
Voltage, electric potential difference, electric pressure or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points, which is defined as the work needed per unit of charge to move a test charge between the two points. In the International System of Units, the derived unit for voltage is named volt. In SI units, work per unit charge is expressed as joules per coulomb, where 1 volt = 1 joule per 1 coulomb. The old SI definition for volt used power and current; starting in 1990, the quantum Hall and Josephson effect were used, and recently (2019) fundamental physical constants have been introduced for the definition of all SI units and derived units. Voltage or electric potential difference is denoted symbolically by , simplified V, or U, for instance in the context of Ohm's or Kirchhoff's circuit laws.

Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. A common source of DC power is a battery cell in a flashlight. The abbreviations AC and DC are often used to mean simply alternating and direct, as when they modify current or voltage.
Mains electricity, also known by the American English terms utility power, power grid, domestic power, and wall power, or in some parts of Canada as hydro, is a general-purpose alternating-current (AC) electric power supply. It is the form of electrical power that is delivered to homes and businesses through the electric grid in many parts of the world. People use this electricity to power everyday items—such as domestic appliances, televisions and lamps—by plugging them into a wall outlet.

A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a result, power supplies are sometimes referred to as electric power converters. Some power supplies are separate standalone pieces of equipment, while others are built into the load appliances that they power. Examples of the latter include power supplies found in desktop computers and consumer electronics devices. Other functions that power supplies may perform include limiting the current drawn by the load to safe levels, shutting off the current in the event of an electrical fault, power conditioning to prevent electronic noise or voltage surges on the input from reaching the load, power-factor correction, and storing energy so it can continue to power the load in the event of a temporary interruption in the source power.
Power-line communication carries data on a conductor that is also used simultaneously for AC electric power transmission or electric power distribution to consumers.

A power cord, line cord, or mains cable is an electrical cable that temporarily connects an appliance to the mains electricity supply via a wall socket or extension cord. The terms are generally used for cables using a power plug to connect to a single-phase alternating current power source at the local line voltage. The terms power cable, mains lead, flex or kettle lead are also used. A lamp cord is a light-weight, ungrounded, single-insulated two-wire cord used for small loads such as a table or floor lamp.

The utility frequency, (power) line frequency or mains frequency is the nominal frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in a wide area synchronous grid transmitted from a power station to the end-user. In large parts of the world this is 50 Hz, although in the Americas and parts of Asia it is typically 60 Hz. Current usage by country or region is given in the list of mains electricity by country.

An adapter or adaptor is a device that converts attributes of one electrical device or system to those of an otherwise incompatible device or system. Some modify power or signal attributes, while others merely adapt the physical form of one connector to another.

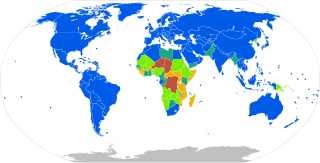
Mains electricity by country includes a list of countries and territories, with the plugs, voltages and frequencies they commonly use for providing electrical power to low voltage appliances, equipment, and lighting typically found in homes and offices. Some countries have more than one voltage available. For example, in North America most sockets are attached to a 120 V supply, but there is a 240 V supply available for large appliances. Often different sockets are mandated for different voltage or current levels.

The term All American Five is a colloquial name for mass-produced, superheterodyne radio receivers that used five vacuum tubes in their design. These radio sets were designed to receive amplitude modulation (AM) broadcasts in the medium wave band, and were manufactured in the United States from the mid-1930s until the early 1960s. By eliminating a power transformer, cost of the units was kept low; the same principle was later applied to television receivers. Variations in the design for lower cost, shortwave bands, better performance or special power supplies existed, although many sets used an identical set of vacuum tubes.
The HVDC Sileru–Barsoor is a high voltage direct current transmission system between Sileru and Barsoor in India. It is in service since 1989 as the first HVDC line in the country. The HVDC Sileru–Barsoor is a bipolar HVDC with a voltage of 200 kV and a transmission rate of 400 megawatts. The HVDC Sileru–Barsoor couples two asynchronously operated parts of Indian electricity mains over a 196 kilometres (122 mi) long overhead line, which was originally a double-circuit 220 kV AC line from which three conductors are paralleled.
Mains hum, electric hum, cycle hum, or power line hum is a sound associated with alternating current which is twice the frequency of the mains electricity. The fundamental frequency of this sound is usually double that of fundamental 50/60 Hz, i.e. 100/120 Hz, depending on the local power-line frequency. The sound often has heavy harmonic content above 50/60 Hz. Because of the presence of mains current in mains-powered audio equipment as well as ubiquitous AC electromagnetic fields from nearby appliances and wiring, 50/60 Hz electrical noise can get into audio systems, and is heard as mains hum from their speakers. Mains hum may also be heard coming from powerful electric power grid equipment such as utility transformers, caused by mechanical vibrations induced by magnetostriction in magnetic core. Onboard aircraft the frequency heard is often higher pitched, due to the use of 400 Hz AC power in these settings because 400 Hz transformers are much smaller and lighter.
A voltage converter is an electric power converter which changes the voltage of an electrical power source. It may be combined with other components to create a power supply.
International Standard IEC 60038, IEC standard voltages, defines a set of standard voltages for use in low voltage and high voltage AC and DC electricity supply systems.

An AC/DC receiver design is a style of power supply of vacuum tube radio or television receivers that eliminated the bulky and expensive mains transformer. A side-effect of the design was that the receiver could in principle operate from a DC supply as well as an AC supply. Consequently, they were known as "AC/DC receivers".
This article reports production, consumption, exports and imports of electricity by country. Dependent territories, not fully recognized countries and supranational entities are not ranked. By default countries are ranked by their total electricity production. All data is taken from CIA World Factbook.
Electric energy by country may refer to:

Mechanical, electrical and plumbing (MEP) refers to these aspects of building design and construction. In commercial buildings, these elements are often designed by a specialized engineering firm. MEP's design is important for planning, decision-making, accurate documentation, performance- and cost-estimation, construction, and operating/maintaining the resulting facilities.

Heating films are a method of electric resistance heating, providing relatively low temperatures over large areas. Heating films can be directly installed to provide underfloor heating, wall radiant heating and ceiling radiant heating.











