Related Research Articles
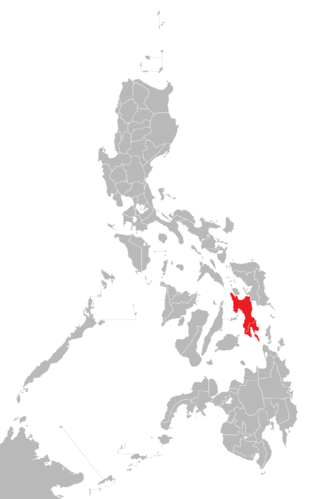
Leyte is an island in the Visayas group of islands in the Philippines. It is eighth-largest and sixth-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total population of 2,626,970 as of 2020 census.

Leyte, officially the Province of Leyte, is a province in the Philippines located in the Eastern Visayas region, occupying the northern three-quarters of Leyte Island. Its capital is the city of Tacloban, administered independently from the province. Leyte is situated west of Samar Island, north of Southern Leyte and south of Biliran. To the west across the Camotes Sea is the province of Cebu.

Southern Leyte, officially the Province of Southern Leyte, is a province in the Philippines located in the Eastern Visayas region. Its capital is the city of Maasin. Southern Leyte comprised the third congressional district Leyte until it was made into an independent province in 1959. Southern Leyte includes Limasawa, an island to the south where the first Roman Catholic Mass in Philippine soil is believed to have taken place and thus considered to be the birthplace of Roman Catholicism in the Philippines.

Samar, officially the Province of Samar, formerly named Western Samar, is a province in the Philippines located in the Eastern Visayas region. Its capital is the city of Catbalogan. It is bordered by Northern Samar, Eastern Samar, Leyte and Leyte Gulf, and includes several islands in the Samar Sea. Samar is connected to the island of Leyte via the San Juanico Bridge.

Ormoc, officially the City of Ormoc, is a 1st class independent component city in the Eastern Visayas region of the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 230,998 inhabitants, making it the second most-populous city in the province of Leyte after the provincial capital of Tacloban. Ormoc is the economic, cultural, commercial and transportation hub of western Leyte.

Tacloban, officially the City of Tacloban, is highly urbanized city in the Eastern Visayas region of the Philippines. The city is autonomous from the province of Leyte, although it serves as its provincial capital. According to the 2020 census, Tacloban has a population of 251,881, making it the most populous city in the Eastern Visayas. The city is located 360 miles (580 km) southeast from Manila.

Baybay, officially the City of Baybay, is a 1st class component city in the province of Leyte, Philippines. It has a population of 111,848 people.

Carigara, officially the Municipality of Carigara, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Leyte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 54,656 people.

Palo, officially the Municipality of Palo, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Leyte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 76,213 people, making it the most populous municipality (non-city) in the province.

Tanauan, officially the Municipality of Tanauan, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Leyte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 57,455 people.

The Waray people are a subgroup of the larger ethnolinguistic group Bisaya people, who constitute the 4th largest Filipino ethnolinguistic group in the Philippines. Their primary language is the Waray language, an Austronesian language native to the islands of Samar, Leyte and Biliran, which together comprise the Eastern Visayas Region of the Philippines. Waray people inhabit most of Samar where they are called Samareños/Samarnons, the northern part of the island of Leyte where they are called Leyteños, and the island of Biliran. In Leyte island, the Waray-speaking people are separated from the Cebuano-speaking Leyteños by the island's mountain range at the middle.
Ballet Philippines (BP) is a ballet company in the Philippines founded in 1969 by Alice Reyes with the support of Eddie Elejar and the Cultural Center of the Philippines. Proficient in both ballet and modern dance, the company synthesizes diverse dance and movement forms into distinctively Filipino contemporary expressions. These include classical ballet, avant-garde choreography, traditional and modern dance, martial arts, and aerial movements.

Daniel Z. Romualdez Airport, also known as Tacloban City Airport, is a regional airport serving the general area of Tacloban, a highly urbanized city in the Leyte island of the Philippines. It is the main gateway from Manila and Cebu to Eastern Visayas. It is classified as a Class 1 principal airport by the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines. In 2022, Daniel Z. Romualdez Airport served 1.48 million passengers, making it the seventh-busiest in the country.

Aliwan Fiesta is an annual event that gathers different cultural festivals of the Philippines in Star City Complex in Pasay wherein contingents compete in dance parade and float competitions. Organized by Manila Broadcasting Company (MBC) together with Cultural Center of the Philippines (CCP) and the cities of Manila and Pasay, the event is dubbed as "the Philippines' Grandest Fiesta," with prizes totaling P3 million. Aliwan Fiesta, which began in 2003, aims to showcase the different Filipino cultures and heritage not only to the people in Metro Manila but also to the rest of the world. The contingents, meanwhile, aim to promote their respective regions both economically and tourism-wise. It was originally organized as a visual extravaganza for the Christmas season, but it has since been held during the summer months of either April or May. Aliwan is a Tagalog word for "entertainment" or "amusement." Aliwan Fiesta festivities are covered live on DZRH News Television annually.
The Hiyas ng Maynilad Dance Troupe is the official and premiere cultural dance company of the Pamantasan ng Lungsod ng Maynila. The company, consisting of student-performers under the umbrella PLM President's Committee on Arts and Culture, made its debut performance during the University's anniversary celebration in 1982. Since then, it has presented dances in costumes that reflect the traditional culture of the Philippines. Together with the PLM Rondalla, the company has also appeared as the Hiyas ng Maynilad and Cultural Group.
Tacloban, Philippines, has a variety of public and private educational institutions. Foremost of these are the University of the Philippines in the Visayas - Tacloban College, Eastern Visayas State University, the Leyte Progressive High School, a provincial branch of the Technical Education and Skills Development Authority, the Leyte Normal University, the Liceo del Verbo Divino formerly known as the Divine Word University of Tacloban and the St. Therese Educational Foundation of Tacloban, Inc. otherwise known as STEFTI.

Pope Francis made a pastoral and state visit to the Philippines from January 15 to 19, 2015. He was the third pontiff to visit the Philippines after Paul VI in 1970 and John Paul II in 1981 and 1995, and officially the first papal visit in the 21st century and 3rd millennium after the title was originally scheduled for World Meeting of Families in 2003 but postponed due to John Paul II was unable to attend because of the progression of his Parkinson's disease. Besides Manila, Francis visited Tacloban and Palo, Leyte, to encourage the victims of Typhoon Haiyan (Yolanda) and Typhoon Hagupit (Ruby). The Filipinos nicknamed Francis Lolo Kiko as a term of endearment, which he commended. Around 6–7 million attended Francis' final Papal Mass at Luneta, surpassing the crowd at World Youth Day 1995 in the same venue and making it the largest papal crowd in history. The theme of Francis' 2015 visit was "Mercy and Compassion".
Waray is an Austronesian language and the fifth-most-spoken native regional language of the Philippines, native to Eastern Visayas. It is the native language of the Waray people and second language of the Abaknon people of Capul, Northern Samar, and some Cebuano-speaking peoples of western and southern parts of Leyte island. It is the third most spoken language among the Bisayan languages, only behind Cebuano and Hiligaynon.

Eastern Visayas is an administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region VIII. It consists of three main islands, Samar, Leyte and Biliran. The region has six provinces, one independent city and one highly urbanized city namely, Biliran, Leyte, Northern Samar, Samar, Eastern Samar, Southern Leyte, Ormoc and Tacloban. The highly urbanized city of Tacloban is the sole regional center. These provinces and cities occupy the easternmost islands of the Visayas group of islands.

Louis Bulaong is a Filipino writer best known for his science fiction novels Escapist Dream and Otaku Girl.
References
- ↑ "Leyte Kalipayan Dance Company PDO". Spring Rain Global Consultancy. Retrieved 2023-11-05.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "A Brief History". Leyte Kalipayan Dance Company. Archived from the original on February 17, 2006. Retrieved 27 June 2018.
- 1 2 "Leyte Kalipayan Dance Troupe". artseducation.culturalcenter.gov.ph. Cultural Center of the Philippines.
- 1 2 "Leyte Kalipayan Dance Company". festivalvitosha.com. 2020-07-09. Retrieved 2023-11-05.
- ↑ "Leyte dance troupe wows audiences in Switzerland". GMA News Online. 2009-09-10. Retrieved 2024-01-10.