This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
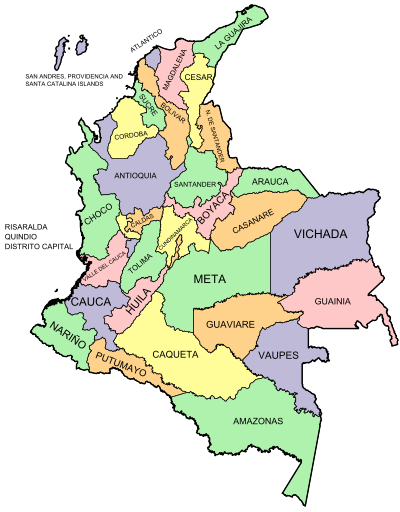
This is a list of Department Assemblies in the Republic of Colombia.
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page . (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

This is a list of Department Assemblies in the Republic of Colombia.

Cartago is a city in southwestern Colombia, about 187 miles (301 km) west of Bogotá. It is in the extreme northern portion of the Valle del Cauca. It is located very close to the city of Pereira, Risaralda about a 20-minute drive. It is the sixth largest city in Valle after Cali, Palmira, Buenaventura, Tuluá and Jamundí. Per the 2018 Colombian census, Cartago's population was 142,902.

Santiago de Cali, or Cali, is the capital of the Valle del Cauca department, and the most populous city in southwest Colombia, with 2,280,522 residents estimate by DANE in 2023. The city spans 560.3 km2 (216.3 sq mi) with 120.9 km2 (46.7 sq mi) of urban area, making Cali the second-largest city in the country by area and the third most populous after Bogotá and Medellín. As the only major Colombian city with access to the Pacific Coast, Cali is the main urban and economic center in the south of the country, and has one of Colombia's fastest-growing economies. The city was founded on 25 July 1536 by the Spanish explorer Sebastián de Belalcázar.

Valle del Cauca, or Cauca Valley, is a department in western Colombia abutting the Pacific Ocean. Its capital is Santiago de Cali. Other cities such as Buenaventura, Buga, Cartago, Palmira and Tuluá have great economical, political, social and cultural influence on the department's life. Valle del Cauca has the largest number of independent towns with over 100,000 inhabitants in the country, counting six within its borders. Buenaventura has the largest and busiest seaport in Colombia, moving about 8,500,000 tons of merchandise annually.
The Norte del Valle Cartel, or North Valley Cartel, was a drug cartel that operated principally in the north of the Valle del Cauca department of Colombia, most notably the coastal city of Buenaventura. It rose to prominence during the 1990s, after the Cali and Medellín Cartels fragmented, and it was known as one of the most powerful organizations in the illegal drug trade. The drug cartel was led by the brothers Luis Enrique and Javier Antonio Calle Serna, alias "Los Comba", until its takedown in 2008 by the authorities of Colombia and Venezuela, with cooperation of the United States DEA.

Diego León Montoya Sánchez, also known as Don Diego, is a Colombian former crime boss and leader of the Norte del Valle drug cartel. On October 25, 2002, Montoya was listed as a Specially Designated Narcotics Trafficker on the United States Department of Treasury's Specially Designated National List.
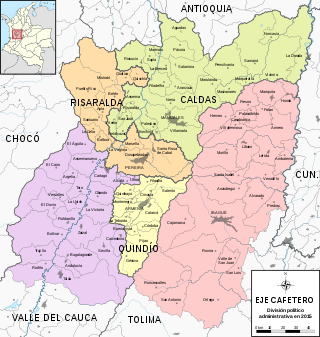
The Colombian coffee region, also known as the Coffee Triangle is a part of the Paisa region in the rural area of Colombia. It is famous for growing and producing the majority of Colombian coffee. There are four departments in the area: Caldas, Quindío, Risaralda and Tolima. The most visited cities are Manizales, Armenia, Pereira, and Ibagué.

The Cordillera Occidental is the lowest in elevation of the three branches of the Colombian Andes. The average altitude is 2,000 m (6,600 ft) and the highest peak is Cerro Tatamá at 4,100 m (13,500 ft). The range extends from south to north dividing from the Colombian Massif in Nariño Department, passes north through Cauca, Valle del Cauca, Risaralda, Chocó, and Caldas Departments to the Paramillo Massif in Antioquia and Córdoba Departments. The cordillera is paralleled on the east by the Cauca river. From this massif the range divides further to form the Serranías de Ayapel, San Jerónimo and Abibe. Only to recede into the Caribbean plain and the Sinú River valley.

The governor of Valle del Cauca is the maximum administrative and political authority in the Valle del Cauca Department of Colombia. This political official is elected by popular vote by means of a simple majority system and for a period of four years. The current governor of Valle del Cauca is Dilian Francisca Toro.

The Valle del Cauca Deputies hostage crisis refers to the kidnapping of 12 Deputies of the Assembly of Valle del Cauca, Colombia, on April 12, 2002 by members of the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC) to pressure a prisoner exchange between them and the government and to negotiate the demilitarization of the municipalities of Florida and Pradera to initiate peace dialogues.

Carlos Alberto "Beto" Rentería Mantilla was a former Colombian narcotrafficker and crime boss, presumed leader of the Norte del Valle Cartel. Rentería was believed by the United States government to be holding a leadership position within the drug cartel, he had been labeled "one of Colombia's most powerful and sophisticated narcotics traffickers" by Adam Szubin, Director of the Office of Foreign Assets Control, United States Department of the Treasury. The Attorney General of Colombia and the Colombian National Police accuse Rentería of drug trafficking and money laundering.

The Department Assembly of Valle del Cauca is the department assembly of the Colombian Valle del Cauca Department. The assembly is part of the Colombian legislative branch of government at a Provincial level and its main function is to debate, approve or change the local ordinances.

The University of Valle, also called Univalle, is a public, departmental, coeducational, research university based primarily in the city of Cali, Valle del Cauca, Colombia. It is the largest higher education institution by student population in the southwest of the country, and the third in Colombia, with more than 30,000 students. The university was established by ordinance No. 12 of 1945, by the Departmental Assembly as the Industrial University of Valle del Cauca, under the leadership of Tulio Ramírez Rojas and Severo Reyes Gamboa.

The University of the Pacific, is a public, national university based primarily in the city of Buenaventura, Valle del Cauca, Colombia. The university also has several satellite campuses across the Pacific Region in the cities of Guapi in the Cauca Department and Tumaco in the Nariño Department.

The Central Unit of Valle del Cauca, also called UCEVA, is a public, departmental university based in the city of Tuluá, Valle del Cauca, Colombia.
Marco Fidel Suárez Air Base is a Colombian military base assigned to the Colombian Aerospace Force Military Aviation School. The base is located in Cali, a city in the Valle del Cauca department of Colombia. It is named for Marco Fidel Suárez, a former president of Colombia.
The Paraíso Fault or Palmira-Buga Fault is a thrust fault with minor dextral lateral movement in the department of Valle del Cauca in southwestern Colombia. The fault is part of the megaregional Romeral Fault System and has a total length of 35.3 kilometres (21.9 mi) and runs along an average north-northwest to south-southeast strike of 012.5 ± 3 in the Cauca Basin and the Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes.
The Argelia Fault is an inactive dextral oblique thrust fault in the departments of Risaralda and Valle del Cauca in Colombia. The fault has a total length of 59.4 kilometres (36.9 mi) and runs along an average north to south strike of 014.5 ± 18 in the Western Ranges of the Colombian Andes.
The Naya-Micay Fault is a dextral oblique thrust fault in the departments of Cauca and Valle del Cauca in Colombia. The fault has a total length of 158.2 kilometres (98.3 mi) and runs along an average northeast to southwest strike of 034.1 ± 12 in the Tumaco Basin along the Pacific Coast of Colombia.
The Toro Fault is a sinistral strike-slip fault in the departments of Valle del Cauca and Risaralda in western Colombia. The fault has a total length of 61.9 kilometres (38.5 mi) and runs along an average north to south strike of 006.6 ± 8 in the Western Ranges of the Colombian Andes.