
Music notation or musical notation is any system used to visually represent aurally perceived music played with instruments or sung by the human voice through the use of written, printed, or otherwise-produced symbols, including notation for durations of absence of sound such as rests.
In music, an accidental is a note of a pitch that is not a member of the scale or mode indicated by the most recently applied key signature. In musical notation, the flat, natural and sharp symbols, among others, mark such notes—and those symbols are also called accidentals. In some kinds of musical style, there are also the half sharp as well as half flat, sometimes also called quarter tone.
In Western musical notation, the staff or stave (UK) is a set of five horizontal lines and four spaces that each represent a different musical pitch or in the case of a percussion staff, different percussion instruments. Appropriate music symbols, depending on the intended effect, are placed on the staff according to their corresponding pitch or function. Musical notes are placed by pitch, percussion notes are placed by instrument, and rests and other symbols are placed by convention.

A quarter note (American) or crotchet (British) is a musical note played for one quarter of the duration of a whole note. Quarter notes are notated with a filled-in oval note head and a straight, flagless stem. The stem usually points upwards if it is below the middle line of the staff, and downwards if it is on or above the middle line. An upward stem is placed on the right side of the notehead, a downward stem is placed on the left. The Unicode symbol is U+2669.

In music, a half note (American) or minim (British) is a note played for half the duration of a whole note and twice the duration of a quarter note. It was given its Latin name because it was the shortest of the five note values used in early medieval music notation. Half notes are notated with a hollow oval notehead like a whole note and straight note stem with no flags like a quarter note. The half rest denotes a silence of the same duration. Half rests are drawn as filled-in rectangles sitting on top of the middle line of the musical staff, although in polyphonic music the rest may need to be moved to a different line or even a ledger line. As with all notes with stems, half notes are drawn with upward stems on the right when they are below the middle line of the staff and downward stems on the left when they are on or above the middle line. In vocal music, notes on the middle line have a downward stem instead of an upward stem.

An eighth note (American) or a quaver (British) is a musical note played for one eighth the duration of a whole note (semibreve). Its length relative to other rhythmic values is as expected—e.g., half the duration of a quarter note (crotchet), one quarter the duration of a half note (minim), and twice the value of a sixteenth note. It is the equivalent of the fusa in mensural notation.

In music, a double whole note (American), breve, or double note lasts two times as long as a whole note. It is the second-longest note value still in use in modern music notation. The longest notated note is the longa, which could be double or triple the length of a breve, although its use is most commonly found in early music. The longest notated note is the maxima.

In music, a thirty-second note (American) or demisemiquaver (British) is a note played for 1⁄32 of the duration of a whole note. It lasts half as long as a sixteenth note and twice as long as a sixty-fourth.
In music notation, a sixty-fourth note, or hemidemisemiquaver or semidemisemiquaver (British), sometimes called a half-thirty-second note, is a note played for half the duration of a thirty-second note, hence the name. It first occurs in the late 17th century and, apart from rare occurrences of hundred twenty-eighth notes (semihemidemisemiquavers) and two hundred fifty-sixth notes (demisemihemidemisemiquavers), it is the shortest value found in musical notation.

In Western musical notation, a dotted note is a note with a small dot written after it. In modern practice, the first dot increases the duration of the basic note by half of its original value. This means that a dotted note is equivalent to writing the basic note tied to a note of half the value – for instance, a dotted half note is equivalent to a half note tied to a quarter note. Subsequent dots add progressively halved value, as shown in the example to the right.
A rest is the absence of a sound for a defined period of time in music, or one of the musical notation signs used to indicate that.
In music, an accent is an emphasis, stress, or stronger attack placed on a particular note or set of notes, or chord, either as a result of its context or specifically indicated by an accent mark. Accents contribute to the articulation and prosody of a performance of a musical phrase. Accents may be written into a score or part by a composer, or added by the performer as part of their interpretation of a musical piece.

Organ tablature is a form of musical notation used by the north German Baroque organ school, although there are also forms of organ tablature from other countries such as Italy, Spain, Poland, and England. Portions of Johann Sebastian Bach's Orgelbüchlein are written in tablature, as are a great deal of the surviving manuscripts of the organ works of Dieterich Buxtehude and other north German organ composers of the Baroque era.

Alla breve – also known as cut time or cut common time – is a musical meter notated by the time signature symbol , which is the equivalent of 2
2. The term is Italian for "on the breve", originally meaning that the beat was counted on the breve.

In music notation, a note value indicates the relative duration of a note, using the texture or shape of the notehead, the presence or absence of a stem, and the presence or absence of flags/beams/hooks/tails. Unmodified note values are fractional powers of two, for example one, one-half, one fourth, etc.

Mensural notation is the musical notation system used for polyphonic European vocal music from the late 13th century until the early 17th century. The term "mensural" refers to the ability of this system to describe precisely measured rhythmic durations in terms of numerical proportions between note values. Its modern name is inspired by the terminology of medieval theorists, who used terms like musica mensurata or cantus mensurabilis to refer to the rhythmically defined polyphonic music of their age, as opposed to musica plana or musica choralis, i.e., Gregorian plainchant. Mensural notation was employed principally for compositions in the tradition of vocal polyphony, whereas plainchant retained its own, older system of neume notation throughout the period. Besides these, some purely instrumental music could be written in various forms of instrument-specific tablature notation.
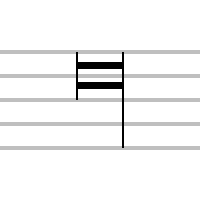
A longa, long, quadruple note (Am.), or quadruple whole note is a musical note that could be either twice or three times as long as a breve, four or six times as long as a semibreve, that appears in early music. The number of breves in a long was determined by the "modus" or "mode" of a passage. Sections in perfect mode used three breves to the long while sections in imperfect mode used two breves to the long. Imperfect longs, worth two breves, existed in perfect mode from the earliest sources, while the fourteenth century saw the introduction of perfect longs, worth three breves, in imperfect mode through the use of dots of addition.

In music, a 1/16, sixteenth note (American) or semiquaver (British) is a note played for half the duration of an eighth note (quaver), hence the names. It is the equivalent of the semifusa in mensural notation, first found in 15th-century notation.

A maxima, duplex longa, larga, or octuple whole note was a musical note used commonly in thirteenth and fourteenth century music and occasionally until the end of the sixteenth century. It was usually twice or, rarely, three times as long as a longa, four or six or nine times as long as a breve, and 8, 12, 18, or 27 times as long as a semibreve. Like the stem of the longa, the stem of the maxima generally pointed downwards except occasionally when it appeared on the bottom line or space. Before around 1430, the maxima was written with a solid, black body. Over the course of the fifteenth century, like most other note values, the head of the maxima became void.

![Comparison of duple note values ( = 2x, etc.)
.mw-parser-output .hlist dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul{margin:0;padding:0}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt,.mw-parser-output .hlist li{margin:0;display:inline}.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline,.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist.inline ul,.mw-parser-output .hlist dl dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist dl ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist dl ul,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist ol ul,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul dl,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul ol,.mw-parser-output .hlist ul ul{display:inline}.mw-parser-output .hlist .mw-empty-li{display:none}.mw-parser-output .hlist dt::after{content:": "}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li::after{content:" * ";font-weight:bold}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li:last-child::after{content:none}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dd:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dt:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dd:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dt:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dd:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dt:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li li:first-child::before{content:" (";font-weight:normal}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dd li:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt li:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dd:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li dt:last-child::after,.mw-parser-output .hlist li li:last-child::after{content:")";font-weight:normal}.mw-parser-output .hlist ol{counter-reset:listitem}.mw-parser-output .hlist ol>li{counter-increment:listitem}.mw-parser-output .hlist ol>li::before{content:" "counter(listitem)"\a0 "}.mw-parser-output .hlist dd ol>li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist dt ol>li:first-child::before,.mw-parser-output .hlist li ol>li:first-child::before{content:" ("counter(listitem)"\a0 "}
.mw-parser-output .navbar{display:inline;font-size:88%;font-weight:normal}.mw-parser-output .navbar-collapse{float:left;text-align:left}.mw-parser-output .navbar-boxtext{word-spacing:0}.mw-parser-output .navbar ul{display:inline-block;white-space:nowrap;line-height:inherit}.mw-parser-output .navbar-brackets::before{margin-right:-0.125em;content:"[ "}.mw-parser-output .navbar-brackets::after{margin-left:-0.125em;content:" ]"}.mw-parser-output .navbar li{word-spacing:-0.125em}.mw-parser-output .navbar a>span,.mw-parser-output .navbar a>abbr{text-decoration:inherit}.mw-parser-output .navbar-mini abbr{font-variant:small-caps;border-bottom:none;text-decoration:none;cursor:inherit}.mw-parser-output .navbar-ct-full{font-size:114%;margin:0 7em}.mw-parser-output .navbar-ct-mini{font-size:114%;margin:0 4em}
v
t
e Duple note values comparison.png](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0c/Duple_note_values_comparison.png/220px-Duple_note_values_comparison.png)
 = 2×
= 2×  , etc.)
, etc.) 












