Medieval music encompasses the sacred and secular music of Western Europe during the Middle Ages, from approximately the 6th to 15th centuries. It is the first and longest major era of Western classical music and is followed by the Renaissance music; the two eras comprise what musicologists generally term as early music, preceding the common practice period. Following the traditional division of the Middle Ages, medieval music can be divided into Early (500–1000), High (1000–1300), and Late (1300–1400) medieval music.

Musical notation is any system used to visually represent auditorily perceived music, played with instruments or sung by the human voice through the use of symbols, including notation for durations of absence of sound such as rests. For this reason, the act of deciphering or reading a piece using musical notation, is known as "reading music".

Gregorian chant is the central tradition of Western plainchant, a form of monophonic, unaccompanied sacred song in Latin of the Roman Catholic Church. Gregorian chant developed mainly in western and central Europe during the 9th and 10th centuries, with later additions and redactions. Although popular legend credits Pope Gregory I with inventing Gregorian chant, scholars believe that it arose from a later Carolingian synthesis of the Old Roman chant and Gallican chant.
Organum is, in general, a plainchant melody with at least one added voice to enhance the harmony, developed in the Middle Ages. Depending on the mode and form of the chant, a supporting bass line may be sung on the same text, the melody may be followed in parallel motion, or a combination of both of these techniques may be employed. As no real independent second voice exists, this is a form of heterophony. In its earliest stages, organum involved two musical voices: a Gregorian chant melody, and the same melody transposed by a consonant interval, usually a perfect fifth or fourth. In these cases the composition often began and ended on a unison, the added voice keeping to the initial tone until the first part has reached a fifth or fourth, from where both voices proceeded in parallel harmony, with the reverse process at the end. Organum was originally improvised; while one singer performed a notated melody, another singer—singing "by ear"—provided the unnotated second melody. Over time, composers began to write added parts that were not just simple transpositions, thus creating true polyphony.

Ars antiqua, also called ars veterum or ars vetus, is a term used by modern scholars to refer to the Medieval music of Europe during the High Middle Ages, between approximately 1170 and 1310. This covers the period of the Notre-Dame school of polyphony, and the subsequent years which saw the early development of the motet, a highly varied choral musical composition. Usually the term ars antiqua is restricted to sacred (church) or polyphonic music, excluding the secular (non-religious) monophonic songs of the troubadours, and trouvères. Although colloquially the term ars antiqua is used more loosely to mean all European music of the 13th century, and from slightly before.

The conductus was a sacred Latin song in the Middle Ages, one whose poetry and music were newly composed. It is non-liturgical since its Latin lyric borrows little from previous chants. The conductus was northern French equivalent of the versus, which flourished in Aquitaine. It was originally found in the twelfth-century Aquitanian repertories. But major collections of conducti were preserved in Paris. The conductus typically includes one, two, or three voices. A small number of the conducti are for four voices. Stylistically, the conductus is a type of discant. Its form can be strophic or through-composed form. The genre flourished from the early twelfth century to the middle of thirteenth century. It was one of the principal types of vocal composition of the ars antiqua period of medieval music history.

A neume is the basic element of Western and Eastern systems of musical notation prior to the invention of five-line staff notation.
Franco of Cologne was a German music theorist and possibly a composer. He was one of the most influential theorists of the Late Middle Ages, and was the first to propose an idea which was to transform musical notation permanently: that the duration of any note should be determined by its appearance on the page, and not from context alone. The result was Franconian notation, described most famously in his Ars cantus mensurabilis.
Johannes de Garlandia was a French music theorist of the late ars antiqua period of medieval music. He is known for his work on the first treatise to explore the practice of musical notation of rhythm, De Mensurabili Musica.

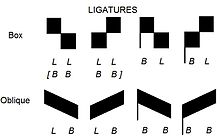
In medieval music, the rhythmic modes were set patterns of long and short durations. The value of each note is not determined by the form of the written note, but rather by its position within a group of notes written as a single figure called a ligature, and by the position of the ligature relative to other ligatures. Modal notation was developed by the composers of the Notre Dame school from 1170 to 1250, replacing the even and unmeasured rhythm of early polyphony and plainchant with patterns based on the metric feet of classical poetry, and was the first step towards the development of modern mensural notation. The rhythmic modes of Notre Dame Polyphony were the first coherent system of rhythmic notation developed in Western music since antiquity.

In music notation, a note value indicates the relative duration of a note, using the texture or shape of the notehead, the presence or absence of a stem, and the presence or absence of flags/beams/hooks/tails. Unmodified note values are fractional powers of two, for example one, one-half, one fourth, etc.
Petrus de Cruce was active as a cleric, composer and music theorist in the late part of the 13th century. His main contribution was to the notational system.

Mensural notation is the musical notation system used for polyphonic European vocal music from the late 13th century until the early 17th century. The term "mensural" refers to the ability of this system to describe precisely measured rhythmic durations in terms of numerical proportions between note values. Its modern name is inspired by the terminology of medieval theorists, who used terms like musica mensurata or cantus mensurabilis to refer to the rhythmically defined polyphonic music of their age, as opposed to musica plana or musica choralis, i.e., Gregorian plainchant. Mensural notation was employed principally for compositions in the tradition of vocal polyphony, whereas plainchant retained its own, older system of neume notation throughout the period. Besides these, some purely instrumental music could be written in various forms of instrument-specific tablature notation.
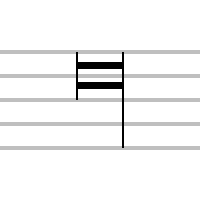
A longa, long, quadruple note (Am.), or quadruple whole note is a musical note that could be either twice or three times as long as a breve, four or six times as long as a semibreve, that appears in early music. The number of breves in a long was determined by the "modus" or "mode" of a passage. Sections in perfect mode used three breves to the long while sections in imperfect mode used two breves to the long. Imperfect longs, worth two breves, existed in perfect mode from the earliest sources, while the fourteenth century saw the introduction of perfect longs, worth three breves, in imperfect mode through the use of dots of addition.

In music, a notehead is the part of a note, usually elliptical in shape, whose placement on the staff indicates the pitch, to which modifications are made that indicate duration. Noteheads may be the same shape but colored completely black or white, indicating the note value. In a whole note, the notehead, shaped differently than shorter notes, is the only component of the note. Shorter note values attach a stem to the notehead, and possibly beams or flags. The longer double whole note can be written with vertical lines surrounding it, two attached noteheads, or a rectangular notehead. An "x" shaped notehead may be used to indicate percussion, percussive effects, or speaking. A square, diamond, or box shaped notehead may be used to indicate a natural or artificial harmonic. A small notehead can be used to indicate a grace note.
A tonary is a liturgical book in the Western Christian Church which lists by incipit various items of Gregorian chant according to the Gregorian mode (tonus) of their melodies within the eight-mode system. Tonaries often include Office antiphons, the mode of which determines the recitation formula for the accompanying text, but a tonary may also or instead list responsories or Mass chants not associated with formulaic recitation. Although some tonaries are stand-alone works, they were frequently used as an appendix to other liturgical books such as antiphonaries, graduals, tropers, and prosers, and are often included in collections of musical treatises.
With regard to early polyphony the term copula has a variety of meanings. At its most basic level, it can be thought of as the linking of notes together to form a melody. "A copula is a rapid, connected discant..." However, it is often considered to be a particular type of polyphonic texture similar to organum, but with modal rhythm. The music theorist Johannes de Garlandia favoured this description of copula. The term refers to music where the lower voice sings long, sustained notes while the higher voices sing faster-moving harmony lines. This style is typical of what is referred to as Notre Dame Polyphony; examples of which can be found in the Magnus Liber Organi. Copula might have implied a strophic construction with much repetition in the various parts, which was characteristic of much of the music written in this idiom. The upper part consists of "antecedent-consequent" phrases, themselves featuring much melodic repetition. The rhythm is notated in copula, unlike in organum. It is, in essence, the "coming together" of these two parts at the cadence that led to the term copula being used, from the Latin meaning "that binds."
In medieval music theory, the Latin term modus can be used in a variety of distinct senses. The most commonly used meaning today relates to the organisation of pitch in scales. Other meanings refer to the notation of rhythms.
De Mensurabili Musica is a musical treatise from the early 13th century and is the first of two treatises traditionally attributed to French music theorist Johannes de Garlandia; the other is de plana musica. De Mensurabili Musica was the first to explain a modal rhythmic system that was already in use at the time: the rhythmic modes. The six rhythmic modes set out by the treatise are all in triple time and are made from combinations of the note values longa (long) and brevis (short) and are given the names trochee, iamb, dactyl, anapest, spondaic and tribrach, although trochee, dactyl and spondaic were much more common. It is evident how influential Garlandia's treatise has been by the number of theorists that have used its ideas. Much of the surviving music of the Notre Dame School from the 13th century is based on the rhythmic modes set out in De Mensurabili Musica.

Ars cantus mensurabilis is a music theory treatise from the mid-13th century, c. 1250–1280 written by German music theorist Franco of Cologne. The treatise was written shortly after De Mensurabili Musica, a treatise by Johannes de Garlandia, which summarised a set of six rhythmic modes in use at the time. In music written in rhythmic modes, the duration of a note could be determined only in context. Ars cantus mensurabilis was the first treatise to suggest that individual notes could have their own durations independent of context. This new rhythmic system was the foundation for the mensural notation system and the ars nova style.