
The European Union (EU) is a political and economic union of 27 member states that are located primarily in Europe. Its members have a combined area of 4,233,255.3 km2 (1,634,469.0 sq mi) and an estimated total population of about 447 million. The EU has developed an internal single market through a standardised system of laws that apply in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where members have agreed to act as one. EU policies aim to ensure the free movement of people, goods, services and capital within the internal market, enact legislation in justice and home affairs and maintain common policies on trade, agriculture, fisheries and regional development. For travel within the Schengen Area, passport controls have been abolished. A monetary union was established in 1999, coming into full force in 2002, and is composed of 19 EU member states which use the euro currency. The EU has often been described as a sui generis political entity.

The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers and domestically usually referred to simply as the Lords, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is granted by appointment or else by heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster.

The House of Commons, domestically often referred to simply as the Commons, is the lower house and de facto primary chamber of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the upper house, the House of Lords, it meets in the Palace of Westminster. Owing to shortage of space, its office accommodation extends into Portcullis House.

The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States and consists of two chambers: the House of Representatives and the Senate. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C. Both senators and representatives are chosen through direct election, though vacancies in the Senate may be filled by a governor appointment. Congress has 535 voting members: 435 representatives and 100 senators. In addition, the House of Representatives currently has six non-voting members, bringing the total membership of the US Congress to 541 or fewer in the case of vacancies.

The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, and approving any changes to the UN Charter. Its powers include establishing peacekeeping operations, enacting international sanctions, and authorizing military action. The UNSC is the only UN body with the authority to issue binding resolutions on member states.

The United Nations member states are the 193 sovereign states that are members of the United Nations (UN) and have equal representation in the UN General Assembly. The UN is the world's largest intergovernmental organization.
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative of the people who live in his/her constituency. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this category includes specifically members of the lower house, as upper houses often have a different title. Member of Congress is an equivalent term in other jurisdictions.

The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding contributions to the arts and sciences, work with charitable and welfare organisations, and public service outside the civil service. It was established on 4 June 1917 by King George V and comprises five classes across both civil and military divisions, the most senior two of which make the recipient either a knight if male or dame if female. There is also the related British Empire Medal, whose recipients are affiliated with, but not members of the order.

The Rajya Sabha or Council of States is the upper house of the bicameral Parliament of India. It currently has a maximum membership of 245, of which 233 are elected by the legislatures of the states and union territories using single transferable votes through Open Ballot while the President can appoint 12 members for their contributions to art, literature, science, and social services. Members sit for staggered terms lasting six years, with elections every year but almost a third of the 233 designates up for election every two years, specifically in even-numbered years. The Rajya Sabha meets in continuous sessions, and unlike the Lok Sabha, being the lower house of the Parliament, the Rajya Sabha, which is the upper house of Parliament, is not subjected to dissolution. However, the Rajya Sabha, like the Lok Sabha can be prorogued by the President.
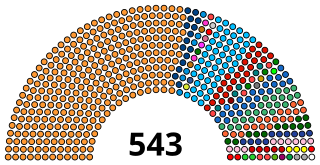
The Lok Sabha, or House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by adult universal suffrage and a first-past-the-post system to represent their respective constituencies, and they hold their seats for five years or until the body is dissolved by the President on the advice of the council of ministers. The house meets in the Lok Sabha Chambers of the Sansad Bhavan, New Delhi.
A subsidiary, subsidiary company or daughter company is a company that is owned or controlled by another company, which is called the parent company, parent, or holding company. The subsidiary can be a company, corporation, or limited liability company. In some cases it is a government or state-owned enterprise.

NCAA Division I (D-I) is the highest level of intercollegiate athletics sanctioned by the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) in the United States. D-I schools include the major collegiate athletic powers, with larger budgets, more elaborate facilities and more athletic scholarships than Divisions II and III as well as many smaller schools committed to the highest level of intercollegiate competition.
A Member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA) is a representative elected by the voters of an electoral district (constituency) to the legislature of State government in the Indian system of government. From each constituency, the people elect one representative who then becomes a member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA). Each state has between seven and nine MLAs for every Member of Parliament (MP) that it has in the Lok Sabha, the lower house of India's bicameral parliament. There are also members in three unicameral legislatures in Union Territories: the Delhi Legislative Assembly, Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly and Puducherry Legislative Assembly.
An independent or nonpartisan politician is a politician not affiliated with any political party. There are numerous reasons why someone may stand for office as an independent:

The European Union (EU) consists of 27 member states. Each member state is party to the founding treaties of the union and thereby shares in the privileges and obligations of membership. Unlike members of other international organisations, the member states of the EU have agreed by treaty to shared sovereignty through the institutions of the European Union in some aspects of government. Member states must agree unanimously for the EU to adopt some policies; for others, collective decision making is by qualified majority voting. Subsidiarity, meaning that decisions are taking collectively if and only if they cannot realistically be taken individually, is a founding principle of the EU.

The Hells Angels Motorcycle Club (HAMC) is a worldwide one-percenter motorcycle club whose members typically ride Harley-Davidson motorcycles.

The United States House of Representatives is the lower house of the United States Congress; the Senate is the upper house. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.

The Commonwealth of Nations, generally known simply as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 54 member states, nearly all former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental aspects, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations between member states.

The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and television program distributor. It is a nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educational television programming to public television stations in the United States, distributing series such as American Experience, America's Test Kitchen, Antiques Roadshow, Arthur, Barney & Friends, Clifford the Big Red Dog, Downton Abbey, Finding Your Roots, Frontline, The Magic School Bus, Masterpiece, Mister Rogers' Neighborhood, Nature, Nova, the PBS NewsHour, Reading Rainbow, Sesame Street, Teletubbies, Keeping up Appearances and This Old House.

The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development is an intergovernmental economic organisation with 37 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a forum of countries describing themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. Generally, OECD members are high-income economies with a very high Human Development Index (HDI) and are regarded as developed countries. As of 2017, the OECD member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of global nominal GDP and 42.8% of global GDP at purchasing power parity. The OECD is an official United Nations observer.















