
A sport utility vehicle (SUV) is a car classification that combines elements of road-going passenger cars with features from off-road vehicles, such as raised ground clearance and four-wheel drive.

An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion. The vehicle can be powered by a collector system, with electricity from extravehicular sources, or can be powered autonomously by a battery or by converting fuel to electricity using a generator or fuel cells. EVs include road and rail vehicles, electric boats and underwater vessels, electric aircraft and electric spacecraft.

Since the start of the twentieth century, the role of cars has become highly important, though controversial. They are used throughout the world and have become the most popular mode of transport in many of the more developed countries. In developing countries cars are fewer and the effects of the car on society are less visible, however they are nonetheless significant. The spread of cars built upon earlier changes in transport brought by railways and bicycles. They introduced sweeping changes in employment patterns, social interactions, infrastructure and the distribution of goods.

The hydrogen economy is an umbrella term for the roles hydrogen can play alongside low-carbon electricity to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases. The aim is to reduce emissions where cheaper and more energy-efficient clean solutions are not available. In this context, hydrogen economy encompasses the production of hydrogen and the use of hydrogen in ways that contribute to phasing-out fossil fuels and limiting climate change.

Sustainable transport refers to ways of transportation that are sustainable in terms of their social and environmental impacts. Components for evaluating sustainability include the particular vehicles used for road, water or air transport; the source of energy; and the infrastructure used to accommodate the transport. Transport operations and logistics as well as transit-oriented development are also involved in evaluation. Transportation sustainability is largely being measured by transportation system effectiveness and efficiency as well as the environmental and climate impacts of the system. Transport systems have significant impacts on the environment, accounting for between 20% and 25% of world energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions. The majority of the emissions, almost 97%, came from direct burning of fossil fuels. In 2019, about 95% of the fuel came from fossil sources. The main source of greenhouse gas emissions in the European Union is transportation. In 2019 it contributes to about 31% of global emissions and 24% of emissions in the EU. In addition, up to the COVID-19 pandemic, emissions have only increased in this one sector. Greenhouse gas emissions from transport are increasing at a faster rate than any other energy using sector. Road transport is also a major contributor to local air pollution and smog.

Scrap consists of recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap has monetary value, especially recovered metals, and non-metallic materials are also recovered for recycling. Once collected, the materials are sorted into types — typically metal scrap will be crushed, shredded, and sorted using mechanical processes.

A green vehicle, clean vehicle, eco-friendly vehicle or environmentally friendly vehicle is a road motor vehicle that produces less harmful impacts to the environment than comparable conventional internal combustion engine vehicles running on gasoline or diesel, or one that uses certain alternative fuels. Presently, in some countries the term is used for any vehicle complying or surpassing the more stringent European emission standards, or California's zero-emissions vehicle standards, or the low-carbon fuel standards enacted in several countries.
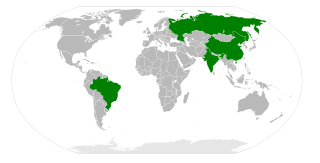
BRIC is a term describing the foreign investment strategies grouping acronym that stands for Brazil, Russia, India, and China. The separate BRICS organisation would go on to become a political and economic organization largely based on such grouping.

Lester Russel Brown is an American environmental analyst, founder of the Worldwatch Institute, and founder and former president of the Earth Policy Institute, a nonprofit research organization based in Washington, D.C. BBC Radio commentator Peter Day referred to him as "one of the great pioneer environmentalists."
Sustainable urban infrastructure expands on the concept of urban infrastructure by adding the sustainability element with the expectation of improved and more resilient urban development. In the construction and physical and organizational structures that enable cities to function, sustainability also aims to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising the capabilities of the future generations.
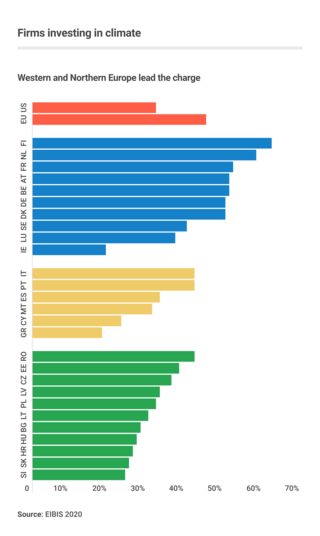
Business action on climate change is a topic which since 2000 includes a range of activities relating to climate change, and to influencing political decisions on climate change-related regulation, such as the Kyoto Protocol. Major multinationals have played and to some extent continue to play a significant role in the politics of climate change, especially in the United States, through lobbying of government and funding of climate change deniers. Business also plays a key role in the mitigation of climate change, through decisions to invest in researching and implementing new energy technologies and energy efficiency measures.

A sustainable city, eco-city, or green city is a city designed with consideration for social, economic, environmental impact, and resilient habitat for existing populations, without compromising the ability of future generations to experience the same. The UN Sustainable Development Goal 11 defines sustainable cities as those that are dedicated to achieving green sustainability, social sustainability and economic sustainability. They are committed to doing so by enabling opportunities for all through a design focused on inclusivity as well as maintaining a sustainable economic growth. The focus will also includes minimizing required inputs of energy, water, and food, and drastically reducing waste, output of heat, air pollution – CO2, methane, and water pollution. Richard Register, a visual artist, first coined the term ecocity in his 1987 book Ecocity Berkeley: Building Cities for a Healthy Future, where he offers innovative city planning solutions that would work anywhere. Other leading figures who envisioned sustainable cities are architect Paul F Downton, who later founded the company Ecopolis Pty Ltd, as well as authors Timothy Beatley and Steffen Lehmann, who have written extensively on the subject. The field of industrial ecology is sometimes used in planning these cities.
The 2000-watt society concept, introduced in 1998 by the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, aims to reduce the average primary energy use of First World citizens to no more than 2,000 watts by 2050, without compromising their standard of living.

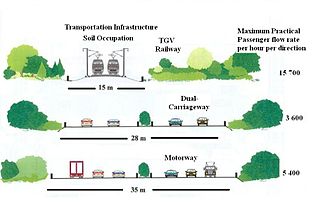
Land transport is the transport or movement of people, animals or goods from one location to another location on land. This is in contrast with other main types of transport such as maritime transport and aviation. The two main forms of land transport can be considered to be rail transport and road transport.

A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people over cargo.
DESERTEC is a non-profit foundation that focuses on the production of renewable energy in desert regions The project aims to create a global renewable energy plan based on the concept of harnessing sustainable powers, from sites where renewable sources of energy are more abundant, and transferring it through high-voltage direct current transmission to consumption centers. The foundation also works on concepts involving green hydrogen. Multiple types of renewable energy sources are envisioned, but their plan is centered around the natural climate of the deserts.
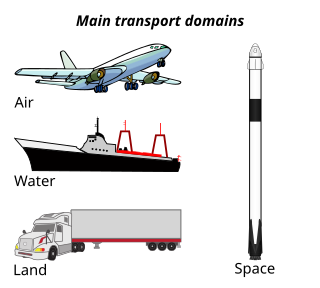
Transport or transportation is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land, water, cable, pipelines, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations. Transport enables human trade, which is essential for the development of civilizations.

The United States is the second-largest single consumer of energy in the world. The U.S. Department of Energy categorizes national energy use in four broad sectors: transportation, residential, commercial, and industrial. Energy usage in transportation and residential sectors is largely controlled by individual domestic consumers. Commercial and industrial energy expenditures are determined by businesses entities and other facility managers. National energy policy has a significant effect on energy usage across all four sectors.

Green urbanism has been defined as the practice of creating communities beneficial to humans and the environment. According to Timothy Beatley, it is an attempt to shape more sustainable places, communities and lifestyles, and consume less of the world's resources. Urban areas are able to lay the groundwork of how environmentally integrated and sustainable city planning can both provide and improve environmental benefits on the local, national, and international levels. Green urbanism is interdisciplinary, combining the collaboration of landscape architects, engineers, urban planners, ecologists, transport planners, physicists, psychologists, sociologists, economists and other specialists in addition to architects and urban designers.

The European Green Deal, approved in 2020, is a set of policy initiatives by the European Commission with the overarching aim of making the European Union (EU) climate neutral in 2050. The plan is to review each existing law on its climate merits, and also introduce new legislation on the circular economy (CE), building renovation, biodiversity, farming and innovation.

















