Related Research Articles

A magnetic anomaly detector (MAD) is an instrument used to detect minute variations in the Earth's magnetic field. The term refers specifically to magnetometers used by military forces to detect submarines ; military MAD equipment is a descendant of geomagnetic survey or aeromagnetic survey instruments used to search for minerals by detecting their disturbance of the normal earth-field.

The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA) is an area where Earth's inner Van Allen radiation belt comes closest to Earth's surface, dipping down to an altitude of 200 kilometres (120 mi). This leads to an increased flux of energetic particles in this region and exposes orbiting satellites to higher-than-usual levels of ionizing radiation.

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of a mixture of molten iron and nickel in Earth's outer core: these convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo.

A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave.

Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With the exception of extremely rare native iron deposits, it is the most magnetic of all the naturally occurring minerals on Earth. Naturally magnetized pieces of magnetite, called lodestone, will attract small pieces of iron, which is how ancient peoples first discovered the property of magnetism.
A telluric current, or Earth current, is an electric current that flows underground or through the sea, resulting from natural and human-induced causes. These currents have extremely low frequency and traverse large areas near or at the Earth's surface. The Earth's crust and mantle are host to telluric currents, with around 32 mechanisms generating them, primarily geomagnetically induced currents caused by changes in the Earth's magnetic field due to solar wind interactions with the magnetosphere or solar radiation's effects on the ionosphere. These currents exhibit diurnal patterns, flowing towards the Sun during the day and towards the poles at night.

Paleomagnetism is the study of prehistoric Earth's magnetic fields recorded in rocks, sediment, or archeological materials. Geophysicists who specialize in paleomagnetism are called paleomagnetists.
The Brunhes–Matuyama reversal, named after Bernard Brunhes and Motonori Matuyama, was a geologic event, approximately 781,000 years ago, when the Earth's magnetic field last underwent reversal. Estimations vary as to the abruptness of the reversal. A 2004 paper estimated that it took over several thousand years; a 2010 paper estimated that it occurred more quickly, perhaps within a human lifetime; a 2019 paper estimated that the reversal lasted 22,000 years.

Rock magnetism is the study of the magnetic properties of rocks, sediments and soils. The field arose out of the need in paleomagnetism to understand how rocks record the Earth's magnetic field. This remanence is carried by minerals, particularly certain strongly magnetic minerals like magnetite. An understanding of remanence helps paleomagnetists to develop methods for measuring the ancient magnetic field and correct for effects like sediment compaction and metamorphism. Rock magnetic methods are used to get a more detailed picture of the source of the distinctive striped pattern in marine magnetic anomalies that provides important information on plate tectonics. They are also used to interpret terrestrial magnetic anomalies in magnetic surveys as well as the strong crustal magnetism on Mars.

Magnetoreception is a sense which allows an organism to detect the Earth's magnetic field. Animals with this sense include some arthropods, molluscs, and vertebrates. The sense is mainly used for orientation and navigation, but it may help some animals to form regional maps. Experiments on migratory birds provide evidence that they make use of a cryptochrome protein in the eye, relying on the quantum radical pair mechanism to perceive magnetic fields. This effect is extremely sensitive to weak magnetic fields, and readily disturbed by radio-frequency interference, unlike a conventional iron compass.
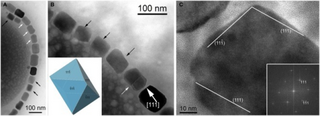
Magnetosomes are membranous structures present in magnetotactic bacteria (MTB). They contain iron-rich magnetic particles that are enclosed within a lipid bilayer membrane. Each magnetosome can often contain 15 to 20 magnetite crystals that form a chain which acts like a compass needle to orient magnetotactic bacteria in geomagnetic fields, thereby simplifying their search for their preferred microaerophilic environments. Recent research has shown that magnetosomes are invaginations of the inner membrane and not freestanding vesicles. Magnetite-bearing magnetosomes have also been found in eukaryotic magnetotactic algae, with each cell containing several thousand crystals.
A geomagnetic reversal is a change in a planet's dipole magnetic field such that the positions of magnetic north and magnetic south are interchanged. The Earth's magnetic field has alternated between periods of normal polarity, in which the predominant direction of the field was the same as the present direction, and reverse polarity, in which it was the opposite. These periods are called chrons.
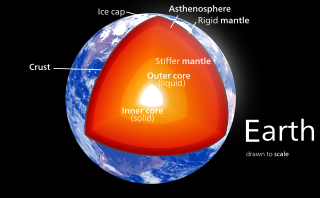
Earth's inner core is the innermost geologic layer of the planet Earth. It is primarily a solid ball with a radius of about 1,220 km (760 mi), which is about 20% of Earth’s radius or 70% of the Moon's radius.

In geophysics, a magnetic anomaly is a local variation in the Earth's magnetic field resulting from variations in the chemistry or magnetism of the rocks. Mapping of variation over an area is valuable in detecting structures obscured by overlying material. The magnetic variation in successive bands of ocean floor parallel with mid-ocean ridges was important evidence for seafloor spreading, a concept central to the theory of plate tectonics.

Magnetofossils are the fossil remains of magnetic particles produced by magnetotactic bacteria (magnetobacteria) and preserved in the geologic record. The oldest definitive magnetofossils formed of the mineral magnetite come from the Cretaceous chalk beds of southern England, while magnetofossil reports, not considered to be robust, extend on Earth to the 1.9-billion-year-old Gunflint Chert; they may include the four-billion-year-old Martian meteorite ALH84001.

The Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis, also known as the Morley–Vine–Matthews hypothesis, was the first key scientific test of the seafloor spreading theory of continental drift and plate tectonics. Its key impact was that it allowed the rates of plate motions at mid-ocean ridges to be computed. It states that the Earth's oceanic crust acts as a recorder of reversals in the geomagnetic field direction as seafloor spreading takes place.
In geophysics, a geomagnetic jerk or secular geomagnetic variation impulse is a relatively sudden change in the second derivative of the Earth's magnetic field with respect to time.
Geomagnetic secular variation refers to changes in the Earth's magnetic field on time scales of about a year or more. These changes mostly reflect changes in the Earth's interior, while more rapid changes mostly originate in the ionosphere or magnetosphere.
The Laschamp or Laschamps event[note 1] was a geomagnetic excursion. It occurred between 42,200 and 41,500 years ago, during the end of the Last Glacial Period. It was discovered from geomagnetic anomalies found in the Laschamps and Olby lava flows near Clermont-Ferrand, France in the 1960s.
The World Digital Magnetic Anomaly Map (WDMAM) was first made available by the Commission for the Geological Map of the World in 2007. Compiled with data from governments and institutes, the project was coordinated by the International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy, and was presented by Mike Purucker of NASA and Colin Reeves of the Netherlands. As of 2007, it was considered to be "the first truly global compilation of lithospheric magnetic field observations." and further improvements dated to 2009 relate to the full spectrum magnetic anomaly grid of the United States and also data of global marine magnetic anomaly.
References
Citations
Works cited
- Geggel, Laura (December 20, 2023). "Iron oxide baked into Mesopotamian bricks confirms ancient magnetic field anomaly". Live Science. Retrieved 2023-12-29.
- Rivera, P.; Pavón-Carrasco, F. J.; Osete, M. L. (2023). "Modeling geomagnetic spikes: the Levantine Iron Age anomaly". Earth Planets Space. 75 (133): 133. Bibcode:2023EP&S...75..133R. doi: 10.1186/s40623-023-01880-x .
Other sources
- Béguin, Annemarieke; Filippidi, Amalia; de Lange, Gert J.; de Groot, Lennart V. (2019). "The evolution of the Levantine Iron Age geomagnetic Anomaly captured in Mediterranean sediments". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 511: 55–66. Bibcode:2019E&PSL.511...55B. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2019.01.021. ISSN 0012-821X. S2CID 134503411.
- Guesgen, Mirjam (December 18, 2023). "Ancient Inscribed Bricks Contain Evidence of Mysterious Magnetic 'Anomaly,' Scientists Find". Vice. Retrieved 2023-12-29.
- Ralls, Eric (December 18, 2023). "Mesopotamian bricks reveal anomaly in Earth's magnetic field 3,000 years ago". Earth.com. Retrieved 2023-12-29.
- Tema, E.; Di Chiara, A.; Herrero-Bervera, E., eds. (2020). Geomagnetic Field Variations in the Past: New Data, Applications and Recent Advances. United Kingdom: Geological Society. ISBN 978-1786204738.