
Sir Alexander Tilloch Galt, was a politician and a father of Canadian Confederation.

Lethbridge is a city in the province of Alberta, Canada. It is Alberta's third-largest city by both population and land area after Calgary and Edmonton, and the largest city in southern Alberta. The nearby Canadian Rocky Mountains contribute to the city's warm summers, mild winters, and windy climate. Lethbridge lies southeast of Calgary on the Oldman River.
The Oldman River is a river in southern Alberta, Canada. It flows roughly west to east from the Rocky Mountains, through the communities of Fort Macleod, Lethbridge, and on to Grassy Lake, where it joins with the Bow River to form the South Saskatchewan River, which eventually drains into the Hudson Bay.

Alberta Provincial Highway No. 3, commonly referred to as Highway 3 and officially named the Crowsnest Highway, is a 324-kilometre (201 mi) highway that traverses southern Alberta, Canada, running from the Crowsnest Pass through Lethbridge to the Trans-Canada Highway in Medicine Hat. Together with British Columbia Highway 3 which begins in Hope, it forms an interprovincial route that serves as an alternate to the Trans-Canada from the Lower Mainland to the Canadian Prairies.

Alberta Provincial Highway No. 4, commonly referred to as Highway 4, is a 103-kilometre (64 mi) highway in southern Alberta, Canada that connects Highway 3 in Lethbridge to Interstate 15 in Montana. It begins in Coutts at Alberta's busiest border crossing, winding north through gentle rolling hills and farmlands in the south of the province. It bypasses Milk River, Warner and Stirling before reaching Lethbridge where it becomes 43 Street and ends at Crowsnest Trail on the east side of the city. In 1995, it was designated as part of the CANAMEX Corridor that links Canada to Mexico and the United States, including the major cities of Salt Lake City, Las Vegas, Los Angeles, and San Diego which lie on Interstate 15. In 1999, the highway was renamed the First Special Service Force Memorial Highway in honour of elite soldiers who travelled to Helena, Montana for training before World War II. Between Lethbridge and Highway 61 near Stirling, Highway 4 is signed as part of the Red Coat Trail, a historic route stretching from southern Alberta into Manitoba that is advertised as that which approximates the path travelled by the North-West Mounted Police on their quest to the prairies.

Diamond City is a hamlet in southern Alberta, Canada within the Lethbridge County. It is located on Highway 25, approximately 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) north of Lethbridge. The community was so named on account of deposits of coal near the original town site, a resource also called "black diamond".

Coleman is an urban community in the Rocky Mountains within the Municipality of Crowsnest Pass in southwest Alberta, Canada. It was formerly incorporated as a town prior to 1979 when it amalgamated with four other municipalities to form Crowsnest Pass.

Lethbridge County is a municipal district in southern Alberta. It is in Census Division No. 2 and part of the Lethbridge census agglomeration. It was known as the County of Lethbridge prior to December 4, 2013. Its name was changed in time for 2014 to coincide with its 50th anniversary.

The modern history of Lethbridge extends to the mid-19th century, when the area was developed from drift mines opened by Nicholas Sheran in 1874, and the North Western Coal and Navigation Company in 1882. Prior to the development of drift mines in the area, Lethbridge, Alberta was known as Coal Banks, and was part of the territory of the Blackfoot Confederacy. The Confederacy was made up of the Kainai Nation, the Northern Peigan, the Southern Peigan (Blackfeet), and the Siksika Nation.
The North Western Coal and Navigation Company, also known as Alberta Railway and Coal Company or Alberta Railway and Irrigation Company, was a coal mining company formed in London, England in 1882 by Sir Alexander Tilloch Galt, one of Canada's Fathers of Confederation. As part of his vision for Canada, Galt was committed to finding industries that would bring settlers to the District of Alberta of the Northwest Territories. The company was founded to create a coal mining industry that could bring settlers to the Northwest Territories. It was based in Lethbridge, Alberta, with his son Elliott Torrance Galt, managing day-to-day operations. The company's superintendent was William Stafford. Money for this company came from a consortium of investors from Canada, England, and the United States.

The Oldman River valley parks system is a continuous collection of eight urban parks in the Oldman River valley of Lethbridge, Alberta, 100 metres (330 ft) below the prairie level. The parks were created in the 1980s as part of the city's Urban Parks Project. Today they are a combined 16 square kilometres (6.2 sq mi) in size and comprise one of the largest urban park systems in North America, and the third largest in Canada.
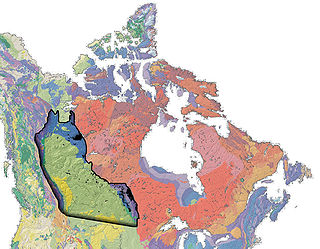
The Western Canada Sedimentary Basin (WCSB) is a vast sedimentary basin underlying 1,400,000 square kilometres (540,000 sq mi) of Western Canada including southwestern Manitoba, southern Saskatchewan, Alberta, northeastern British Columbia and the southwest corner of the Northwest Territories. It consists of a massive wedge of sedimentary rock extending from the Rocky Mountains in the west to the Canadian Shield in the east. This wedge is about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) thick under the Rocky Mountains, but thins to zero at its eastern margins. The WCSB contains one of the world's largest reserves of petroleum and natural gas and supplies much of the North American market, producing more than 16,000,000,000 cubic feet (450,000,000 m3) per day of gas in 2000. It also has huge reserves of coal. Of the provinces and territories within the WCSB, Alberta has most of the oil and gas reserves and almost all of the oil sands.

The Coat of arms of Lethbridge is an official symbol of the city of Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada. It was designed by Reverend John Stanley Chivers and adopted on September 16, 1907.
Coal Banks Trail is a 30-kilometre multipurpose recreational path in Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada. It connects all of the city's major urban parks, all three geographical areas, and many smaller parks. While primarily a community recreation opportunity, the trail is also used for community events, such as the Terry Fox Run and the Moonlight Run.

The Red Coat Trail is a 1,300-kilometre (810 mi) route that approximates the path taken in 1874 by the North-West Mounted Police in their quest to bring law and order to the Canadian West.

Blood 148 is a First Nations reserve in Alberta, Canada. It is inhabited by the Blood (Kainai) First Nation and was established under the provisions of Treaty 7. This reserve is managed from the town of Stand Off on its northwest border and encompasses the majority of lands bounded by the cities of Fort MacLeod, Lethbridge and Cardston. It is traversed by Alberta Highway 2, Highway 5 and Highway 509. The St Mary River and the Belly River are major rivers supplying and draining the lands.

Fairview is a hamlet in southern Alberta, Canada, within Lethbridge County. It is adjacent to the eastern boundary of Lethbridge, approximately 0.3 kilometres (0.19 mi) south of Highway 3. More specifically, it is located on southeast corner of Highway 4 and Highway 512.
The Paul First Nation, more commonly known as the Paul Band, is a First Nations band government based in Wabamun, Alberta of mixed Cree and Nakoda (Stoney) origin. They are party to Treaty Six and had the Buck Lake Indian Reserve 133C and Wabamun Lake Indian Reserve 133A, 133B and 133C allocated to them by the federal government in 1892. However the Buck Lake Reserve was decimated by the Spanish Flu of 1918 and is now largely abandoned.

Hardieville is a residential neighbourhood in the northwest quadrant of Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada. It is located north of Scenic Drive North and west of 13 Street North. It borders Legacy Ridge and Uplands to the southeast.

Commerce is a former village in southern Alberta, Canada within Lethbridge County. It was located within township 9, range 22, west of the fourth meridian, northwest of the City of Lethbridge between the Village of Nobleford and the Town of Picture Butte. It was known as the Village of Coalgate from 1912 to 1913.













