Related Research Articles

The bacterial outer membrane is found in gram-negative bacteria. Its composition is distinct from that of the inner cytoplasmic cell membrane - among other things, the outer leaflet of the outer membrane of many gram-negative bacteria includes a complex lipopolysaccharide whose lipid portion acts as an endotoxin - and in some bacteria such as E. coli it is linked to the cell's peptidoglycan by Braun's lipoprotein.

Casein kinase II subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CSNK2A1 gene.

Interferon-alpha/beta receptor beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNAR2 gene.
Tetraacyldisaccharide 4'-kinase is an enzyme that phosphorylates the 4'-position of a tetraacyldisaccharide 1-phosphate precursor (DS-1-P) of lipopolysaccharide lipid A. This lipid forms outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. This enzyme catalyzes the chemical reaction

Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RPS6KA2 gene.

Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MATK gene.

This gene encodes a member of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase subfamily of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family, and is most highly similar to GRK4 and GRK5. The protein phosphorylates the activated forms of G protein-coupled receptors to regulate their signaling.
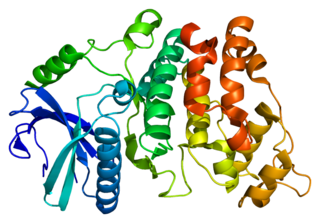
Serine/arginine-Rich Splicing Factor (SRSF) protein kinase-1 SRPK1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SRPK1 gene.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMK1 gene.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase 12 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAP3K12 gene.

Vinexin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SORBS3 gene.

Diacylglycerol kinase delta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DGKD gene.

Interferon-alpha/beta receptor alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNAR1 gene.
Core oligosaccharide is a short chain of sugar residues within Gram-negative lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Core-OS are highly diverse among bacterial species and even within strains of species
Lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid transferase is an enzyme with systematic name CMP-3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate:lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate transferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
(KDO)-lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid transferase is an enzyme with systematic name CMP-3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate:(KDO)-lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate transferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
(KDO)2-lipid IVA (2-8) 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid transferase is an enzyme with systematic name CMP-3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate:(KDO)2-lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate transferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
(KDO)3-lipid IVA (2-4) 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid transferase is an enzyme with systematic name CMP-3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate:(KDO)3-lipid IVA 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonate transferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid kinase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:(KDO)-lipid IVA 3-deoxy-alpha-D-manno-oct-2-ulopyranose 4-phosphotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 1-phosphate adenylyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:D-glycero-beta-D-manno-heptose 1-phosphate adenylyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
References
- ↑ Yethon JA, Whitfield C (February 2001). "Purification and characterization of WaaP from Escherichia coli, a lipopolysaccharide kinase essential for outer membrane stability". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (8): 5498–504. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008255200 . PMID 11069912.
- ↑ White KA, Lin S, Cotter RJ, Raetz CR (1999). "A Haemophilus influenzae gene that encodes a membrane bound 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (Kdo) kinase. Possible involvement of kdo phosphorylation in bacterial virulence". J Biol Chem. 274 (44): 31391–400. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.44.31391 . PMID 10531340.