
Hancock is a city in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The population of Hancock was 4,501 at the 2020 census. The city is located within Houghton County, and is situated upon the Keweenaw Waterway, a channel of Lake Superior that cuts across the Keweenaw Peninsula. Hancock is located across the Keweenaw Waterway from the city of Houghton, and is connected to that city by the Portage Lake Lift Bridge. The city is located within Michigan's Copper Country region.

Ontonagon County is a county in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census, the population was 5,816, making it Michigan's third-least populous county. The county seat is Ontonagon. The county was set off in 1843, and organized in 1848. Its territory had been organized as part of Chippewa and Mackinac counties. With increasing population in the area, more counties were organized. After Ontonagon was organized, it was split to create Gogebic County. It is also the westernmost county in United States that lies within the Eastern Time Zone.

Keweenaw County is a county in the western Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census, the county's population was 2,046, making it Michigan's least populous county. It is also the state's largest county by total area, including the waters of Lake Superior, as well as the state's northernmost county. The county seat is Eagle River.

Houghton County is a county in the Upper Peninsula in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census, the population was 37,361. The county seat and largest city is Houghton. Both the county and the city were named for Michigan State geologist and Detroit Mayor Douglass Houghton.

Ahmeek is a village in Keweenaw County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The village is located within Allouez Township. The population was 127 at the 2020 census. At 0.07 square miles (0.18 km2), it is the smallest municipality in Michigan by land area, and is the only incorporated municipality in Keweenaw County.

Grant Township is a civil township of Keweenaw County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 275 at the 2020 census. Grant Township is one of the most isolated municipalities in Michigan, as it forms the tip of the Keweenaw Peninsula, which projects into Lake Superior.
The Keweenaw Peninsula is a peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. Part of the greater landmass of the Upper Peninsula, the Keweenaw Peninsula projects about 65 miles (105 km) northeasterly into Lake Superior, forming Keweenaw Bay. The peninsula is part of Michigan's Copper Country region, as the region was home to the first major copper mining boom in the United States. Copper mining was active in this region from the 1840s to the 1960s.
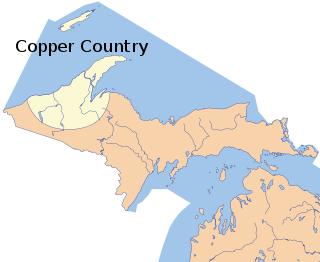
The Copper Country is an area in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan in the United States, including Keweenaw County, Michigan, Houghton, Baraga and Ontonagon counties as well as part of Marquette County. The area is so named as copper mining was prevalent there from 1845 until the late 1960s, with one mine continuing through 1995. The region includes Copper Island, Copper Harbor and Isle Royale. In its heyday in the latter half of the 19th century and the early 20th century, the area was the world's greatest producer of copper.

M-26 is a 96.355-mile-long (155.068 km) state trunkline highway in the U.S. state of Michigan, running from two miles (3.2 km) east of Rockland to its junction with US Highway 41 (US 41) in Copper Harbor. It generally runs southwest-to-northeast in the western half or Michigan's Upper Peninsula. The northernmost segment, which closely parallels the shore of Lake Superior on the west side of the Keweenaw Peninsula, is highly scenic.

Copper Harbor is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) located in Keweenaw County in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is located within Grant Township. The population of the CDP was 136 as of the 2020 census.

The Keweenaw Waterway is a partly natural, partly artificial waterway which cuts across the Keweenaw Peninsula of Michigan; it separates Copper Island from the mainland. Parts of the waterway are variously known as the Keweenaw Waterway, Portage Canal, Portage Lake Canal, Portage River, Lily Pond, Torch Lake, and Portage Lake. The waterway connects to Lake Superior at its north and south entries, with sections known as Portage Lake and Torch Lake in between. The primary tributary to Portage Lake is the Sturgeon River.

The Minesota Mine is a former copper mine near Rockland, Ontonagon County in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The Minesota was one of the most productive and famous early mines in the Michigan Copper Country.

The Quincy Mine is an extensive set of copper mines located near Hancock, Michigan. The mine was owned by the Quincy Mining Company and operated between 1846 and 1945, although some activities continued through the 1970s. The Quincy Mine was known as "Old Reliable," as the Quincy Mine Company paid a dividend to investors every year from 1868 through 1920. The Quincy Mining Company Historic District is a United States National Historic Landmark District; other Quincy Mine properties nearby, including the Quincy Mining Company Stamp Mills, the Quincy Dredge Number Two, and the Quincy Smelter are also historically significant.

Keweenaw National Historical Park is a unit of the U.S. National Park Service. Established in 1992, the park celebrates the life and history of the Keweenaw Peninsula in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. It is a federal-local cooperative park made up of two primary units, the Calumet Unit and the Quincy Unit, and almost two dozen cooperating "Heritage Sites" located on federal, state, and privately owned land in and around the Keweenaw Peninsula. The National Park Service owns approximately 1,700 acres (690 ha) in the Calumet and Quincy Units. Units are located in Baraga, Houghton, Keweenaw, and Ontonagon counties.
This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Houghton County, Michigan.

The following is a list of Registered Historic Places in Keweenaw County, Michigan.
This National Park Service list is complete through NPS recent listings posted January 17, 2025.

In Michigan, copper mining became an important industry in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Its rise marked the start of copper mining as a major industry in the United States.

The Quincy Smelter, also known as the Quincy Smelting Works, is a former copper smelter located on the north side of the Keweenaw Waterway in Ripley, Michigan. It is a contributing property of the Quincy Mining Company Historic District, a National Historic Landmark District. The smelter was built in 1898 by the Quincy Mining Company, operating from 1898 to 1931 and again from 1948 to 1971. The smelter was part of a Superfund site from 1986 to 2013.
Clarence J. Monette was a prolific author and historian from Michigan's Copper Country, writing extensively on Copper Country history. He has published more than sixty books and has written numerous outdoor survival guides.

















