existing laws. The Legislature meets in the Capitol building in Lansing.

The Florida Legislature is the Legislature of the U.S. State of Florida. It is organized as a bicameral body composed of an upper chamber, the Senate, and a lower chamber, the House of Representatives. Article III, Section 1 of the Florida Constitution, adopted in 1968, defines the role of the Legislature and how it is to be constituted. The Legislature is composed of 160 State Legislators. The primary purpose of the Legislature is to enact new laws and amend or repeal existing laws. The Legislature meets in the Florida State Capitol building in Tallahassee.

The House of Representatives was the lower chamber of Fiji's Parliament from 1970 to 2006. It was the more powerful of the two chambers; it alone had the power to initiate legislation. The House of Representatives also had much greater jurisdiction over financial bills; the Senate could not amend them, although it might veto them. Except in the case of amendments to the Constitution, over which a veto of the Senate was absolute, the House of Representatives might override a Senatorial veto by passing the same bill a second time, in the parliamentary session immediately following the one in which it was rejected by the Senate, after a minimum period of six months.

The Belgian Federal Parliament is the bicameral parliament of Belgium. It consists of the Chamber of Representatives and the Senate. It sits in the Palace of the Nation. The Chamber of Representatives is the primary legislative body; the Senate functions only as a meeting place of the federal communities and regions.

Elections in Belgium are organised for legislative bodies only, and not for executive functions. Direct elections take place for the European Parliament, the bicameral Federal Parliament, the Parliaments of the Communities and Regions, the provincial councils, the municipal councils and a few district councils. Voting is mandatory and all elections use proportional representation which in general requires coalition governments.

The Italian Parliament is the national parliament of the Italian Republic. The Parliament is the representative body of Italian citizens and is the successor to the Parliament of the Kingdom of Sardinia (1848–1861) and the Parliament of the Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946). It is a bicameral legislature with 945 elected members and a small number of unelected members (parlamentari). It is composed of the Chamber of Deputies, with 630 members (deputati) elected on a national basis, and the Senate of the Republic, with 315 members (senatori) elected on a regional basis, plus a small number of senators for life, either appointed or ex officio. The two houses are independent from one another and never meet jointly except under circumstances specified by the Constitution.
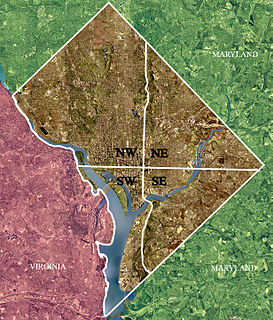
Voting rights of citizens in the District of Columbia differ from the rights of citizens in each of the 50 U.S. states. The United States Constitution grants each state voting representation in both houses of the United States Congress. As the U.S. capital, the District of Columbia is a special federal district, not a state, and therefore does not have voting representation in Congress. The Constitution grants Congress exclusive jurisdiction over the District in "all cases whatsoever".

The Florida Senate is the upper house of the Florida Legislature, the state legislature of the U.S. state of Florida, the Florida House of Representatives being the lower house. Article III, Section 1 of the Constitution of Florida, adopted in 1968, defines the role of the Legislature and how it is to be constituted. The Senate is composed of 40 members, each elected from a single-member district with a population of approximately 470,000 residents. Legislative districts are drawn on the basis of population figures, provided by the federal decennial census. Senators' terms begin immediately, upon their election. The Senate Chamber is located in the State Capitol building.

The Parliament of Albania or Kuvendi is the unicameral representative body of the citizens of the Republic of Albania; it is Albania's legislature. The Parliament is composed of not less than 140 members elected to a four-year term on the basis of direct, universal, periodic and equal suffrage by secret ballot. The Parliament is presided over by a Speaker of the Parliament, who is assisted by at least one deputy speaker. The electoral system is based on party-list proportional representation. There are 12 multi-seat constituencies, corresponding to the country's administrative divisions.

The House of Representatives is the lower house of the National Assembly of Thailand, the legislative branch of the Thai government. The system of government of Thailand is that of a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary democracy. The system of the Thai legislative branch is modelled after the Westminster system. The House of Representatives has 500 members, all of which are democratically elected: 375 members were directly elected through single constituency elections, while the other 125 are elected through party-list proportional representation. The roles and powers of the House of Representatives were enshrined in the Constitution of 2017.

The National Assembly of Thailand is the bicameral legislative branch of the government of Thailand. It convenes in the Parliament House, Dusit District, Bangkok.

The Greek Senate was the upper chamber of the parliament in Greece, extant several times in the country's history.

The United States House of Representatives is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they comprise the legislature of the United States.

Full general elections were held in Belgium on 2 June 1912.

Partial general elections were held in Belgium on 11 June, 18 June and 15 July 1878. The result was a victory for the Liberal Party, which won 72 of the 132 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 36 of the 66 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 62.5%, although only 56,640 people were eligible to vote.



















